Industrial IoT Innovations: Technology Reshaping Manufacturing

Industrial IoT Innovations: Technology Reshaping Manufacturing
In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, the integration of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) technologies has emerged as a transformative force, reshaping not only the way products are created but also redefining the very environments in which manufacturing occurs. For design and architecture professionals, industry insiders, and sophisticated design enthusiasts, understanding the profound implications of IIoT innovations is crucial. From smart factories to sustainable production processes, these advancements are revolutionizing the built environment, offering fresh perspectives on space utilization, material selection, and environmental impact.
The Rise of Smart Factories: A New Architectural Paradigm
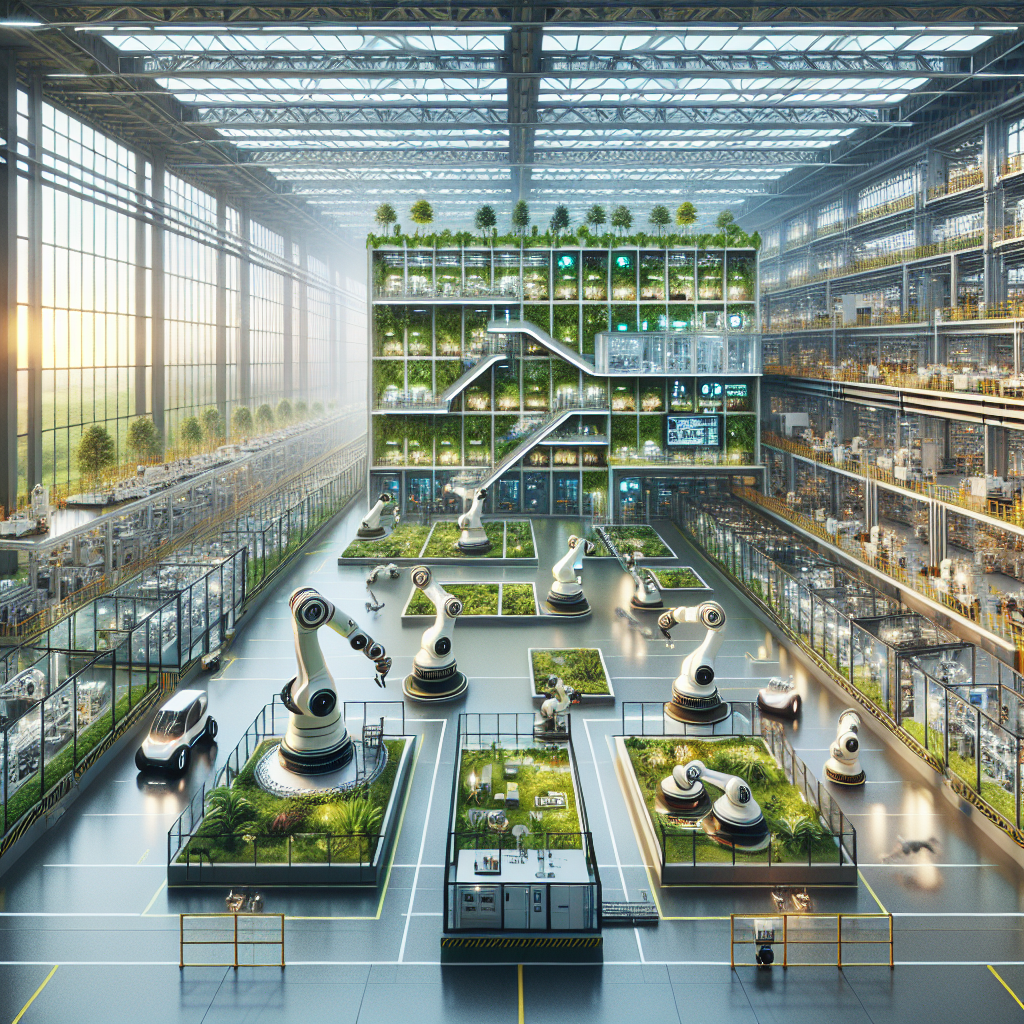
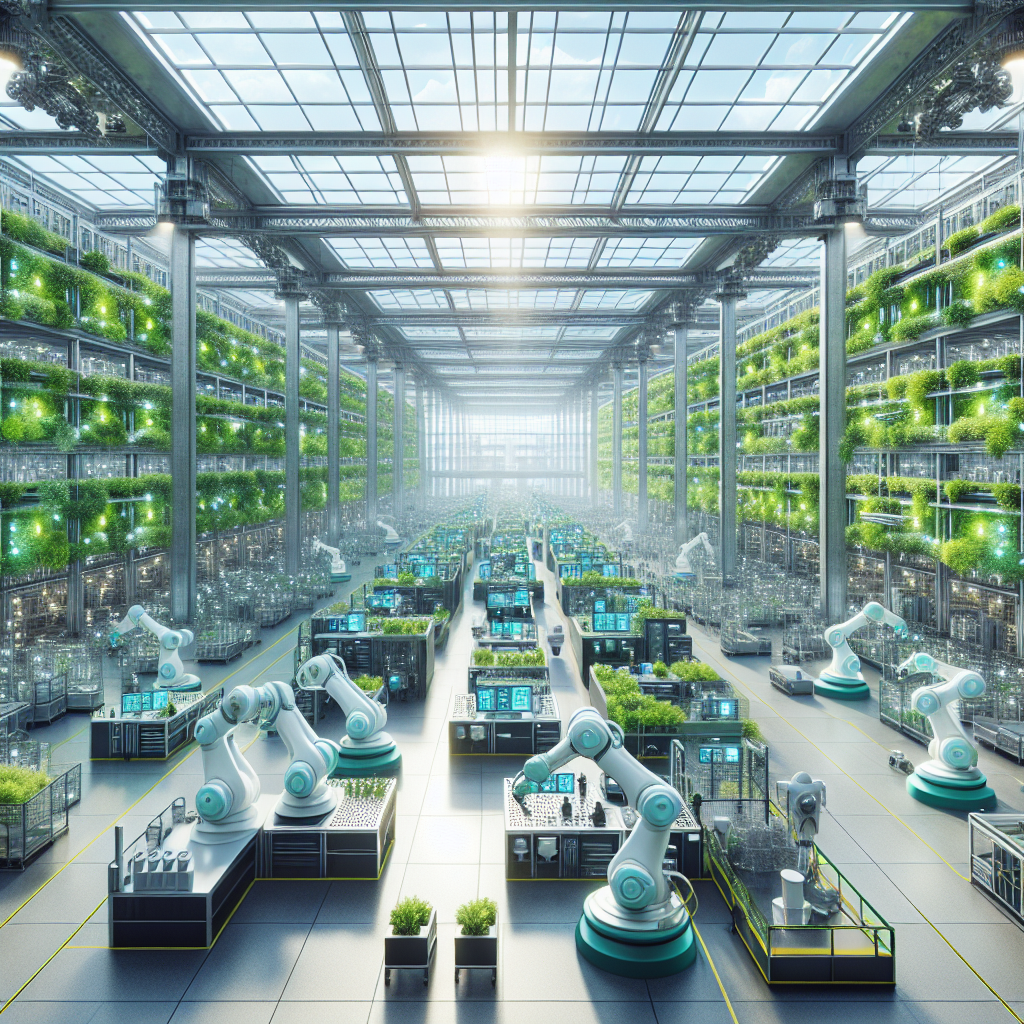
At the forefront of this industrial renaissance is the concept of the smart factory. These advanced manufacturing facilities seamlessly integrate digital technologies, robotics, and IoT sensors to optimize production efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance safety. The architectural implications are profound: factories are no longer mere utilitarian spaces but sophisticated, interconnected ecosystems designed for maximum flexibility and sustainability.
