Vertical Farming: Sustainable Agriculture Solutions for Urban Spaces

Vertical Farming: Sustainable Agriculture Solutions for Urban Spaces
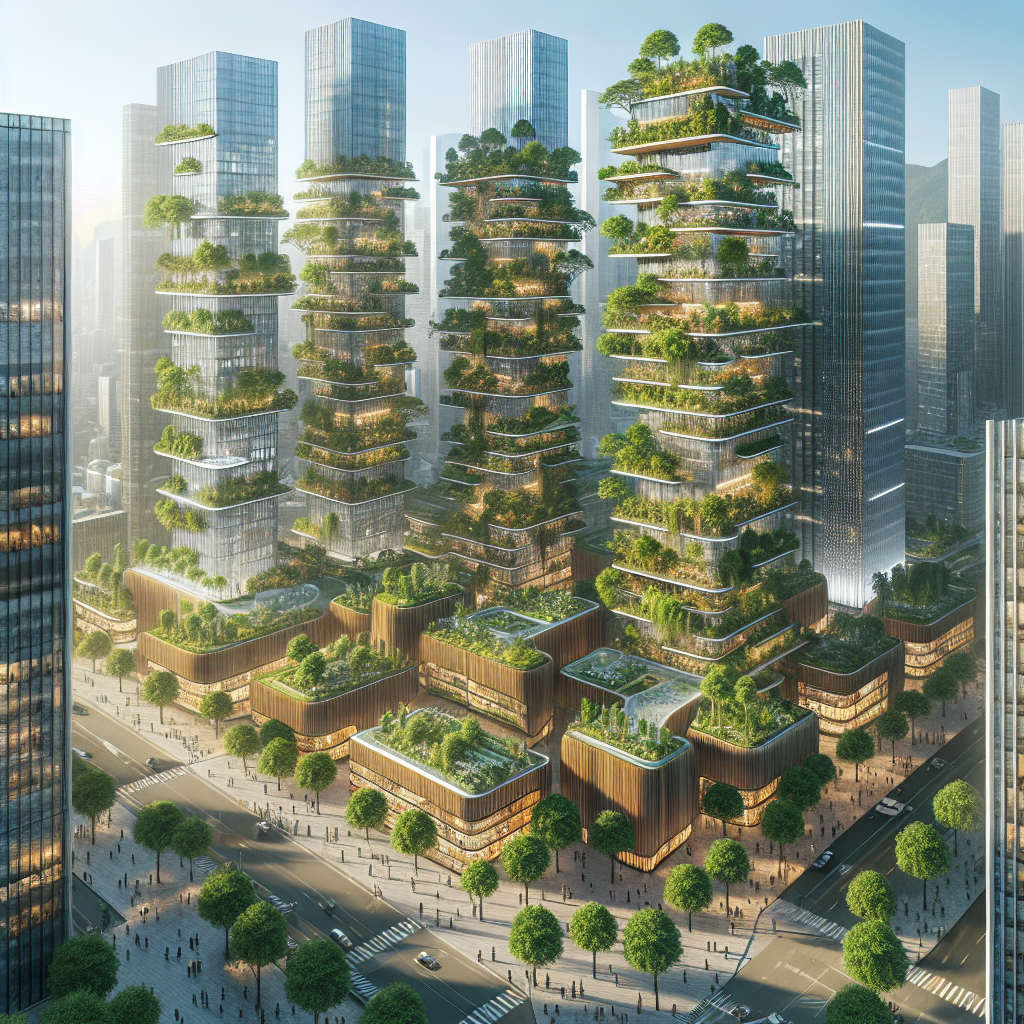
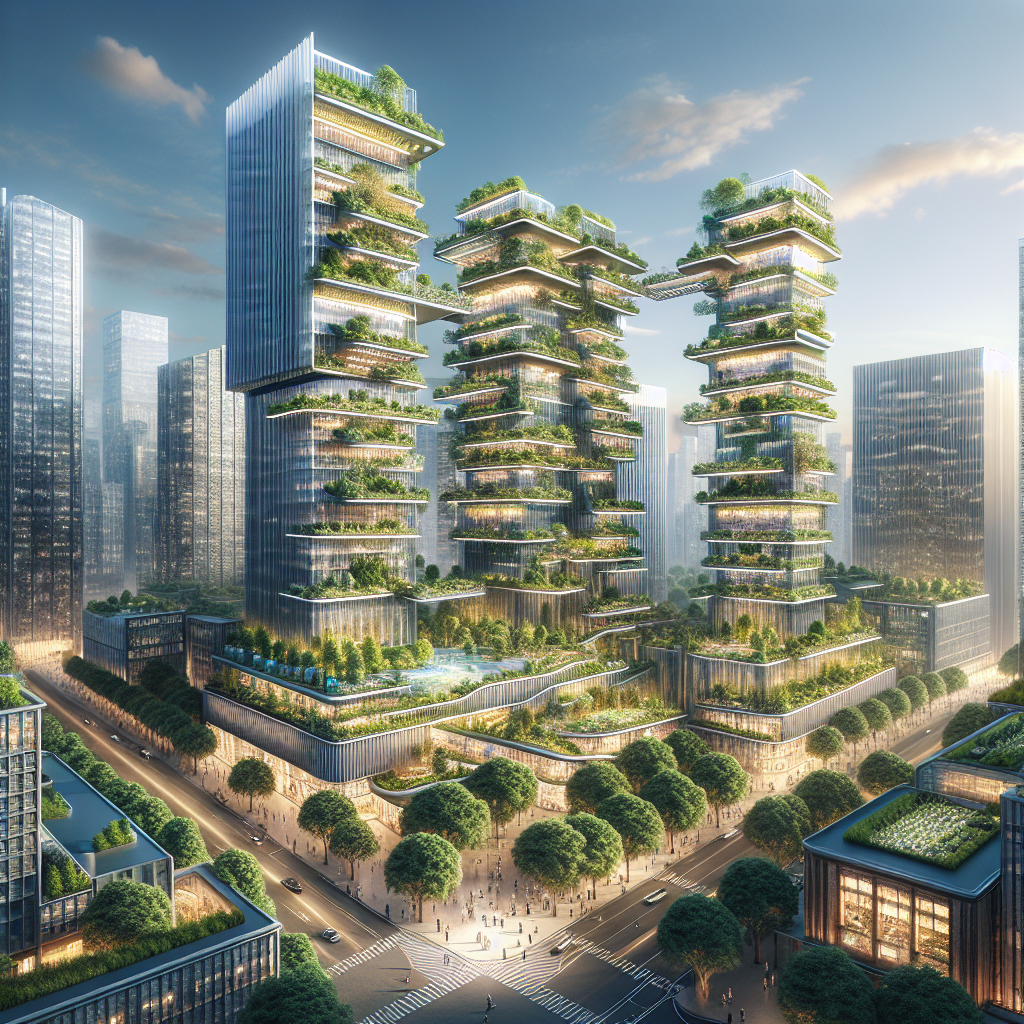
As urban populations surge and cities expand vertically, architects and designers face an unprecedented challenge: how to sustainably feed a rapidly growing urban populace. Amidst glass skyscrapers and concrete jungles, a green revolution is quietly taking root—vertical farming. More than a futuristic vision, vertical farming represents a pragmatic, sustainable, and aesthetically captivating solution for urban agriculture, transforming cityscapes into verdant oases of food production.
The Rise of Vertical Farming: Cultivating Innovation
Vertical farming is an innovative agricultural practice where crops are grown in vertically stacked layers within controlled environments. Utilizing advanced hydroponic, aeroponic, or aquaponic systems, these urban farms drastically reduce land use, water consumption, and transportation emissions. According to a recent study published by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), vertical farms use up to 95% less water compared to traditional agriculture, significantly mitigating environmental impacts.
