Indoor Plant Walls: Design Trends That Purify and Beautify

Indoor Plant Walls: Design Trends That Purify and Beautify
In the evolving landscape of contemporary interiors, indoor plant walls—also known as vertical gardens or living walls—have transcended their role as decorative features to become integral elements of architectural and interior design. These lush, vertical ecosystems are not only celebrated for their aesthetic appeal but also for their ability to purify indoor air, regulate humidity, and enhance well-being. As the design world increasingly embraces biophilic design principles, plant walls are emerging as both a visual statement and a functional necessity in high-end residential, commercial, and hospitality projects.
The Rise of Indoor Plant Walls in Contemporary Design
The concept of vertical greenery is not new. From the legendary Hanging Gardens of Babylon to the moss-covered courtyards of Japanese temples, architects have long sought to integrate vegetation into built environments. What distinguishes today’s plant walls is the sophistication of their modular systems, irrigation technologies, and sustainable substrates. These innovations allow designers to create verdant installations that thrive indoors with minimal maintenance, transforming sterile walls into dynamic, living canvases.
According to a 2023 report by the World Green Building Council, biophilic features such as indoor greenery can increase workplace productivity by up to 15% and reduce stress levels significantly. For architects and designers, this data underscores the importance of plant walls not just as visual enhancements but as strategic investments in human-centered environments.
Health and Environmental Benefits
Indoor plant walls are more than ornamental; they function as natural air filters. Studies by NASA in the late 20th century, further validated by contemporary