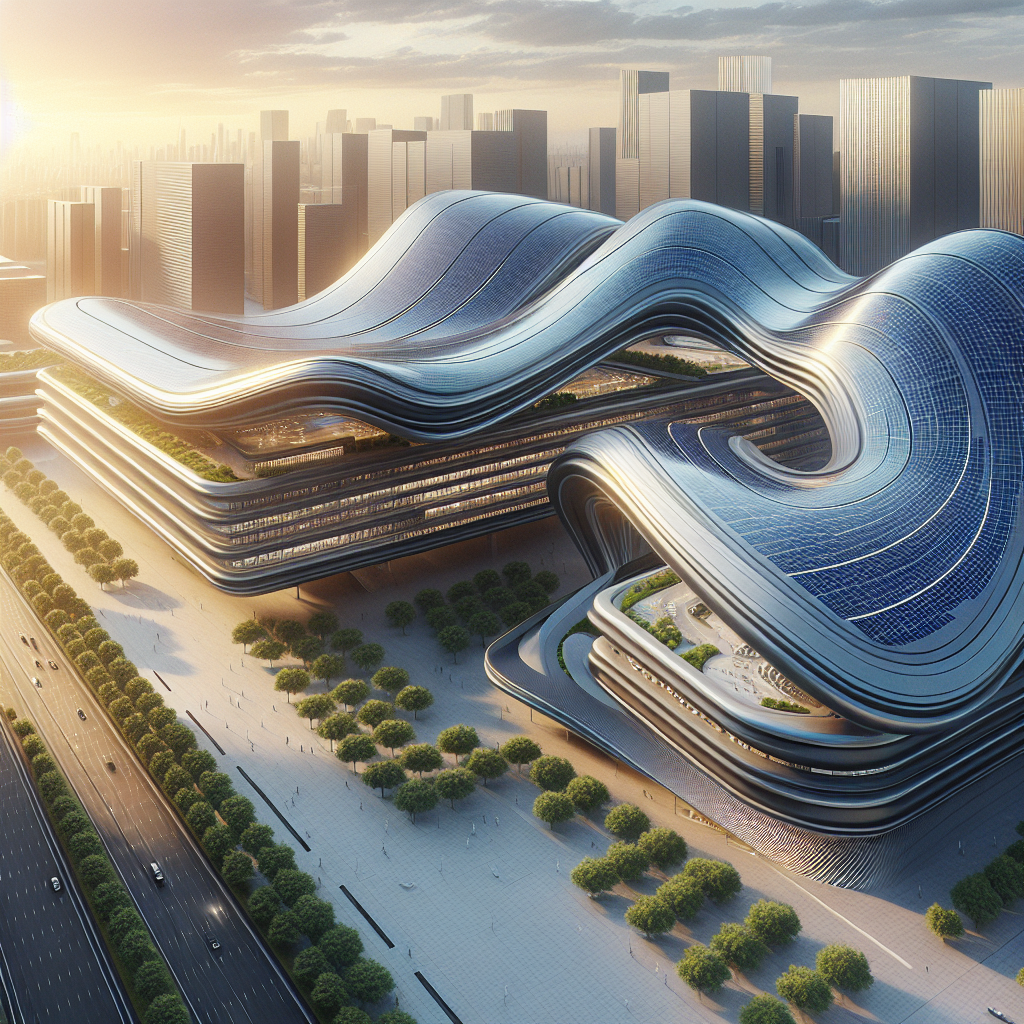
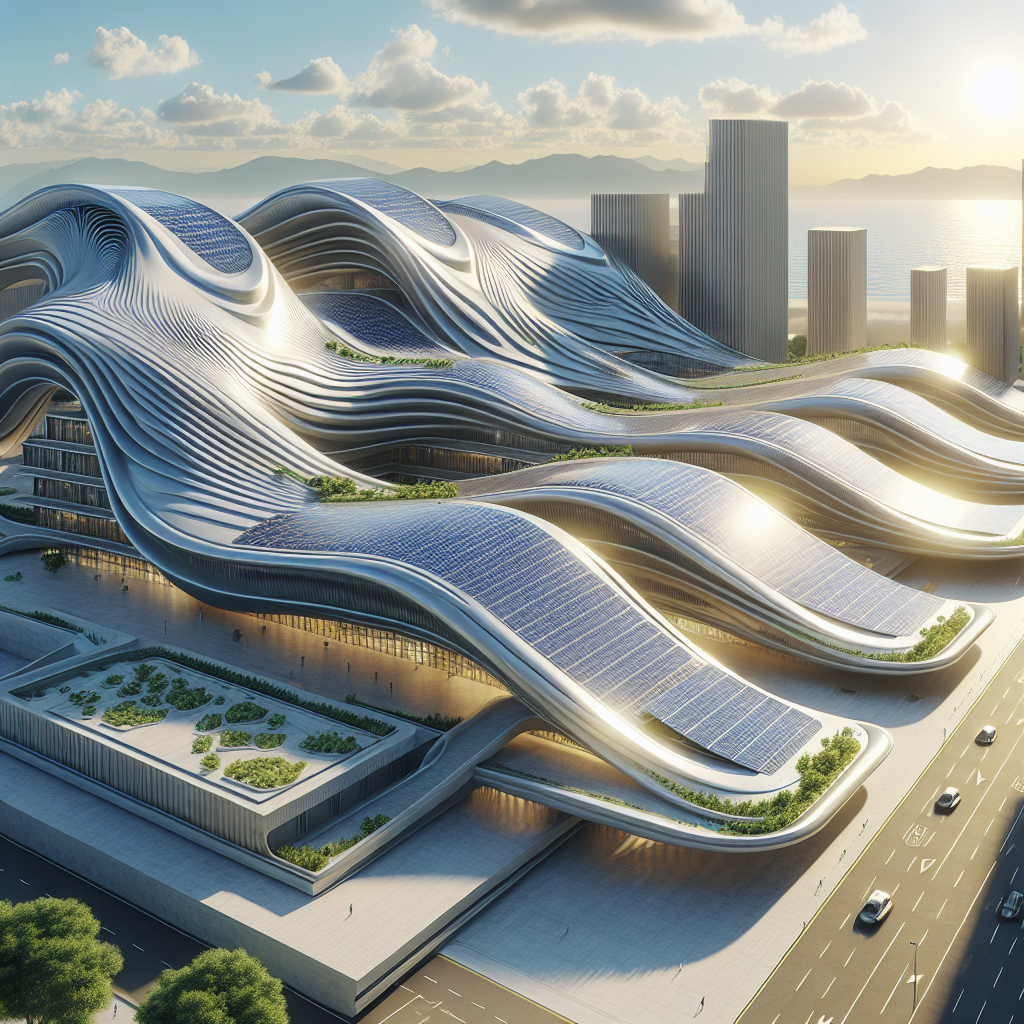
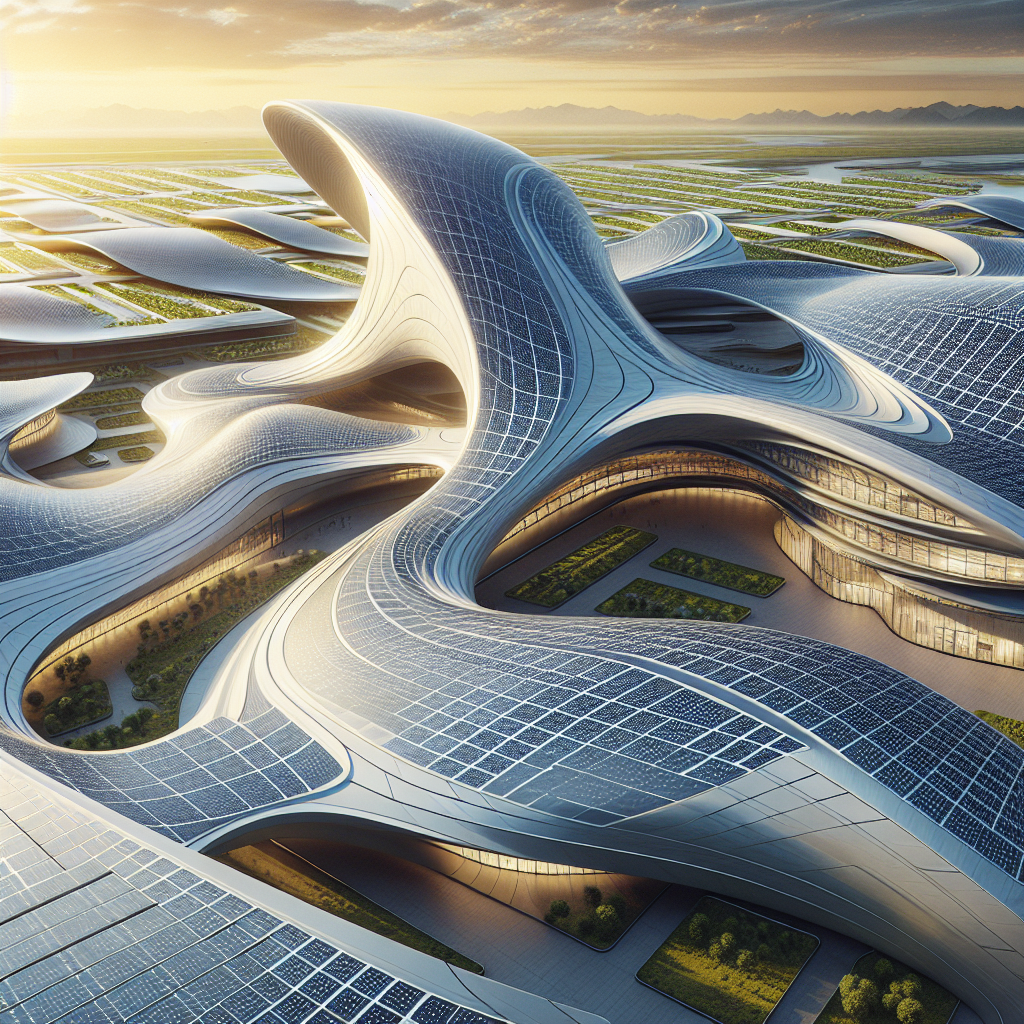
Sinuous solar roofing: wave-like panels capturing optimal sun angles
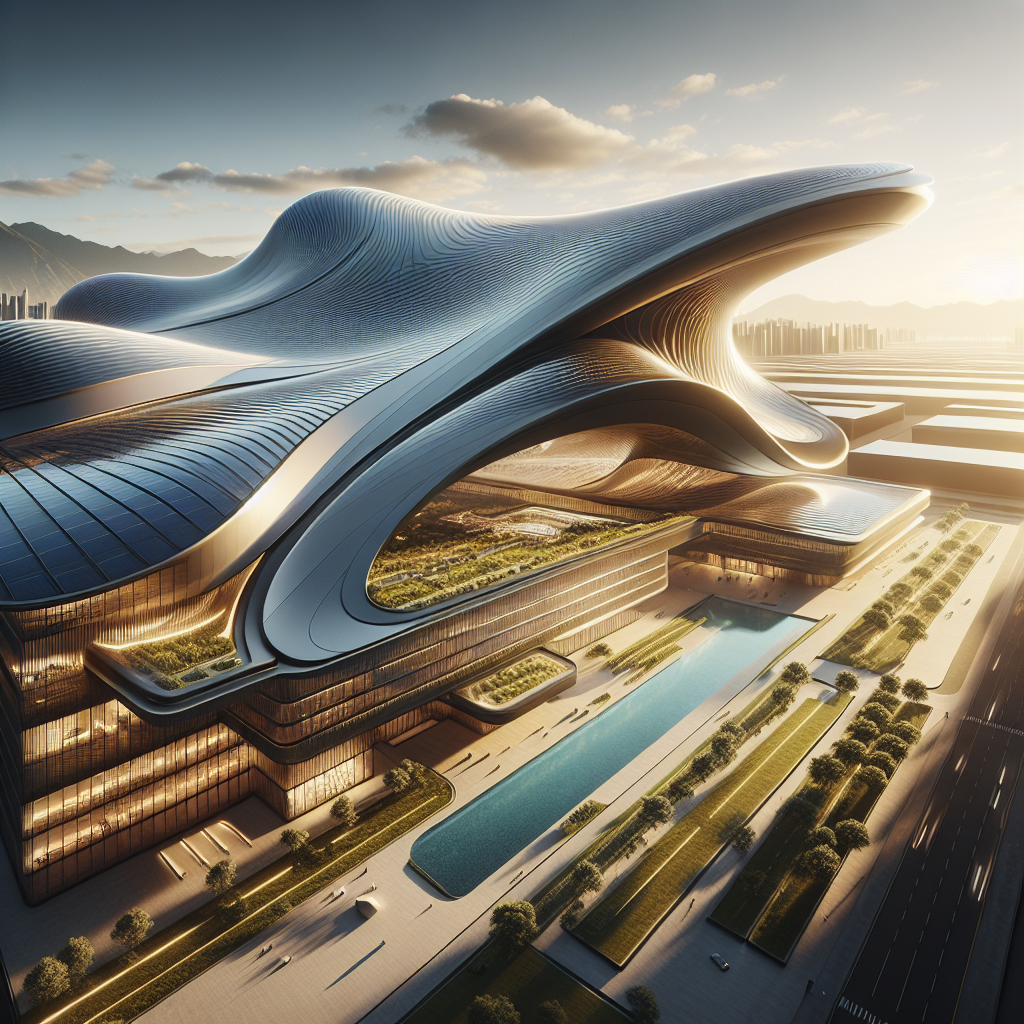

Sinuous Solar Roofing: Wave-Like Panels Capturing Optimal Sun Angles
In the realm of sustainable architecture, solar energy has long been heralded as a key player in achieving carbon neutrality. Yet, traditional solar panels often come with aesthetic compromises, appearing as rigid, rectangular additions