Sonic corridor illusions: in fractal patterns mesmerizing repetition
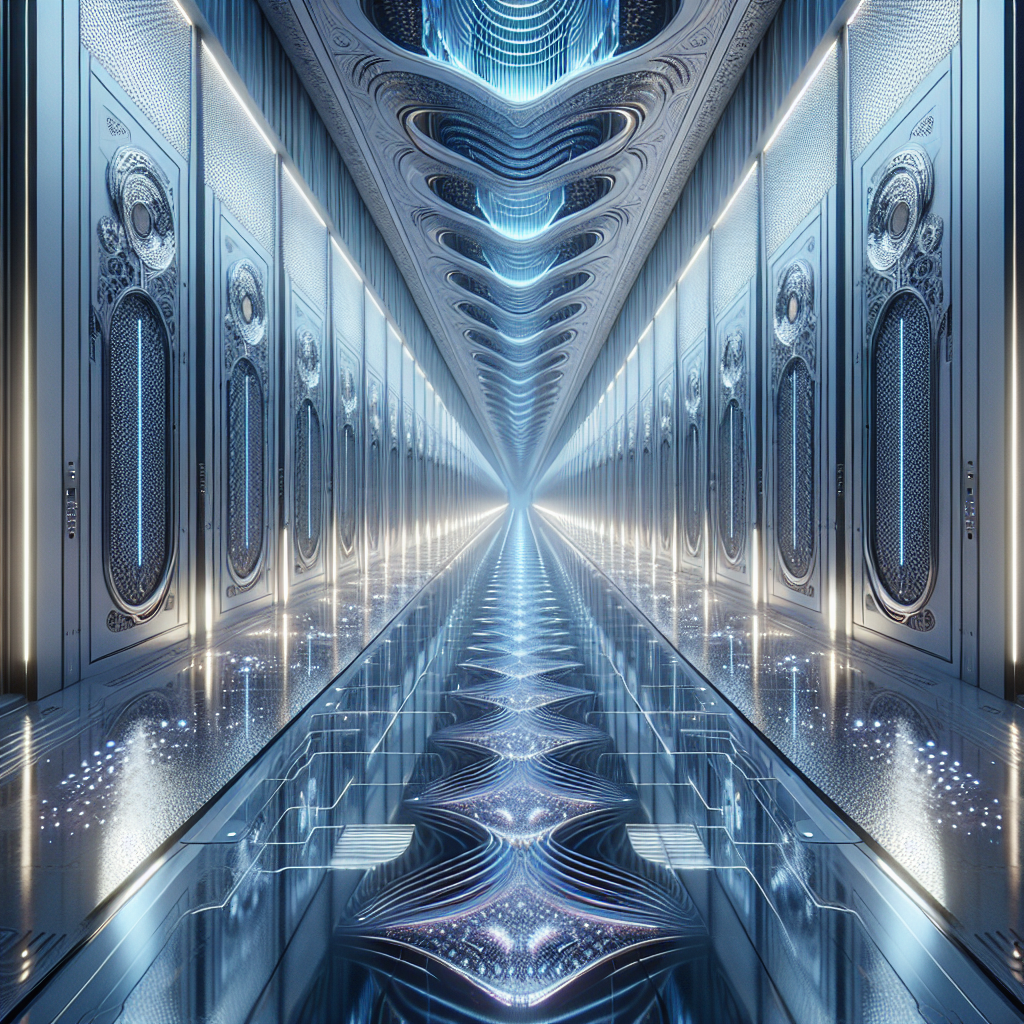

In the world of architecture and interior design, sensory experiences are paramount. Designers and architects continuously explore innovative methods to engage and captivate users, transcending traditional visual aesthetics. Among these explorations, sonic corridor illusions emerge as a compelling trend, blending sound, architecture, and fractal patterns to create mesmerizing, immersive spaces. These auditory illusions, integrated within architectural corridors, employ repetitive fractal designs to alter perception, evoke emotions, and redefine spatial experiences.
The Intersection of Sound and Architecture
Architecture has long been considered a visual art form, yet sound profoundly influences how we perceive and interact with spaces. Sonic architecture—designing spaces based on rhythmic vibrations and auditory experiences—has increasingly gained attention for its ability to shape emotional responses and enhance spatial awareness. Corridors, often transitional and overlooked spaces, present a unique opportunity for sonic experimentation. By embedding fractal patterns into acoustic designs, architects transform mundane passageways into dynamic sensory experiences.
Fractal patterns, characterized by infinitely repeating geometric shapes at varying scales, are abundant in nature and art. From the intricate branching of trees to the spiraling patterns of seashells, fractals evoke a sense of harmony and intrigue. When applied to sound and spatial design, these patterns create auditory illusions that challenge and delight the senses.
Understanding Sonic Corridor Illusions
Sonic corridor illusions leverage the repetitive nature of fractal patterns to manipulate auditory perception. As individuals traverse these corridors, carefully orchestrated sounds resonate, overlap, and repeat, creating a captivating illusion of infinite space or shifting dimensions. This auditory phenomenon, known as the Shepard tone, is an auditory illusion of a perpetually rising or falling pitch, which, when combined with fractal-inspired architectural elements, amplifies the sense of infinite continuity.
