Kinetic Facade Design: Transforming Architecture with Movement

Kinetic Facade Design: Transforming Architecture with Movement
Architecture, traditionally perceived as static and permanent, is experiencing a transformative shift towards dynamism and adaptability. At the forefront of this evolution is the innovative realm of kinetic facade design, a discipline that merges technology, aesthetics, and functionality to create buildings that move, breathe, and respond to their environments. These facades not only captivate with their visual spectacle but also enhance sustainability, occupant comfort, and urban resilience. As architects and designers increasingly embrace movement as a fundamental design principle, kinetic facades are redefining our built environment, bringing architecture to life in unprecedented ways.
The Essence of Kinetic Facades: Architecture in Motion
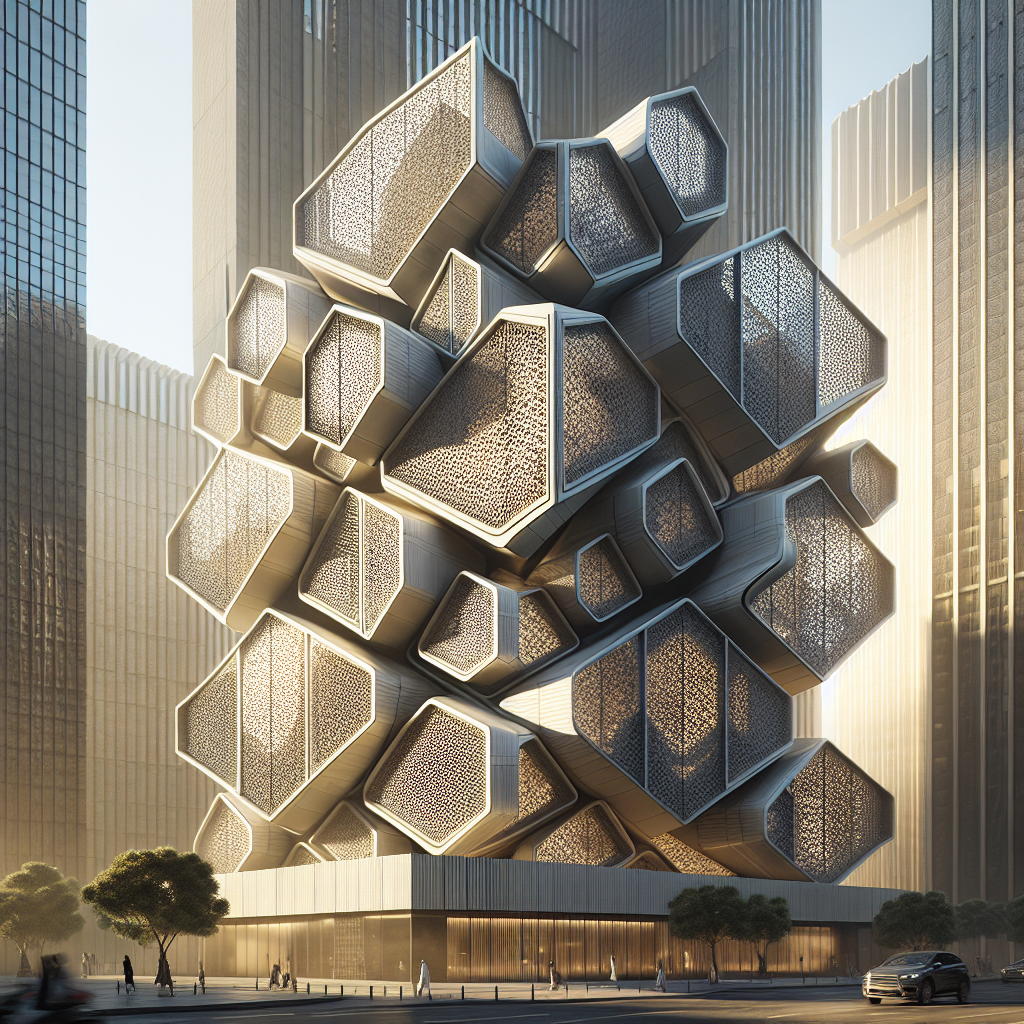
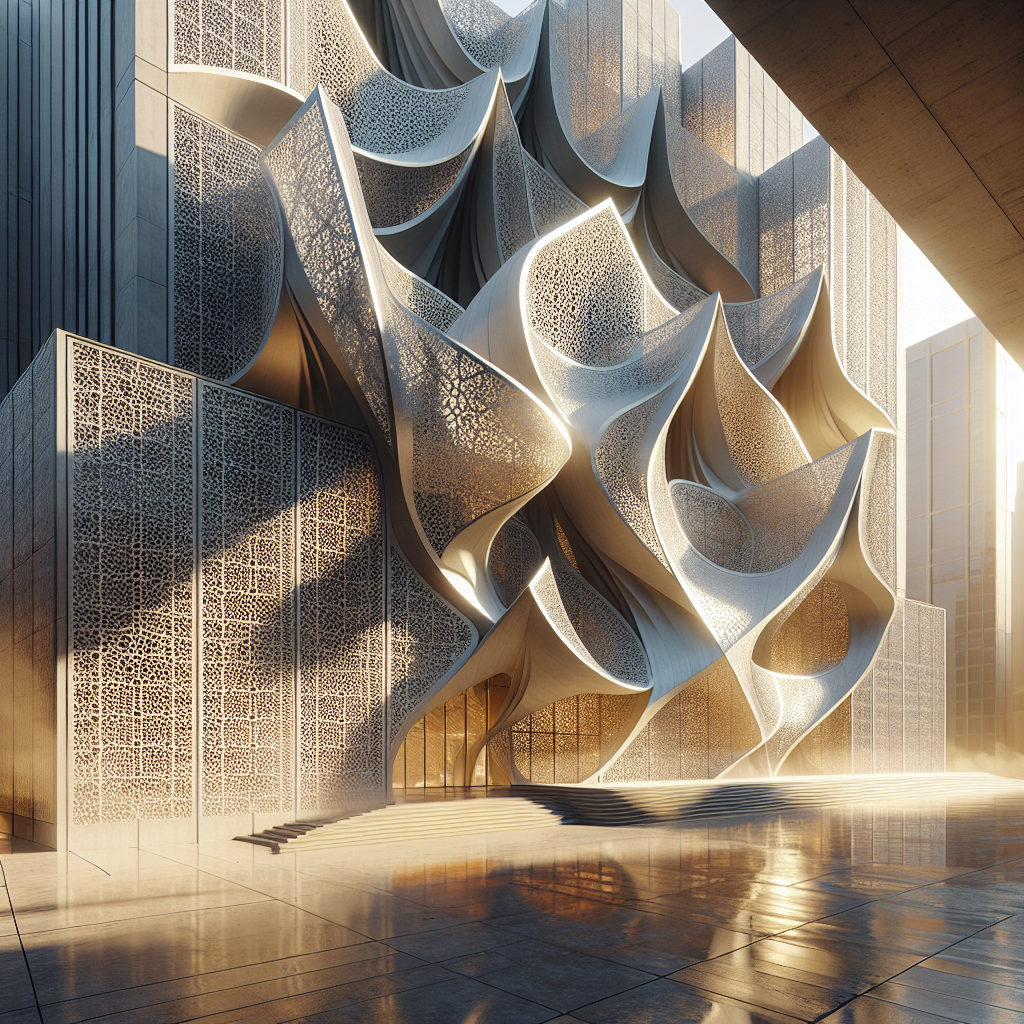
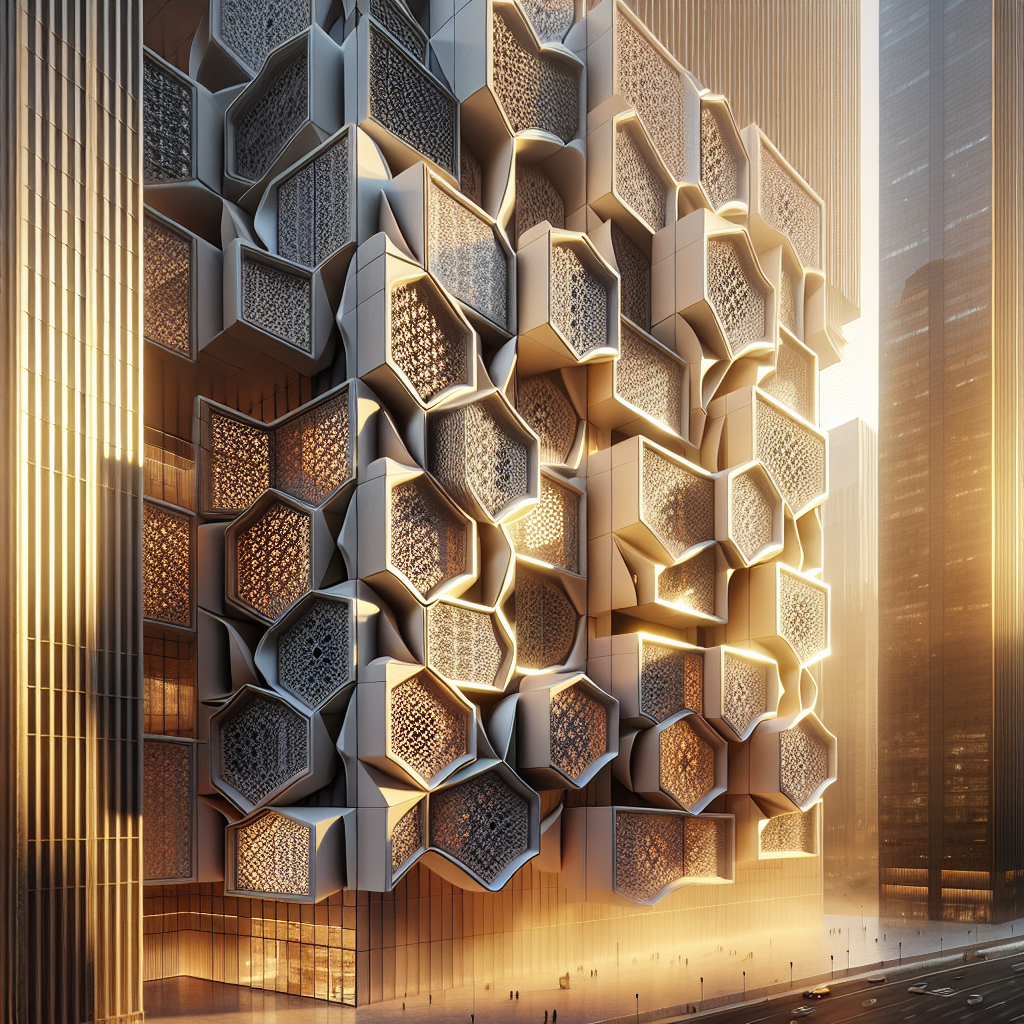
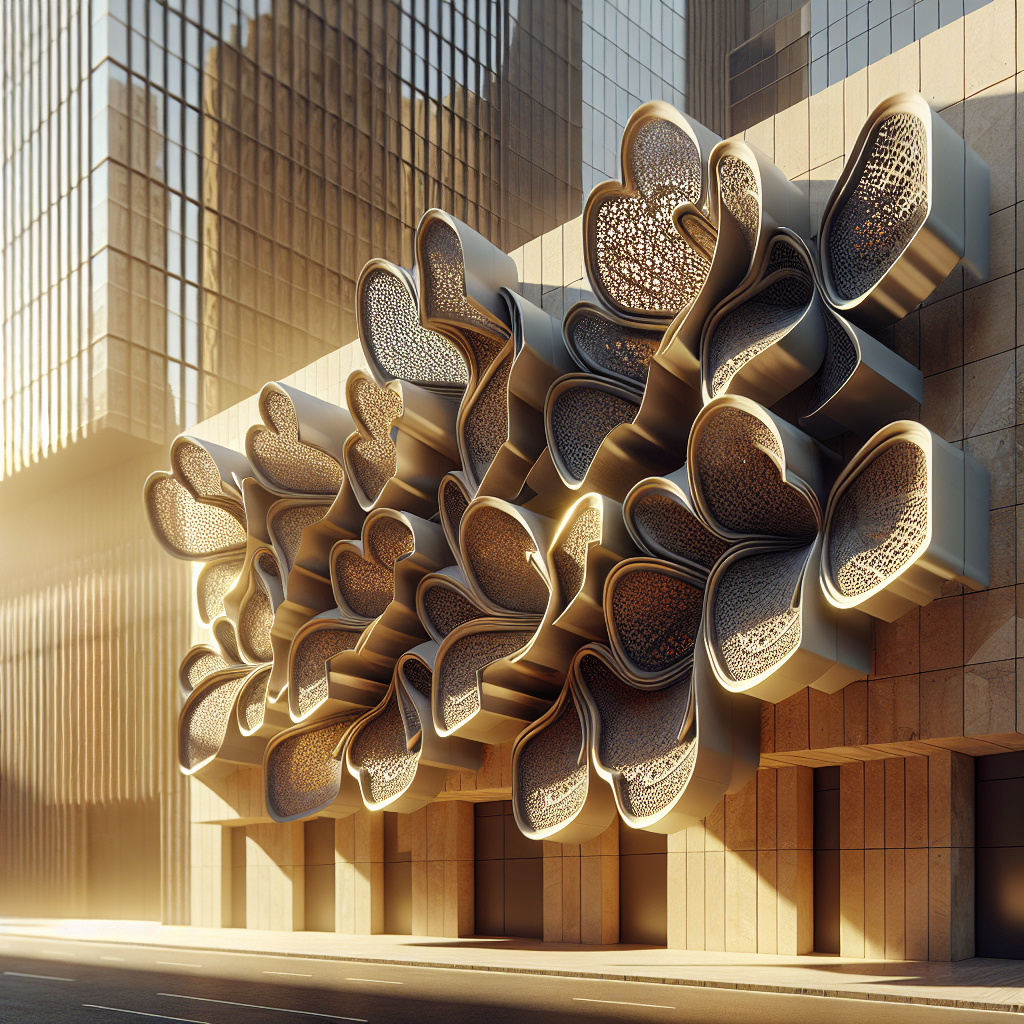
Kinetic facades are architectural systems designed to dynamically alter their appearance, structure, or function in response to environmental stimuli, user interaction, or programmed sequences. This concept challenges traditional notions of architecture as a static entity, introducing an element of fluidity and responsiveness. Whether through rotating panels, sliding screens, or undulating surfaces, kinetic facades create a dialogue between buildings and their surroundings, adapting to changing conditions such as sunlight, temperature, wind, and human activity.
Imagine a building whose exterior gently shifts throughout the day, opening like petals in the morning sun and closing as twilight approaches. Picture facades that ripple like waves, responding to the rhythm of urban life. These dynamic structures are not mere fantasies but tangible realities, reshaping skylines and redefining architectural possibilities.
Balancing Aesthetics and Functionality
While kinetic facades undeniably offer striking visual appeal, their value extends far beyond aesthetics. By actively responding to environmental conditions, these facades significantly enhance building performance and occupant comfort. For instance, adjustable shading systems can reduce solar heat gain, optimizing energy efficiency and lowering cooling costs. Similarly, responsive ventilation panels improve indoor air quality and thermal comfort, creating healthier and more pleasant interior environments.
A prime example is the Al Bahr Towers in Abu Dhabi, whose iconic facade comprises a series of automated shading panels inspired by traditional Islamic latticework, or mashrabiya. These panels dynamically open and close in response to sunlight, reducing solar gain by up to 50% and significantly lowering energy consumption. Such innovations underscore the potential of kinetic facades to harmonize form and function, beauty and sustainability.
