Smart Home Security Cameras That Save Energy
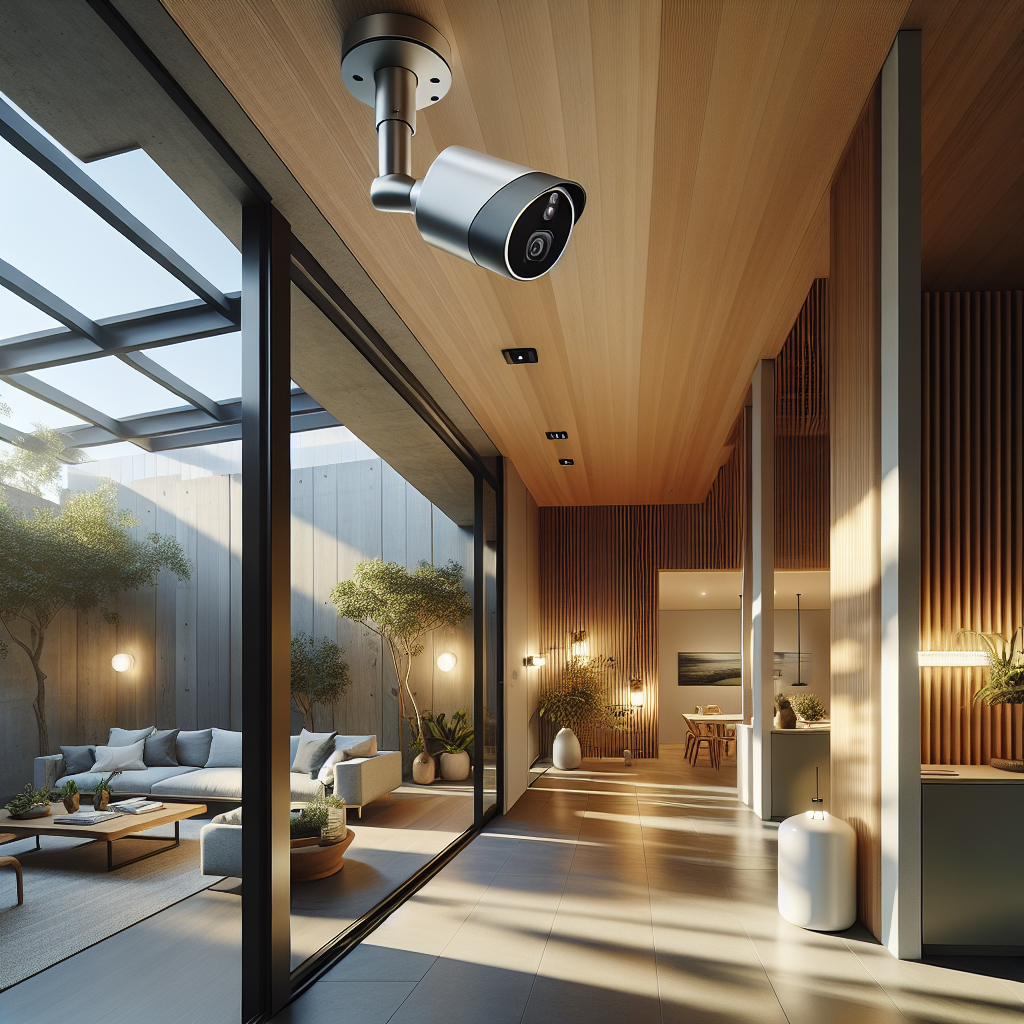

In the evolving landscape of residential design, where sustainability and technology converge, the role of smart home security cameras has transcended mere surveillance. Today, these devices are being reimagined not only as guardians of domestic privacy but also as instruments of energy efficiency. For architects, interior designers, and design-forward homeowners, the question is no longer whether to integrate security cameras into a home, but how to do so in a way that aligns with broader ecological and aesthetic ambitions. This shift signals a new era where security technology harmonizes with architectural vision and environmental responsibility.
The Rise of Energy-Saving Smart Security Cameras
Traditionally, home security systems were energy-intensive, relying on continuous recording and heavy-duty hardware. The new generation of energy-efficient smart cameras has upended this model. By leveraging artificial intelligence, motion detection, and low-power connectivity protocols such as Zigbee and Z-Wave, these devices consume significantly less energy while maintaining robust security performance. Some models even integrate solar-powered modules, reducing reliance on grid electricity and aligning with the architectural trend toward net-zero energy homes.
