Adaptable amphibious homes: floating foundations for flood-prone regions

Adaptable Amphibious Homes: Floating Foundations for Flood-Prone Regions
In an era marked by climate unpredictability and rising sea levels, the architecture and design world faces an urgent challenge: creating resilient, adaptable living spaces capable of withstanding the increasing frequency of floods. Enter the concept of amphibious homes, an innovative architectural solution designed to float gracefully above floodwaters, seamlessly adapting to changing environmental conditions. These dynamic structures are not merely practical responses to climate change; they embody a sophisticated blend of engineering ingenuity, sustainable design, and aesthetic elegance, captivating architects, designers, and urban planners alike.
The Rise of Amphibious Architecture: Necessity Meets Innovation
Flooding has emerged as one of the most destructive natural disasters globally, impacting millions of people annually. According to recent data from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), sea levels are projected to rise significantly by the end of the century, intensifying flood risks for coastal and riverside communities. This looming threat has catalyzed a wave of architectural innovation, inspiring designers to rethink traditional housing paradigms and embrace adaptive, resilient structures.
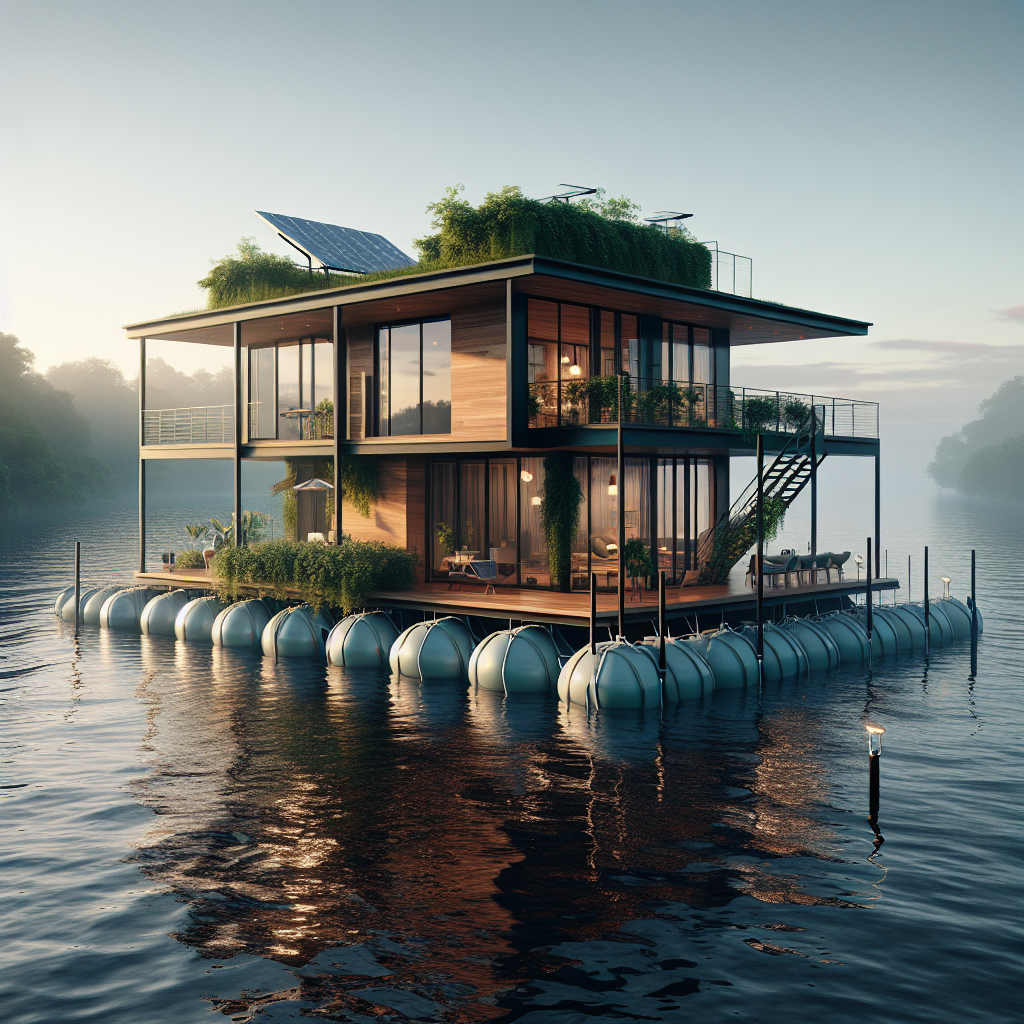
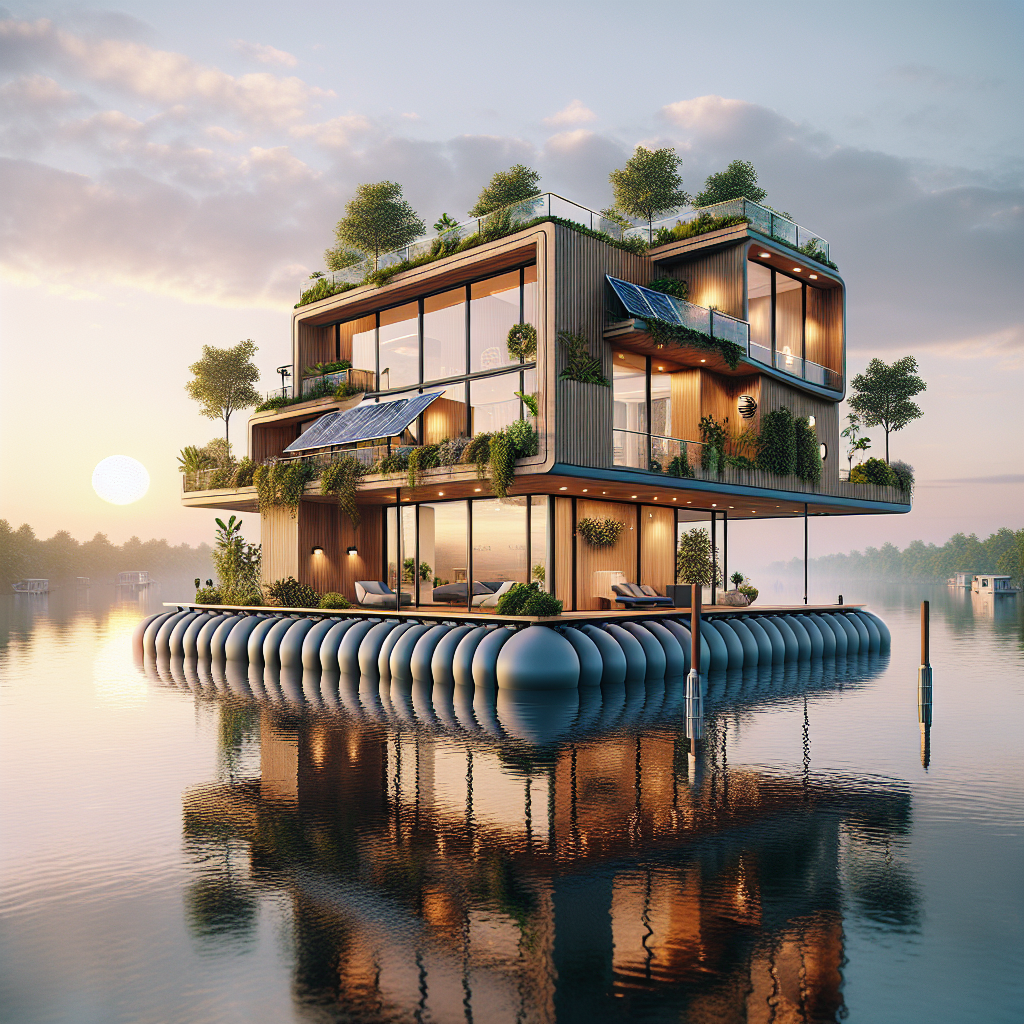
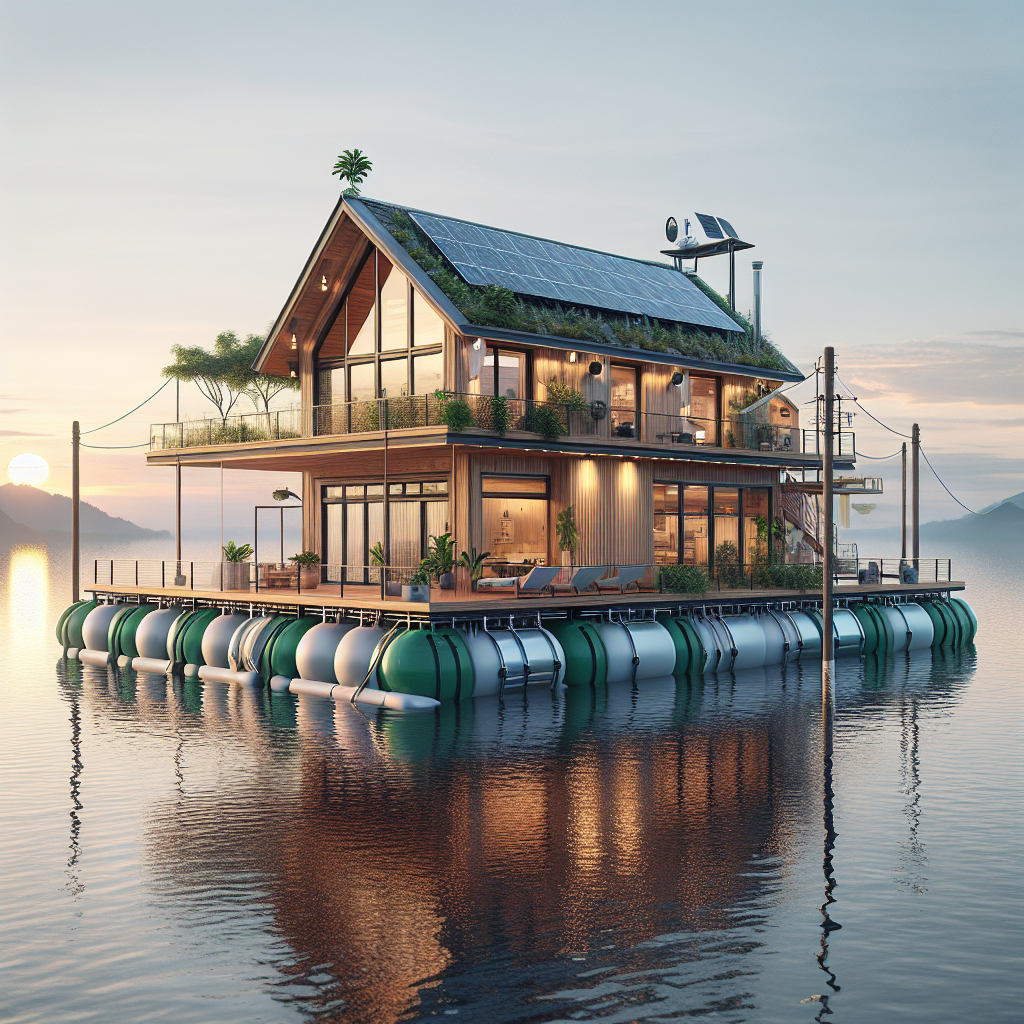
