Phygital design bridging: physical objects with NFT-based ownership

Phygital Design Bridging: Physical Objects with NFT-Based Ownership
In the rarefied realms of architecture and design, innovation often emerges at the intersection of the tangible and intangible. Today, as digital landscapes evolve, the boundaries between physical and virtual realities are increasingly blurred. One groundbreaking development capturing the imagination of designers, architects, and collectors alike is the rise of phygital design—the seamless integration of physical objects with NFT-based ownership. This innovative fusion not only reshapes our understanding of ownership and authenticity but also introduces a compelling new dimension to the creative industries.
The Emergence of Phygital Design
At its core, phygital design combines the physical presence of objects with digital verification through blockchain technology. NFTs, or non-fungible tokens, are unique digital assets stored on a blockchain, ensuring authenticity, provenance, and ownership. By linking these digital tokens to tangible items, designers and architects can create a verifiable digital identity for physical creations, enhancing their value and exclusivity.
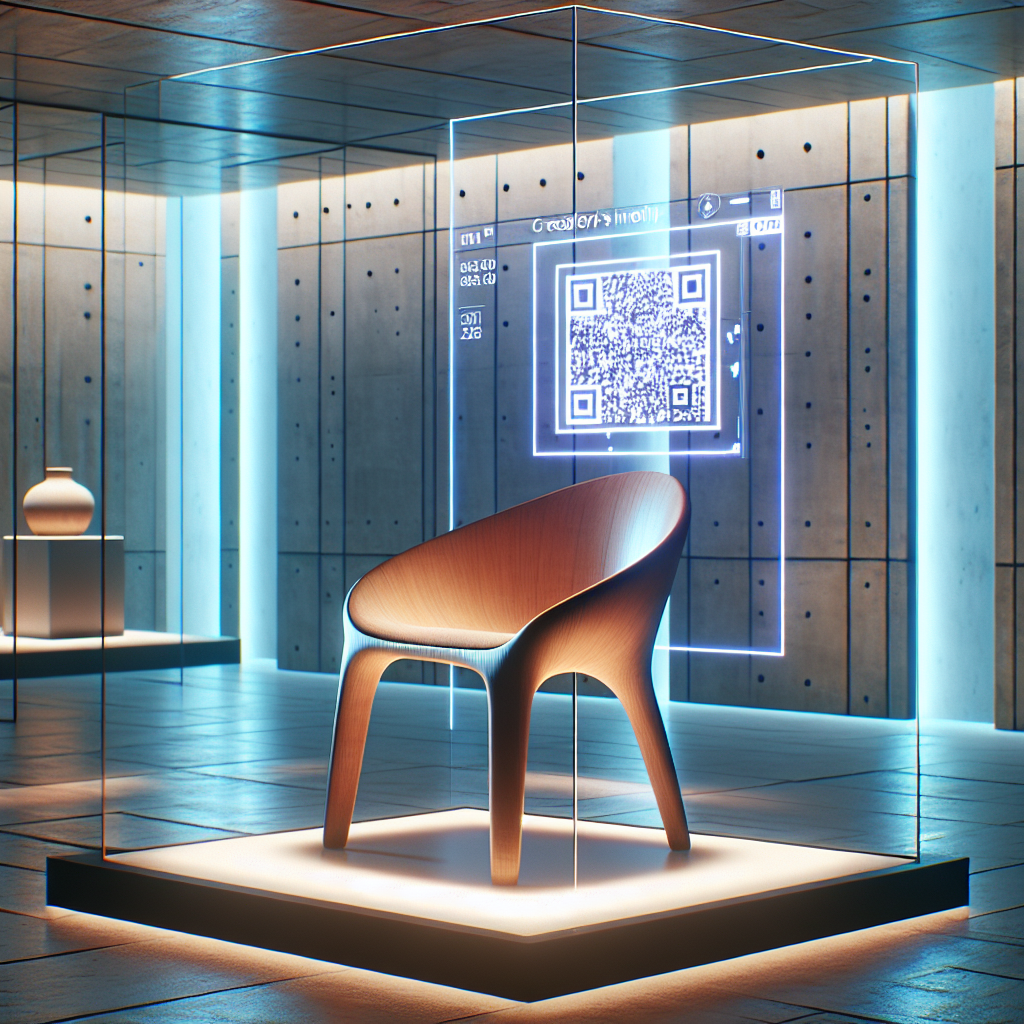
Consider, for instance, a meticulously crafted piece of furniture—a sculptural chair that embodies the spirit of contemporary minimalism. Traditionally, ownership and authenticity might be proven through certificates or documentation, susceptible to loss or forgery. With phygital design, however, the chair’s provenance is immutably recorded on the blockchain, accessible via a simple scan of an embedded QR code or NFC chip. This digital passport not only authenticates the item but also tracks its history, adding layers of narrative and exclusivity that resonate deeply with collectors and enthusiasts.