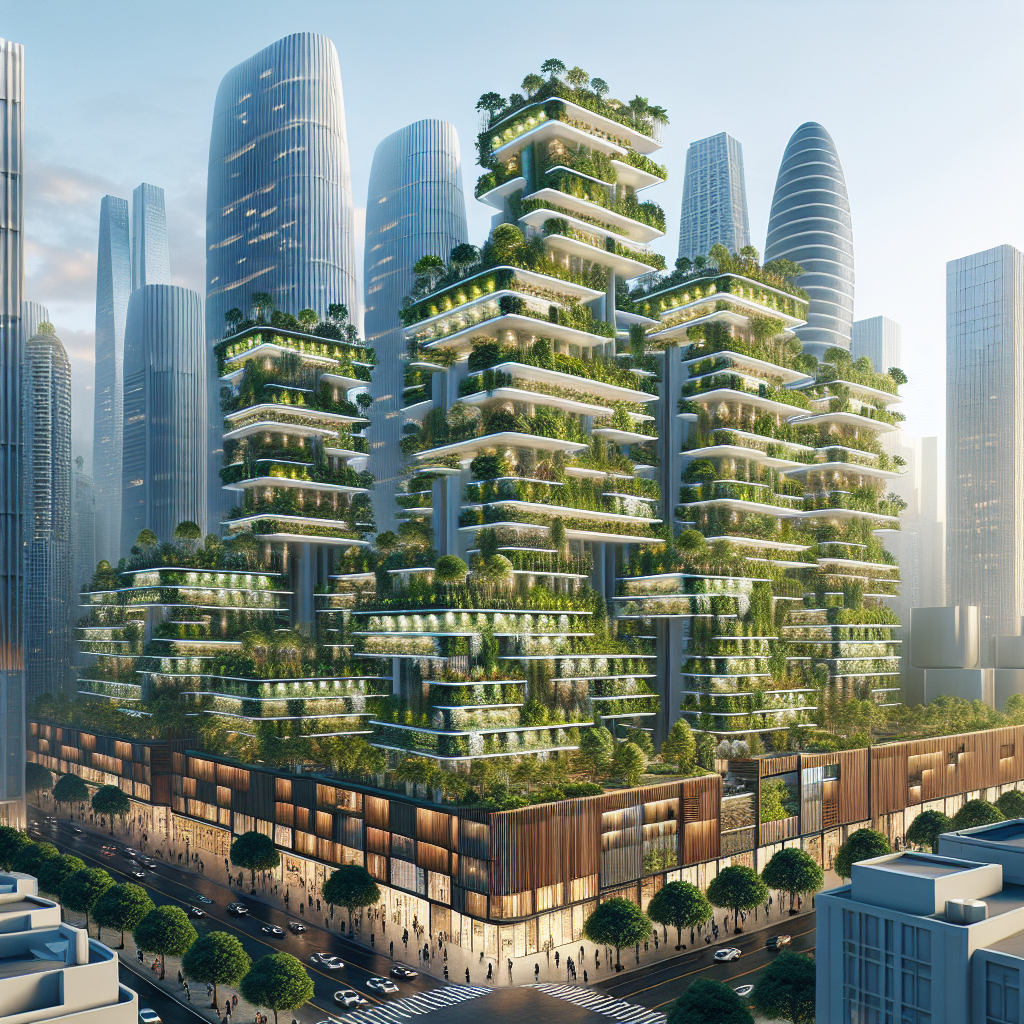
Architecturally, vertical farms are as visually compelling as they are functional. Imagine sleek glass towers interwoven with lush greenery, illuminated by energy-efficient LED lights, creating vibrant living sculptures that redefine urban aesthetics. These farms not only enhance the visual landscape but also contribute positively to air quality and urban biodiversity.
Architectural Integration: Blending Form and Function
Integrating vertical farms into urban architecture demands a sophisticated design approach, harmonizing agricultural productivity with architectural elegance. Renowned architectural firms such as BIG (Bjarke Ingels Group) and Foster + Partners have already begun incorporating vertical farming into their urban designs, seamlessly blending agriculture with residential and commercial spaces.
A prime example is the Bosco Verticale in Milan, Italy, designed by Stefano Boeri Architetti. This iconic pair of residential towers is enveloped in over 900 trees and thousands of shrubs, transforming the building into a vertical forest. Although primarily a residential project, Bosco Verticale has inspired architects worldwide to envision similar vertical structures dedicated entirely to agriculture, emphasizing the synergy between sustainable architecture and urban farming.