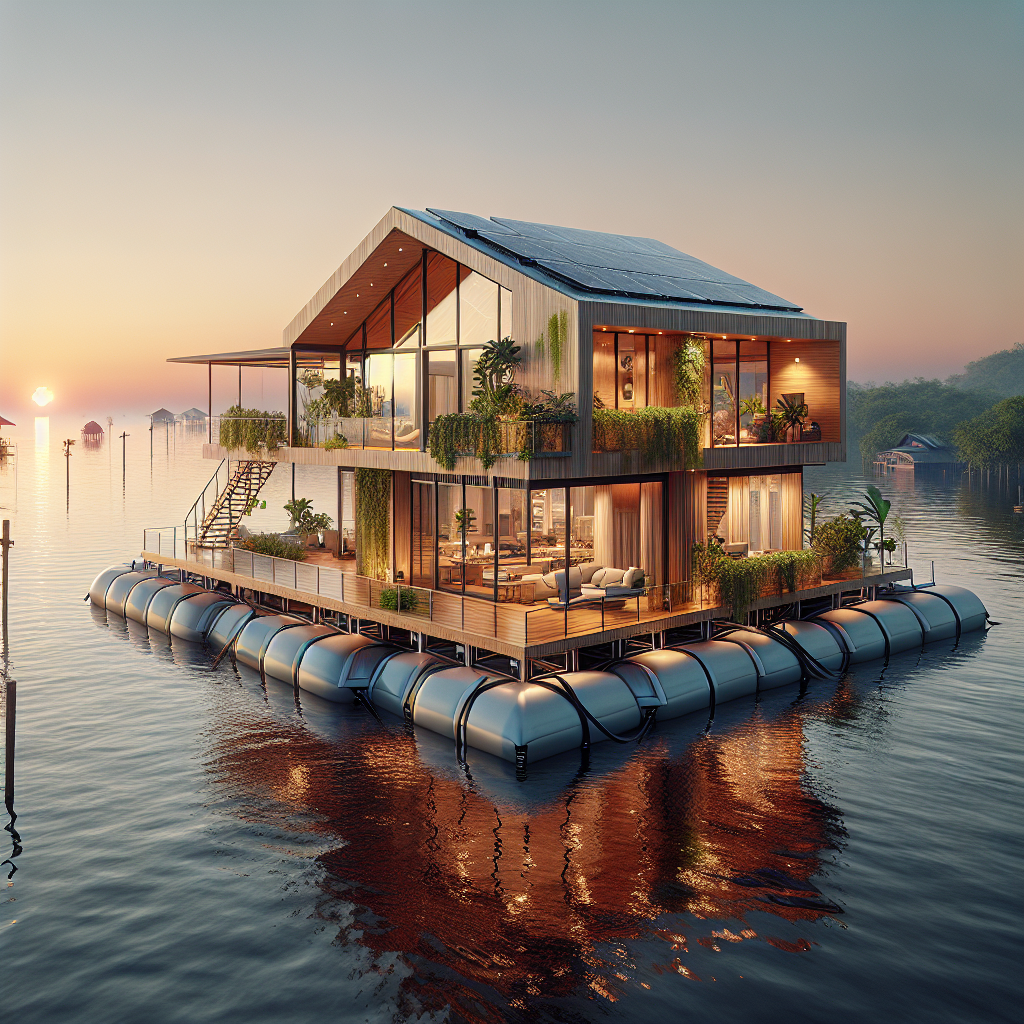
Amphibious homes, unlike conventional fixed foundations, are designed to rest on solid ground during normal conditions but rise and float atop floodwaters when necessary. Utilizing buoyant foundations, typically constructed from lightweight materials such as expanded polystyrene or recycled plastic pontoons, these homes remain tethered to vertical guideposts, ensuring stability and preventing lateral drift during flooding events.
Designing for Adaptability: Aesthetic and Functional Harmony
Far from mere functional constructs, amphibious homes represent a harmonious marriage of form and function. Contemporary designs emphasize open, airy interiors, expansive glazing, and natural materials, echoing the principles of biophilic design to foster human well-being and connection to nature. Interiors often feature modular, flexible layouts, allowing residents to adapt spaces according to changing needs and circumstances.
One striking example is the pioneering amphibious residence by Dutch architecture firm Waterstudio.NL, situated along the Maas River in the Netherlands. This elegant structure, characterized by sleek lines, expansive windows, and sustainable timber cladding, rises gracefully with floodwaters, transforming potential disaster into a serene, floating experience. Inside, minimalist interiors, punctuated by organic textures and warm wood tones, create an inviting sanctuary that remains intimately connected to its aquatic surroundings.