that clash with architectural elegance. Today, however, a new generation of sinuous solar roofing is emerging, combining cutting-edge technology with sculptural beauty. These wave-like panels not only capture optimal sun angles but also enhance the visual harmony of contemporary buildings.
The Fusion of Form and Function
Architects and designers have increasingly recognized the need to integrate renewable energy solutions seamlessly into building aesthetics. Sinuous solar roofing, characterized by its undulating, wave-like forms, is revolutionizing the way we perceive solar installations. Unlike conventional flat panels, these curved photovoltaic surfaces maximize sunlight absorption throughout the day, adapting to varying sun angles and orientations. The result is a significant increase in energy efficiency, paired with a striking visual impact.
Inspired by natural forms and biomimicry, architects are drawing from the elegance of ocean waves and sand dunes to create these dynamic structures. This approach aligns with the growing trend of biophilic design, which emphasizes connections between architecture and nature to enhance human well-being and environmental sustainability.
Engineering Innovation: How It Works
The effectiveness of sinuous solar roofing lies in its ability to optimize solar exposure through curvature. Traditional flat panels are most efficient when directly facing the sun, but their efficiency diminishes significantly as the sun moves across the sky. Curved solar panels, however, can maintain a higher level of efficiency by capturing sunlight from multiple angles simultaneously.