Moreover, innovative materials and construction techniques are essential in achieving sustainability goals. Recent advancements, such as timber-based skyscrapers, offer renewable, carbon-sequestering alternatives to traditional steel and concrete, aligning perfectly with the eco-friendly ethos of vertical farming.
Interior Design and Vertical Farming: Creating Human-Centric Spaces
Interior designers play a pivotal role in shaping vertical farms into spaces that are not only productive but also inviting and human-centric. Thoughtful design can transform vertical farms into communal hubs, educational centers, or serene retreats, enhancing urban life quality.
Biophilic design principles, which emphasize the human connection to nature, are particularly relevant in vertical farming interiors. As explored in our previous article on biophilic design, incorporating natural elements into built environments significantly improves human health and well-being. Vertical farms, with their abundant greenery and natural light, inherently embody these principles, creating spaces that nurture both plants and people.
Imagine interiors featuring minimalist wooden furniture, sleek modular planting systems, and soft, diffused lighting, creating an atmosphere of tranquility and purpose. Designers increasingly use sustainable materials like reclaimed wood, recycled metals, and biodegradable textiles, further enhancing the environmental credentials of these spaces.
Technological Innovations: Pioneering Sustainable Agriculture
Technology is the backbone of vertical farming, enabling precise control over environmental conditions to optimize crop yields. Advanced sensors, artificial intelligence (AI), and automation systems meticulously monitor and adjust variables such as temperature, humidity, nutrient levels, and lighting, ensuring optimal plant growth conditions.
Emerging technologies, such as sand printing, explored in our article on sand printing technology, offer exciting possibilities for constructing sustainable, modular vertical farm structures. Additionally, AI-driven systems analyze vast amounts of data to predict crop yields, optimize resource use, and even detect plant diseases early, significantly enhancing efficiency and productivity.
Companies like AeroFarms in Newark, New Jersey, exemplify this technological prowess. AeroFarms’ flagship facility, housed in a repurposed steel mill, produces leafy greens year-round using aeroponic technology, LED lighting, and AI-driven analytics. This innovative approach yields up to 390 times more produce per square foot compared to traditional farming methods, demonstrating the immense potential of vertical farming technology.
Environmental and Social Benefits: Transforming Urban Life
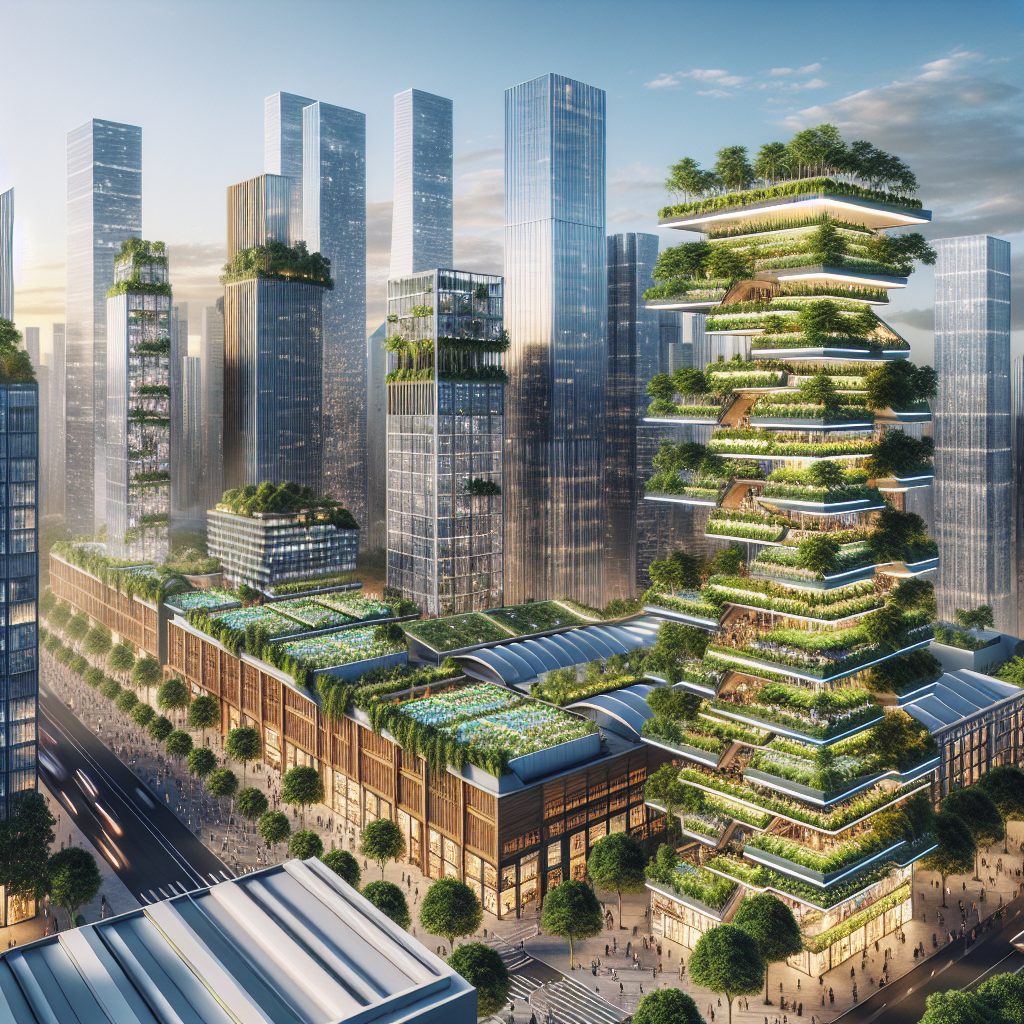