Architects achieve these illusions through meticulous acoustic planning, employing materials and geometries that enhance sound propagation and reflection. For instance, the use of reflective surfaces, strategic placement of acoustic panels, and integration of advanced sound systems contribute to the creation of these mesmerizing auditory experiences.
Case Study: The Infinite Echo Corridor at Tokyo’s Sensory Pavilion
A striking example of sonic corridor illusions is the Infinite Echo Corridor at Tokyo’s renowned Sensory Pavilion. Designed by acclaimed architect Akira Tanaka, this corridor exemplifies the seamless integration of fractal patterns and sonic architecture. Visitors walking through the corridor encounter walls adorned with intricately patterned acoustic panels, inspired by the recursive geometry of natural fractals. As they progress, subtle, repetitive sounds envelop them, creating an auditory illusion of infinite expansion.
The corridor’s acoustic design employs a combination of directional speakers and reflective surfaces, meticulously calibrated to produce overlapping sound waves. This precise orchestration results in a continuously evolving auditory experience, compelling visitors to pause, reflect, and immerse themselves fully in the sensory journey.
Fractal Patterns: Nature’s Blueprint for Mesmerizing Design
Fractal geometry, first coined by mathematician Benoît Mandelbrot, has significantly influenced contemporary design and architecture. Defined by self-similarity and repetition at multiple scales, fractals resonate deeply with human perception, evoking feelings of familiarity and wonder. Architectural designs inspired by fractals often achieve a harmonious balance between complexity and simplicity, creating visually and acoustically captivating spaces.
Incorporating fractal patterns into sonic corridor illusions enhances the auditory experience by aligning sound propagation with visual aesthetics. The repetitive geometries guide sound waves, amplifying specific frequencies and creating intricate acoustic textures. This synergy between visual and auditory fractals results in spaces that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also profoundly immersive.
Applications and Innovations in Contemporary Design
The integration of sonic corridor illusions extends beyond artistic installations, finding practical applications in various architectural contexts. Museums, galleries, hospitality venues, and wellness centers increasingly embrace this innovative approach to enhance visitor experiences. For example, wellness retreats utilize fractal-inspired sonic corridors to induce relaxation and mindfulness, while museums employ these illusions to create engaging, interactive exhibits.
Advancements in digital fabrication and parametric design further facilitate the creation of complex fractal geometries. Techniques such as digital fabrication and parametric modeling enable architects to precisely control acoustic properties, optimizing sound diffusion and reflection. These technological innovations empower designers to experiment boldly, pushing the boundaries of sensory architecture.
The Psychological Impact of Sonic Fractal Spaces
Emerging research underscores the profound psychological impact of fractal patterns and sonic illusions on human well-being. Studies indicate that exposure to fractal geometries reduces stress, enhances cognitive function, and promotes emotional well-being. Similarly, auditory illusions like the Shepard tone elicit strong emotional responses, ranging from awe and curiosity to tranquility and introspection.
By combining these visual and auditory elements, sonic corridor illusions create environments that deeply resonate with occupants, fostering emotional connections and enhancing spatial experiences. This holistic approach aligns with broader trends in biophilic design, which emphasizes the integration of natural patterns and sensory stimuli to promote health and well-being. For more insights into biophilic design, explore our article on biophilic design and its impact on human health and well-being.
Future Prospects: Expanding the Boundaries of Sensory Architecture
As architects and designers continue to explore the intersection of sound, fractal patterns, and spatial design, the potential for innovation remains vast. Emerging technologies, such as augmented reality and virtual reality, offer new avenues for creating immersive sonic experiences. These tools enable designers to simulate and refine auditory illusions, optimizing acoustic environments before physical construction begins. To delve deeper into these technological advancements, read our exploration of augmented reality in design innovation.
Moreover, the growing emphasis on sustainability and eco-conscious design encourages architects to explore environmentally friendly materials and construction methods. The integration of biodegradable acoustic panels, recycled materials, and sustainable fabrication techniques aligns with the industry’s commitment to environmental stewardship. This approach resonates with broader initiatives toward achieving net-zero emissions, as discussed in our article on the path to net-zero in design and architecture.
Conclusion: A Symphony of Design and Perception
Sonic corridor illusions, enriched by fractal patterns and innovative acoustic design, represent a compelling evolution in contemporary architecture. By transcending traditional visual aesthetics and embracing auditory experiences, architects create spaces that profoundly engage and inspire occupants. As sensory architecture continues to evolve, the harmonious integration of sound, geometry, and perception promises to redefine our understanding of space, inviting us to explore new dimensions of design and experience.
In embracing these mesmerizing sonic illusions, architects and designers craft environments that resonate deeply with human perception, enriching our interactions with the built world and fostering a profound sense of wonder and connection.
❮
❯