Bridging the Gap: Real-World Applications
Across the globe, visionary designers and architects are already harnessing the potential of phygital design. In Milan’s vibrant design districts, renowned studios have begun integrating NFTs into limited-edition furniture collections. During the recent Salone del Mobile, several designers showcased physical pieces paired with NFT certificates, transforming traditional collectibles into dynamic, digitally-augmented artifacts. This trend echoes the city’s longstanding reputation as a hub of innovation, as detailed in our exploration of Milan’s Brera Design District.
In architecture, phygital design is equally transformative. Imagine a sustainable timber skyscraper, a modern marvel constructed from renewable materials. By linking each structural component to an NFT, architects can provide comprehensive transparency regarding sourcing, environmental impact, and maintenance history. This approach aligns seamlessly with the industry’s ongoing commitment to sustainability, as exemplified by the rise of wooden skyscrapers worldwide.
Enhancing Value Through Digital Provenance
The allure of phygital design extends beyond mere novelty. By embedding NFTs into physical objects, creators establish an unbreakable chain of custody, significantly enhancing an item’s perceived and actual value. For collectors, this digital provenance provides unparalleled assurance of authenticity, safeguarding investments and elevating the prestige of ownership.
Moreover, NFTs enable creators to retain a connection to their work even after initial sales. Through smart contracts embedded within NFTs, designers can receive royalties from secondary market transactions, ensuring ongoing recognition and financial benefit. This innovative economic model empowers creators, fostering a more equitable and sustainable design ecosystem.
Case Study: The Intersection of Art and Architecture
One compelling example of phygital design in action is the recent collaboration between renowned architect Bjarke Ingels and digital artist Refik Anadol. Their joint project, unveiled in New York City, featured a striking architectural pavilion constructed from recycled aluminum panels. Each panel was digitally mapped and linked to an NFT, allowing collectors to own a piece of the physical structure alongside its digital counterpart. This groundbreaking fusion of architecture and digital art exemplifies the transformative potential of phygital design, reshaping perceptions of ownership and engagement.
Such collaborations highlight the increasing fluidity between disciplines, as explored in our previous analysis of interactive installations engaging people with art and design. By embracing digital technologies, architects and designers can expand their creative horizons, forging new pathways for artistic expression and audience interaction.
Phygital Design and Sustainability
Beyond aesthetics and economics, phygital design also holds significant implications for sustainability. By providing transparent, verifiable records of materials, sourcing, and manufacturing processes, NFTs empower consumers to make informed, environmentally-conscious decisions. This aligns closely with the industry’s broader commitment to sustainable practices, as highlighted in our exploration of zero-waste masterpieces and circular economy principles.
For instance, a furniture designer utilizing reclaimed materials can embed detailed sustainability data within an NFT, accessible to potential buyers through augmented reality interfaces. This level of transparency not only enhances consumer trust but also incentivizes designers to adopt responsible practices, fostering a virtuous cycle of innovation and accountability.
The Future of Phygital Design
As digital technologies continue to evolve, the potential applications of phygital design are virtually limitless. Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) integrations promise immersive experiences, allowing collectors to visualize digital counterparts of physical objects within their own spaces. Imagine previewing a bespoke lighting fixture in your living room through AR, confident in its authenticity and provenance thanks to its NFT certification.
Moreover, the rise of decentralized metaverse platforms offers intriguing possibilities for phygital design. Physical objects linked to NFTs can exist simultaneously in virtual worlds, allowing owners to showcase their collections in digital galleries or virtual homes. This convergence of physical and digital realms underscores the transformative potential of phygital design, redefining our relationship with objects and spaces.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its immense promise, phygital design is not without challenges. Issues surrounding blockchain energy consumption, data privacy, and technological accessibility must be thoughtfully addressed. Designers and architects must navigate these complexities responsibly, ensuring that innovations align with ethical and environmental standards.
Furthermore, widespread adoption of phygital design requires education and awareness among consumers and industry professionals alike. As with any emerging technology, clear communication and transparency are essential to building trust and fostering meaningful engagement.
Conclusion: A New Era of Design Innovation
Phygital design represents a paradigm shift, bridging the tangible and intangible in unprecedented ways. By harnessing the power of NFTs and blockchain technology, designers and architects can enhance authenticity, sustainability, and economic equity within their industries. As we continue to explore this exciting frontier, the possibilities for innovation and creativity are boundless, promising a future where physical objects and digital identities coexist seamlessly.
In embracing phygital design, we step boldly into a new era—one defined by interconnectedness, transparency, and limitless potential. The future of design is here, and it is undeniably phygital.