Case Study: The Buoyant Beauty of Makoko Floating Homes
In Lagos, Nigeria, the innovative Makoko Floating Homes project has garnered international acclaim for its visionary approach to amphibious architecture. Designed by architect Kunlé Adeyemi and his firm NLÉ, these floating structures provide sustainable, resilient housing solutions for the densely populated, flood-prone Makoko community. Constructed from locally sourced bamboo and recycled plastic barrels, the homes showcase a compelling blend of sustainability, affordability, and cultural sensitivity.
Visually striking, the Makoko homes feature triangular roofs reminiscent of traditional Nigerian architecture, while open-air terraces and vibrant façades celebrate local craftsmanship and identity. Beyond aesthetics, the homes incorporate rainwater harvesting systems, solar panels, and composting toilets, exemplifying a holistic approach to sustainable living. This innovative project has not only improved residents’ quality of life but also inspired global conversations about adaptive architecture in vulnerable communities.
Materials and Technologies: Building Resilience from the Ground Up
The success of amphibious homes hinges on the strategic selection of materials and technologies capable of withstanding harsh environmental conditions. Lightweight, durable materials such as aluminum, recycled plastics, and sustainably harvested timber have emerged as preferred choices, offering structural integrity, buoyancy, and environmental sustainability. Moreover, advanced waterproofing membranes, corrosion-resistant coatings, and resilient insulation materials further enhance durability and occupant comfort.
Innovative construction techniques, including modular and prefabricated systems, have significantly streamlined the building process, reducing costs and minimizing environmental impact. Digital fabrication technologies, such as 3D printing, are increasingly employed to create customized, efficient structural components, underscoring the role of digital fabrication in shaping the future of resilient architecture.
Urban Integration: Amphibious Homes in the Cityscape
As urban areas grapple with increasing flood risks, integrating amphibious architecture into existing cityscapes presents both challenges and opportunities. Thoughtful urban planning and zoning policies are essential to accommodate these adaptive structures, ensuring harmonious coexistence with traditional buildings and infrastructure. In cities like Amsterdam and Rotterdam, floating neighborhoods have already emerged as vibrant, sustainable communities, redefining urban living and inspiring global adoption.
Moreover, amphibious homes align seamlessly with broader trends in sustainable urban development, including green roofs, vertical gardens, and urban farming initiatives. These complementary strategies collectively enhance urban resilience, biodiversity, and livability, demonstrating the transformative potential of integrated, adaptive design solutions.
Challenges and Future Prospects: Navigating Uncharted Waters
Despite their promise, amphibious homes face several challenges, including regulatory hurdles, public perception, and scalability concerns. Building codes and zoning regulations often lag behind innovative architectural practices, necessitating proactive policy advocacy and stakeholder engagement. Additionally, widespread adoption requires public education and awareness campaigns to dispel misconceptions and highlight the benefits of adaptive architecture.
Looking ahead, the evolution of amphibious homes will likely intersect with advancements in smart home technology, artificial intelligence, and sustainable energy systems. Emerging innovations, such as self-sufficient floating communities powered by renewable energy and equipped with autonomous mobility systems, promise to redefine the boundaries of adaptive architecture. Indeed, the convergence of technology and design, as explored in our previous article on smart home technology, underscores the limitless potential of amphibious architecture in shaping resilient, sustainable futures.
A Visionary Response to Climate Change
Amphibious homes represent more than a pragmatic response to flooding; they embody a visionary approach to architecture and urban planning, one that embraces adaptability, sustainability, and human-centric design. By seamlessly integrating aesthetics, functionality, and resilience, these floating foundations offer compelling solutions for flood-prone regions worldwide, inspiring architects, designers, and communities to reimagine the possibilities of adaptive living.
As climate change continues to reshape our world, amphibious architecture stands as a testament to human ingenuity and creativity, offering hope and inspiration for a more resilient, sustainable future. Through continued innovation, collaboration, and visionary thinking, the design community can navigate the rising tides of uncertainty, crafting homes and communities that not only survive but thrive amidst change.
For further insights into resilient design strategies, explore our article on disaster-resistant and resilient building design.