According to a 2024 report by MarketsandMarkets, the global smart home security market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 17.2% through 2030, with energy-efficient solutions leading adoption. This growth reflects not only consumer demand for safety but also a heightened awareness of environmental impact.
Design Integration: Cameras as Architectural Elements
For design professionals, the challenge lies in ensuring that these devices do not disrupt the visual harmony of a space. Contemporary smart cameras are increasingly conceived as design objects—sleek, sculptural, and often customizable in finish. Matte ceramic housings, brushed aluminum casings, and even wood veneers allow them to blend seamlessly into interiors. In high-end projects, cameras are recessed into architectural niches, concealed within lighting fixtures, or integrated into the geometry of facades.
Consider the case of a recent residential project in Copenhagen, where architects integrated cylindrical cameras into the rhythm of vertical timber cladding. The devices disappeared into the architecture, their presence felt only through the subtle glow of LED indicators. This approach echoes the principles of biophilic design, where technology recedes into the background, allowing natural materials and spatial experience to dominate.
Energy Efficiency Meets Smart Intelligence
Energy-saving cameras achieve their efficiency through several key innovations:
- Adaptive Recording: Cameras activate only when motion or sound is detected, reducing unnecessary power draw.
- AI-Powered Analytics: Advanced models distinguish between humans, pets, and environmental triggers, preventing false alerts and redundant recordings.
- Low-Power Connectivity: By using protocols optimized for minimal energy consumption, these devices extend battery life to months rather than days.
- Solar Integration: Compact solar panels now power outdoor cameras, making them nearly self-sufficient in energy terms.
These innovations resonate with the broader movement toward smart home automation, where devices are designed to anticipate human needs while minimizing ecological impact.
Case Study: The Minimalist Loft in Berlin
In a Berlin loft designed by Studio K, energy-efficient security cameras were embedded into the architectural lighting system. The cameras drew power from the same low-voltage track as the LED luminaires, reducing wiring complexity and energy redundancy. Their cylindrical forms mirrored the spotlights, creating a visual rhythm across the ceiling. The result was a home that felt both secure and serene, with technology integrated so elegantly that it became indistinguishable from the architecture itself.
This project illustrates how smart security technology can be a catalyst for design innovation, rather than a compromise. It also demonstrates the potential for architects to collaborate with technology manufacturers in creating solutions tailored to spatial aesthetics.
Trends Shaping the Future of Energy-Saving Security
Several trends are defining the trajectory of smart, energy-conscious security systems:
- Invisible Design: Cameras that merge with architectural elements, from window frames to wall panels, will dominate luxury projects.
- Energy Autonomy: Solar-powered and kinetic energy-harvesting cameras will become standard in outdoor applications.
- Data-Driven Sustainability: Cameras will not only secure homes but also monitor energy usage patterns, contributing to broader household efficiency.
- Integration with Smart Ecosystems: Security cameras will interact with lighting, HVAC, and shading systems, ensuring that energy-saving strategies are holistic rather than isolated.
These shifts echo the broader architectural ambition of designing homes that are not only intelligent but also sustainably future-proof.
Critical Perspectives: Balancing Privacy, Design, and Ecology
While the promise of energy-saving cameras is compelling, critical questions remain. For instance, how do we balance the discreet integration of cameras with the ethical imperative of transparency in surveillance? And how do we ensure that the push for energy efficiency does not come at the expense of data security? These questions are particularly relevant in the context of IoT security, where vulnerabilities can compromise both privacy and trust.
Architects and designers must therefore approach these technologies with discernment, ensuring that they serve human well-being without eroding the values of openness and trust that define contemporary living spaces.
Conclusion: Security as a Sustainable Design Imperative
The evolution of smart home security cameras that save energy reflects a larger cultural and architectural shift: the recognition that sustainability must permeate every layer of design, from structural systems to the smallest devices. For architects and designers, these cameras are no longer afterthoughts but integral components of a holistic design narrative—one that fuses safety, beauty, and ecological responsibility.
As homes become more intelligent, the challenge is not simply to adopt new technologies but to integrate them in ways that honor the integrity of design and the urgency of sustainability. In this light, the humble security camera emerges as a symbol of the future: discreet, efficient, and deeply attuned to the rhythms of contemporary life.