Technological Innovations Driving Kinetic Architecture
The evolution of kinetic facades is closely intertwined with advancements in technology. Sophisticated sensors, actuators, and control systems enable facades to respond intelligently and seamlessly to external stimuli. Materials science plays a crucial role, with innovations such as shape-memory alloys, smart glass, and adaptive textiles expanding the possibilities for dynamic architectural expression.
Moreover, the integration of digital fabrication techniques, such as 3D printing and parametric design, has empowered architects to explore complex, organic forms previously unattainable through conventional methods. As highlighted in our exploration of digital fabrication in design and construction, these technologies facilitate precision, customization, and innovation, fueling the growth of kinetic architecture.
Case Studies: Kinetic Facades in Action
Several landmark projects exemplify the transformative potential of kinetic facades. The Milwaukee Art Museum’s Quadracci Pavilion, designed by Santiago Calatrava, features a stunning brise-soleil that opens and closes like wings, creating a dramatic spectacle while controlling natural light. Similarly, the dynamic facade of the Bund Finance Centre in Shanghai, designed by Foster + Partners and Heatherwick Studio, consists of bronze tubes that rotate gracefully, revealing and concealing the building’s interior spaces.
In the realm of sustainability, the Media-TIC building in Barcelona stands out. Its innovative facade employs ETFE cushions that inflate and deflate in response to sunlight, regulating thermal insulation and reducing energy consumption by up to 20%. Such pioneering projects demonstrate how kinetic facades can simultaneously captivate the imagination and address pressing environmental challenges.
Urban Impact and the Future of Kinetic Facades
As cities grapple with climate change, population growth, and resource scarcity, kinetic facades offer compelling solutions for creating resilient, adaptable urban environments. By integrating movement and responsiveness into building envelopes, architects can enhance urban microclimates, mitigate heat island effects, and foster greater harmony between built and natural environments.
Moreover, kinetic facades contribute to the vitality and dynamism of urban spaces, transforming buildings into interactive landmarks that engage communities and enrich public life. As discussed in our article on designing public spaces for people and the environment, architecture that responds to human needs and environmental conditions can profoundly impact urban livability and sustainability.
Challenges and Considerations in Kinetic Facade Design
Despite their numerous advantages, kinetic facades present unique challenges that architects and designers must navigate. Maintenance and durability are critical considerations, as moving components require regular upkeep and robust engineering to withstand environmental stresses. Additionally, the integration of complex mechanical and electronic systems necessitates careful planning, coordination, and expertise.
Cost is another significant factor, as kinetic facades typically involve higher initial investments compared to static alternatives. However, these costs can be offset by long-term energy savings, improved occupant comfort, and enhanced building performance. As the technology matures and becomes more accessible, kinetic facades are likely to become increasingly prevalent in mainstream architecture.
The Intersection of Kinetic Facades and Biophilic Design
Interestingly, kinetic facades align closely with principles of biophilic design, which emphasizes the integration of natural elements and processes into the built environment. As explored in our piece on biophilic design and its impact on human health and well-being, incorporating nature-inspired movement and adaptability can enhance psychological well-being, reduce stress, and foster deeper connections between occupants and their surroundings.
By mimicking natural phenomena such as leaves rustling in the wind or flowers opening to sunlight, kinetic facades evoke a sense of harmony and vitality, enriching the human experience of architecture. This synergy between kinetic and biophilic design underscores the potential for movement to profoundly enhance both aesthetic and experiential dimensions of buildings.
Conclusion: Embracing the Dynamic Future of Architecture
Kinetic facade design represents a bold departure from traditional architectural paradigms, introducing movement, responsiveness, and adaptability as core design principles. As technology advances and sustainability becomes increasingly imperative, kinetic facades offer architects and designers powerful tools for creating buildings that are not only visually captivating but also environmentally responsible and human-centric.
From enhancing energy efficiency and occupant comfort to revitalizing urban spaces and fostering biophilic connections, kinetic facades embody the dynamic potential of contemporary architecture. As we continue to explore and innovate, the future promises a built environment that moves, breathes, and evolves alongside us, transforming our cities and enriching our lives.
For further insights into how technology shapes architectural futures, explore our analysis of technology’s impact on futuristic city design in Blade Runner 2049.