These innovative panels often utilize flexible photovoltaic cells, allowing architects greater freedom in design. Advanced computational tools and parametric design techniques are instrumental in shaping these complex forms, ensuring optimal solar exposure and structural integrity. Moreover, modern manufacturing methods, including digital fabrication and 3D printing, facilitate the creation of these intricate shapes, bringing previously unattainable designs to life.
Real-World Applications and Architectural Marvels
Several groundbreaking projects worldwide have already embraced sinuous solar roofing, showcasing its potential to redefine sustainable architecture. One notable example is the Al Bahar Towers in Abu Dhabi, which feature dynamic façades inspired by traditional Arabic mashrabiya screens. These façades adapt to sunlight exposure, significantly reducing energy consumption. Similarly, the Copenhagen International School in Denmark boasts a striking wave-like solar façade, combining renewable energy generation with compelling architectural expression.
In urban contexts, sinuous solar roofing can dramatically transform cityscapes, offering both aesthetic appeal and functional benefits. Cities aiming for net-zero targets, such as Paris in preparation for the 2024 Summer Olympics, could greatly benefit from incorporating these innovative solutions into their architectural strategies.
Environmental and Economic Advantages
Beyond aesthetics and energy efficiency, sinuous solar roofing presents substantial environmental and economic advantages. By maximizing solar capture, these panels significantly reduce reliance on fossil fuels, contributing to global efforts to combat climate change. Furthermore, their integration into building envelopes reduces the need for additional structural supports, lowering construction costs and material usage.
Additionally, the longevity and durability of modern photovoltaic materials ensure that these installations remain effective over extended periods, minimizing maintenance and replacement costs. The financial benefits, combined with governmental incentives and subsidies for renewable energy adoption, make sinuous solar roofing an attractive investment for both private and public sectors.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite the numerous advantages, the widespread adoption of sinuous solar roofing faces certain challenges. High initial costs, complex manufacturing processes, and the need for specialized installation expertise can present barriers for some projects. Nonetheless, as technology advances and economies of scale improve, these obstacles are expected to diminish.
Looking ahead, continued innovation in photovoltaic materials, such as perovskite solar cells, promises even greater efficiency and flexibility. Moreover, integrating smart technology and artificial intelligence into solar roofing systems could further optimize energy generation and management, paving the way for smarter, more responsive buildings.
Aesthetic Revolution in Solar Architecture
The rise of sinuous solar roofing marks a significant shift in architectural design, merging sustainability with aesthetic sophistication. As urban environments become increasingly dense, architects must find innovative ways to integrate renewable energy without compromising visual integrity. These wave-like panels offer a compelling solution, enhancing both functionality and beauty.
Furthermore, the architectural community’s embrace of sinuous solar roofing aligns with broader trends toward sustainability and resilience. Projects incorporating these panels often complement other eco-friendly strategies, such as green roofs, vertical gardens, and rainwater harvesting systems, creating holistic approaches to sustainable design.
Embracing a Sustainable Future
As we move toward a future shaped by climate change and resource scarcity, the integration of renewable energy into architecture becomes increasingly critical. Sinuous solar roofing represents a bold step forward, demonstrating that sustainability and aesthetic excellence can coexist harmoniously. Architects, designers, and urban planners must continue to explore and adopt these innovative solutions, ensuring our built environments remain both beautiful and resilient.
Ultimately, the widespread adoption of sinuous solar roofing could redefine our cities, turning them into vibrant, sustainable landscapes that reflect our commitment to environmental stewardship. By embracing this innovative approach, we can pave the way toward a brighter, more sustainable future, one building at a time.
For further reading on solar energy and its architectural applications, explore the comprehensive resources available on Wikipedia’s Solar Energy page. Additionally, insights into biomimicry and its role in contemporary design can be found on Wikipedia’s Biomimetics page. To delve deeper into parametric design methodologies, visit Wikipedia’s Parametric Design page.