Vertical farming addresses critical environmental challenges by significantly reducing agriculture’s ecological footprint. By localizing food production, vertical farms minimize transportation emissions, reduce food waste, and enhance urban resilience. Furthermore, integrating agriculture into urban environments fosters community engagement, education, and social cohesion.
In cities facing climate change challenges, vertical farming can play a crucial role in creating resilient food systems. As discussed in our exploration of climate refuges, innovative design solutions like vertical farming can mitigate urban vulnerabilities, ensuring food security even in extreme conditions.
Socially, vertical farms offer educational opportunities, reconnecting urban residents with food production processes. Community-focused vertical farms often include interactive spaces, workshops, and educational programs, fostering awareness and appreciation for sustainable agriculture among city dwellers.
Challenges and Future Prospects: Navigating the Path Forward
Despite its numerous advantages, vertical farming faces challenges, including high initial investment costs, energy consumption concerns, and technological complexities. Addressing these issues requires continued innovation, collaboration among architects, designers, technologists, and policymakers, and a commitment to sustainable urban development.
As cities continue to evolve, vertical farming will undoubtedly become an integral component of urban planning and architecture. The integration of sustainable agriculture into urban spaces aligns with broader trends toward net-zero design, circular economies, and resilient urban ecosystems, topics extensively covered in our previous articles.
Ultimately, vertical farming represents more than a technological innovation—it embodies a profound shift in how we perceive and interact with urban environments. By embracing vertical farming, architects and designers have the opportunity to create sustainable, beautiful, and nourishing urban spaces, redefining the future of cities for generations to come.
Urban Agriculture Reimagined: A New Architectural Paradigm
Vertical farming is not merely a trend; it is a necessary evolution in urban architecture and design. By thoughtfully integrating agriculture into urban spaces, architects and designers can transform cities into sustainable, resilient, and aesthetically inspiring environments. As we stand at the intersection of innovation, sustainability, and design, vertical farming offers a compelling vision for the future—one where urban spaces flourish with life, nourishment, and beauty.
In embracing this green revolution, we not only address critical environmental and social challenges but also reimagine the very essence of urban living. Vertical farming is more than sustainable agriculture; it is a bold architectural statement, a testament to human ingenuity, and a promise of a brighter, greener urban future.