Consider the futuristic Tesla Gigafactory in Nevada, a sprawling structure that epitomizes the smart factory ethos. Its vast, open interiors are meticulously planned to accommodate automated assembly lines, robotic arms, and sensor-equipped machinery, all communicating in real-time. This architectural approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also significantly reduces energy consumption and environmental impact, aligning with contemporary sustainability goals outlined in our exploration of the path to net-zero for design and architecture.
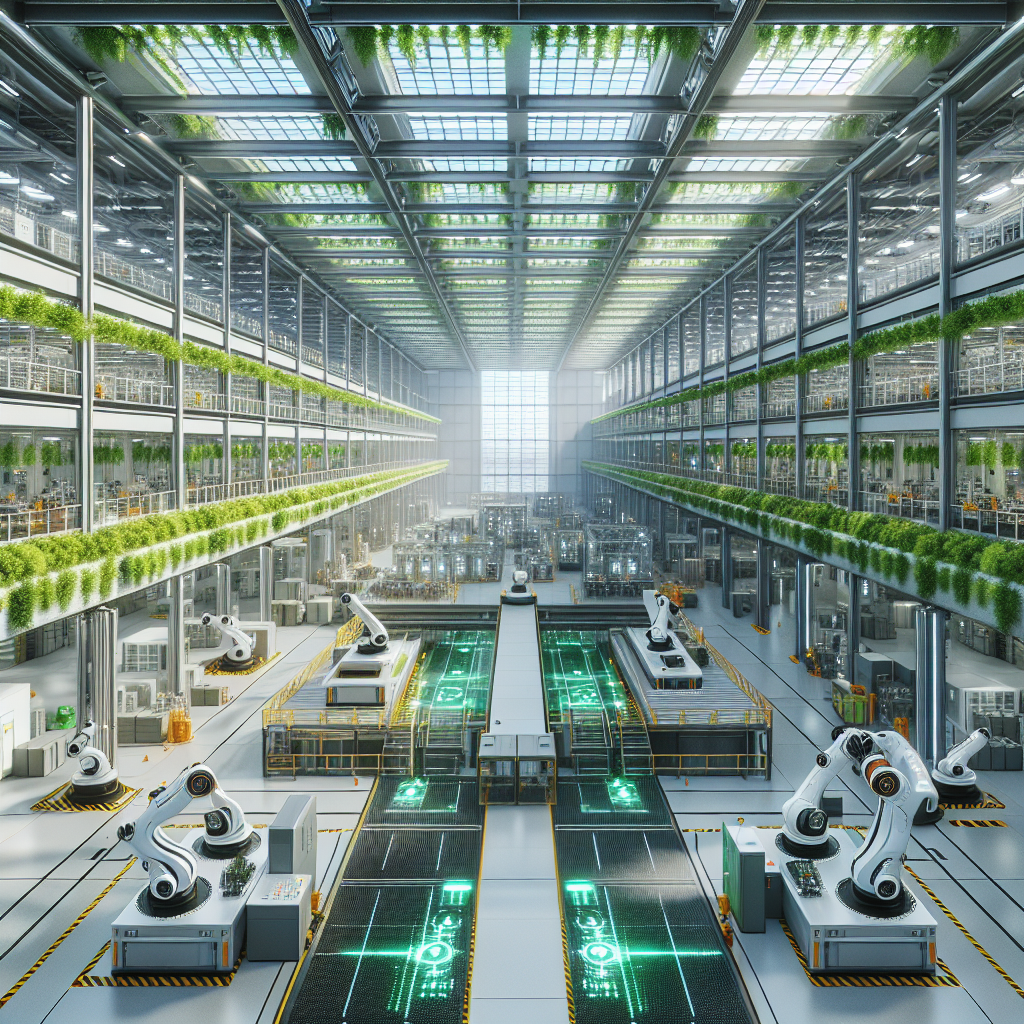
IoT-Driven Sustainability: Redefining Material Use and Waste Reduction
Industrial IoT innovations extend beyond mere efficiency, profoundly influencing sustainability practices within manufacturing. IoT sensors embedded within production lines meticulously monitor material usage, detect inefficiencies, and predict maintenance needs, dramatically reducing waste and resource consumption. This shift toward sustainable manufacturing practices resonates deeply with the principles of zero-waste design and circular economy, where architects and designers are increasingly prioritizing environmental responsibility.
For instance, BMW’s Leipzig plant in Germany employs IoT technologies to track and optimize energy usage, achieving remarkable reductions in energy consumption. Architecturally, the facility integrates natural lighting, green roofs, and passive ventilation systems, demonstrating how IoT-enabled sustainability can inspire innovative architectural solutions. The visual harmony of industrial elements juxtaposed with lush greenery creates an environment that is both functional and aesthetically pleasing, redefining traditional perceptions of industrial architecture.
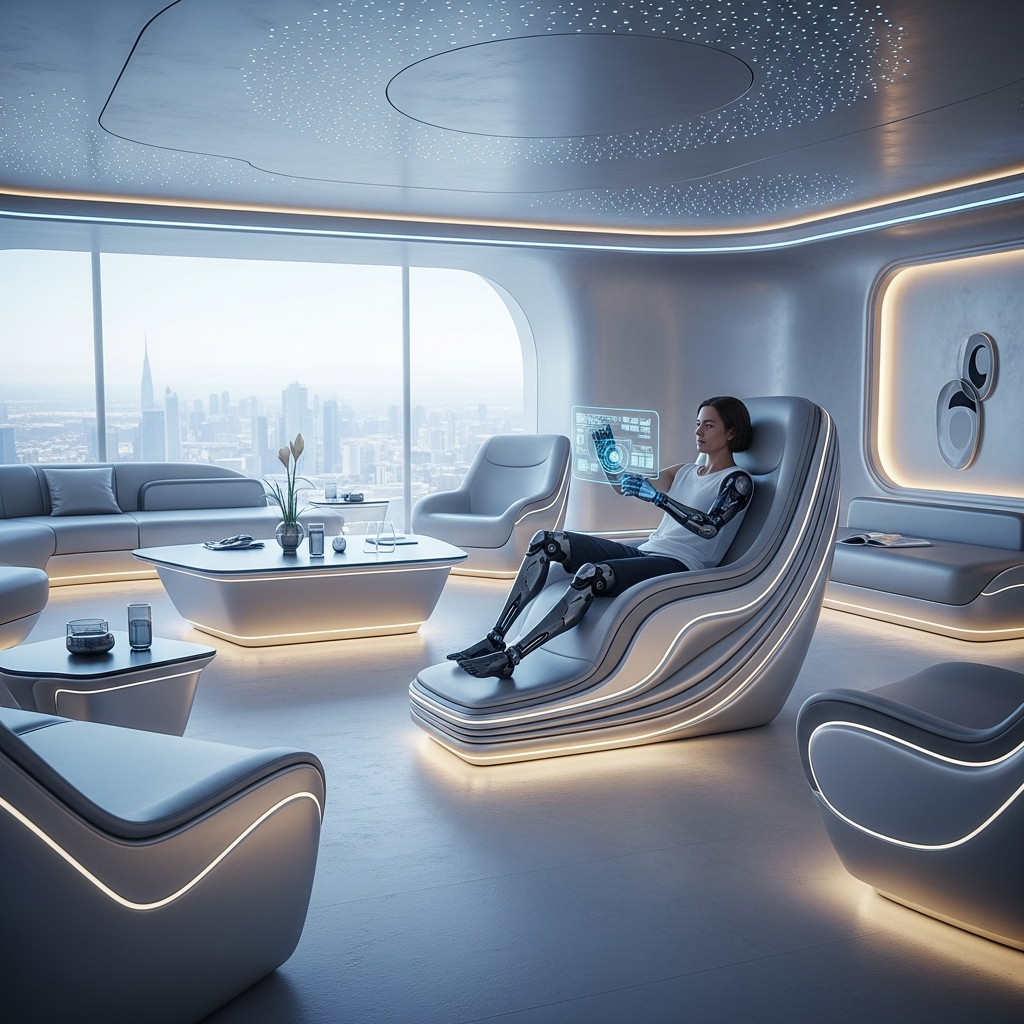
Human-Centric Design: Enhancing Workplace Environments through IoT
Beyond machinery and materials, the human experience within manufacturing environments is undergoing a radical transformation, driven by IoT innovations. Smart wearables, environmental sensors, and adaptive lighting systems are enhancing worker safety, comfort, and productivity. This human-centric approach aligns with broader trends in biophilic design, emphasizing the importance of integrating natural elements and ergonomic considerations into industrial spaces.
A striking example is Adidas’ Speedfactory in Ansbach, Germany, where IoT technologies facilitate a highly responsive and adaptive workplace. The factory’s interiors feature dynamic lighting systems that adjust to workers’ circadian rhythms, sensor-equipped workstations that optimize ergonomics, and abundant greenery that improves air quality and psychological well-being. The result is a manufacturing environment that prioritizes human health and happiness, demonstrating the profound potential of IoT-driven design innovations.
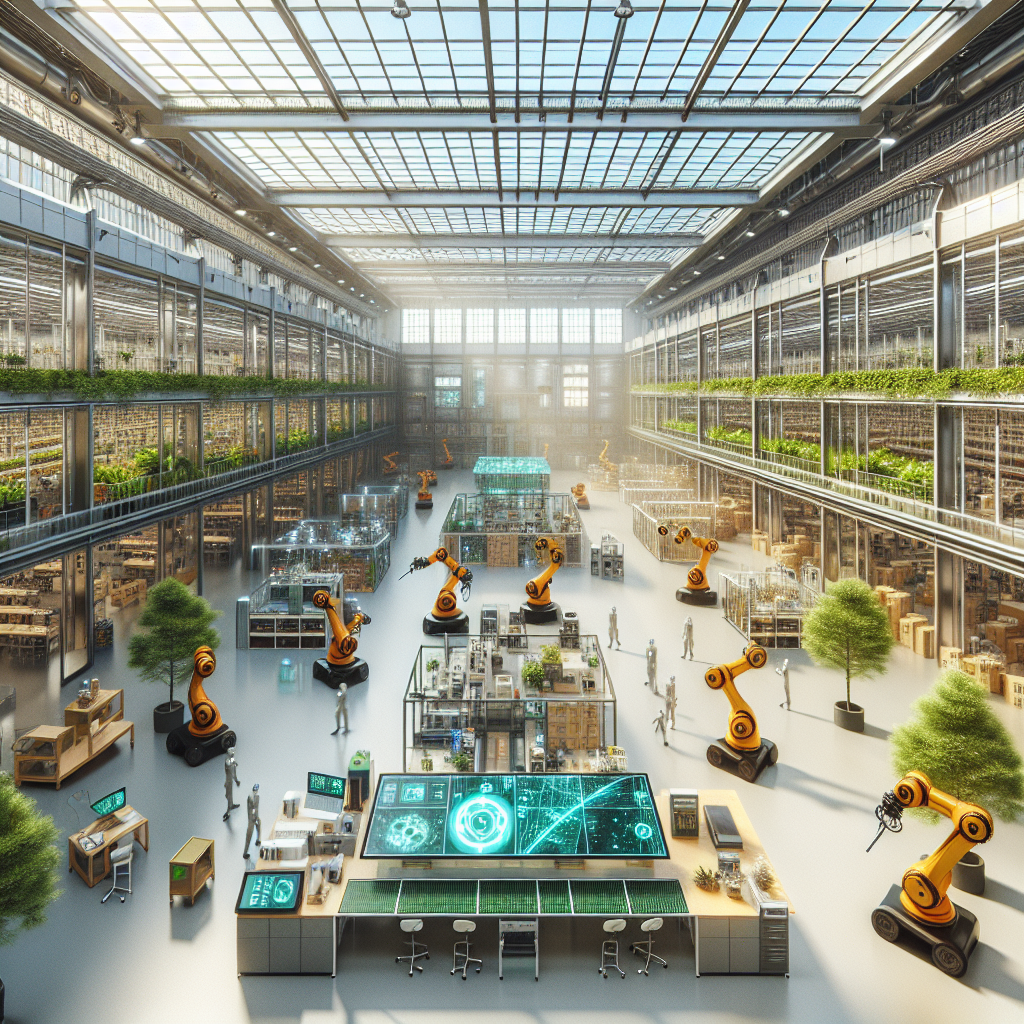
Architectural Flexibility: Modular and Adaptive Manufacturing Spaces
One of the most compelling architectural implications of Industrial IoT is the rise of modular and adaptive manufacturing spaces. IoT-enabled factories are designed for rapid reconfiguration, allowing production lines to swiftly adapt to changing market demands or new product introductions. This architectural flexibility echoes the principles explored in our article on modular design solutions, emphasizing adaptability and responsiveness in contemporary architecture.
Take, for example, the innovative Factory 56 by Mercedes-Benz in Sindelfingen, Germany. Its architectural design incorporates modular elements, movable partitions, and flexible assembly stations, all connected through IoT systems that facilitate seamless reconfiguration. Visually, the factory’s sleek, minimalist interiors exude sophistication, with polished concrete floors, expansive glass facades, and exposed structural elements that highlight the beauty of industrial efficiency.
IoT and Urban Manufacturing: Integrating Production into Cityscapes
As urban populations continue to grow, the integration of manufacturing facilities within city environments presents unique architectural challenges and opportunities. Industrial IoT technologies enable cleaner, quieter, and more compact manufacturing processes, making urban manufacturing not only feasible but desirable. This trend aligns with broader urban design movements such as vertical farming and adaptive reuse, which seek to optimize urban space utilization.
Brooklyn’s New Lab exemplifies this urban manufacturing revolution. Housed within a repurposed shipbuilding facility, New Lab integrates IoT-driven manufacturing processes within a vibrant urban context. Architecturally, the space celebrates its industrial heritage, with exposed steel beams, expansive skylights, and polished concrete surfaces, while IoT technologies ensure minimal environmental impact and seamless integration with the surrounding urban fabric.
Challenges and Considerations: Navigating the IoT Landscape
Despite the immense potential of Industrial IoT innovations, architects and designers must navigate significant challenges, particularly concerning cybersecurity and data privacy. As manufacturing facilities become increasingly interconnected, the risk of cyber threats escalates, necessitating robust security measures and thoughtful architectural planning. The importance of IoT security is explored in-depth in our article on protecting smart devices in a connected world.
Moreover, the integration of IoT technologies requires careful consideration of spatial planning, infrastructure requirements, and environmental impact. Architects must balance technological innovation with aesthetic considerations, ensuring that manufacturing facilities remain visually compelling and contextually appropriate within their surroundings.
The Future of Manufacturing Architecture: Embracing IoT Innovations
As Industrial IoT technologies continue to evolve, their architectural implications will undoubtedly expand, reshaping manufacturing environments in profound and unexpected ways. From smart factories and sustainable practices to human-centric design and urban integration, IoT innovations offer architects and designers unprecedented opportunities to redefine industrial spaces.
Ultimately, embracing these technological advancements requires a visionary approach, one that prioritizes sustainability, flexibility, and human well-being. By thoughtfully integrating IoT innovations into architectural practice, design professionals can create manufacturing environments that are not only efficient and sustainable but also visually inspiring and profoundly human-centric.
In the rapidly changing landscape of manufacturing, the convergence of technology and architecture promises a future where industrial spaces are as beautiful as they are functional, embodying the very essence of innovation and creativity.
For further reading on the intersection of technology and architectural innovation, explore our analysis of technology’s impact on futuristic city design in Blade Runner 2049.
References
- Industrial Internet of Things – Wikipedia
- Smart Factory – Wikipedia
- Sustainable Manufacturing – Wikipedia