research, show that plants can absorb toxins such as benzene, formaldehyde, and trichloroethylene from the air. In urban contexts where indoor air quality is often compromised, plant walls provide a sustainable and aesthetically refined solution.
Beyond air purification, plant walls contribute to thermal regulation. By adding a layer of vegetation, they help stabilize indoor temperatures, reducing reliance on artificial heating and cooling systems. This aligns with broader sustainability goals, echoing the movement toward green architecture and energy-efficient design practices.
Design Trends Shaping Indoor Plant Walls
1. Sculptural Greenery
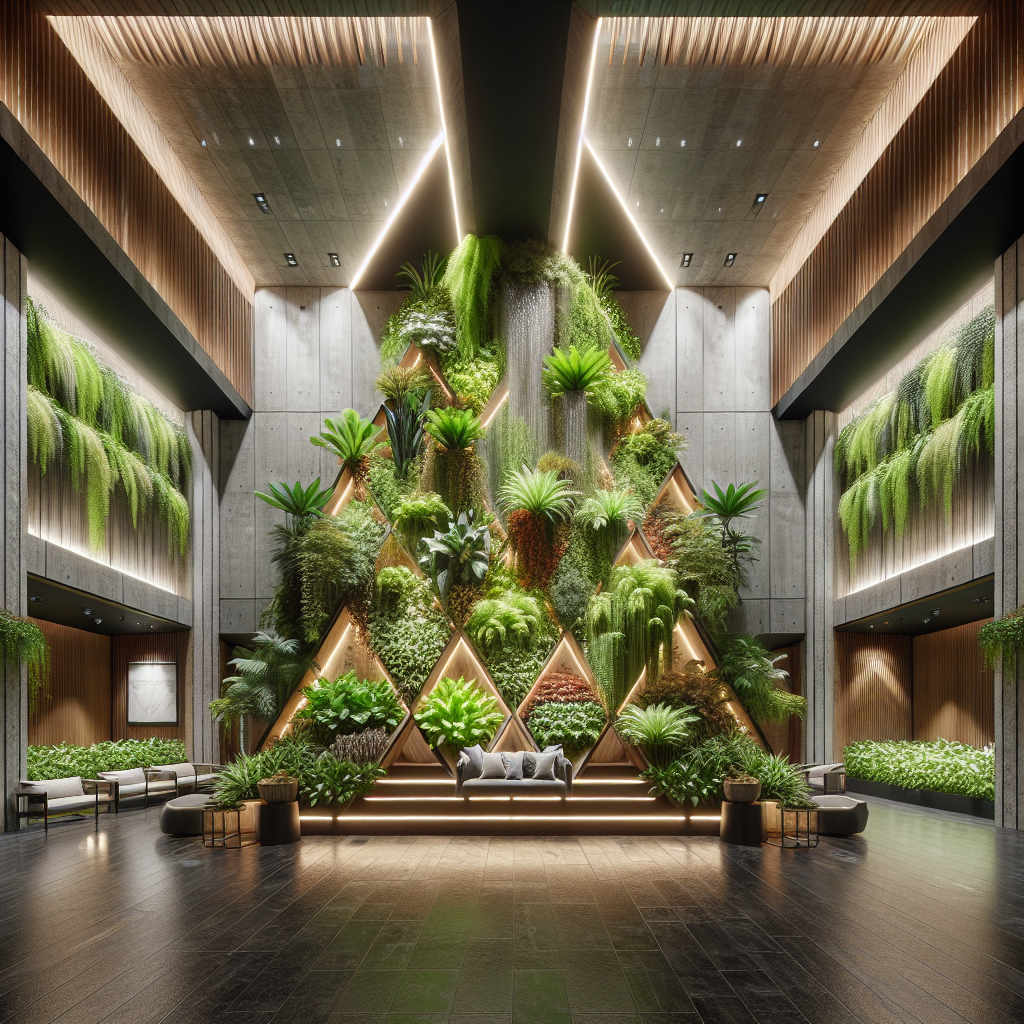
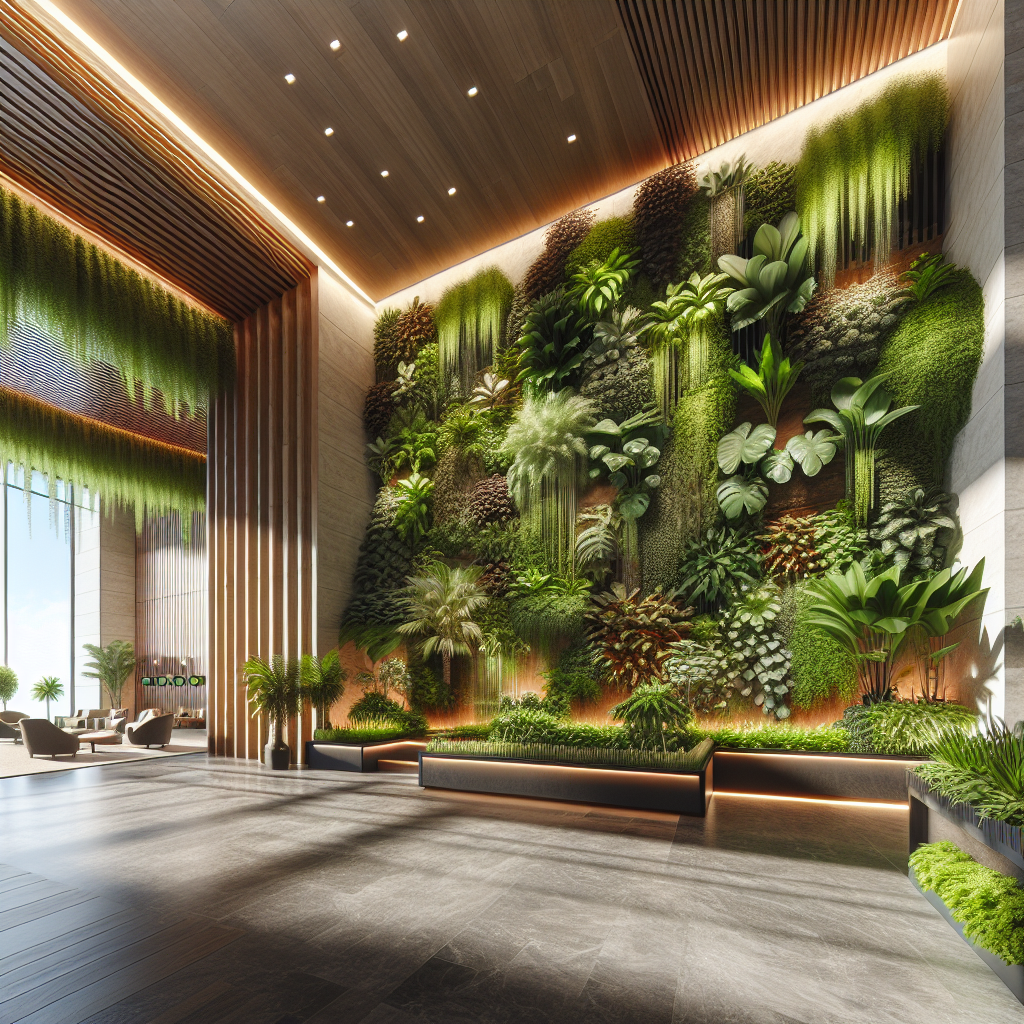
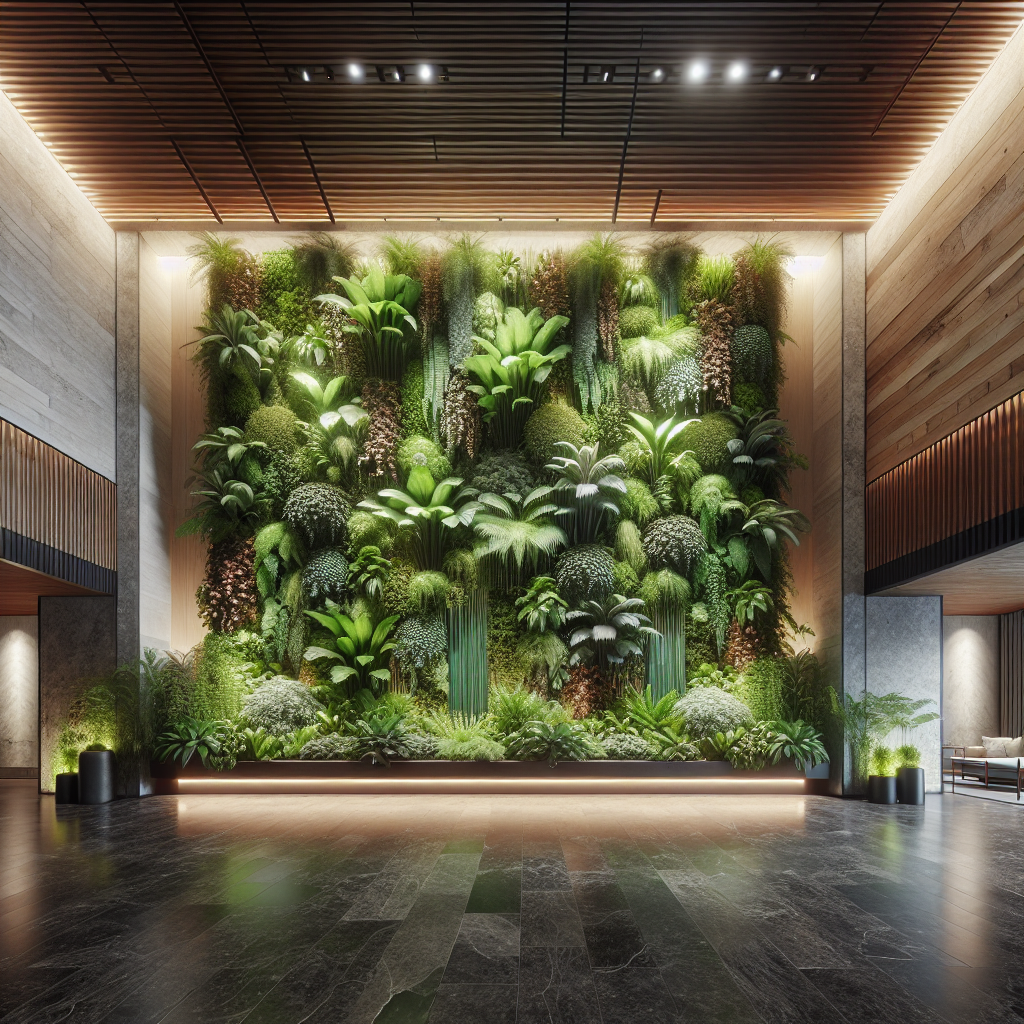
Designers are increasingly treating plant walls as three-dimensional sculptures. Instead of uniform green panels, we now see installations that play with depth, layering, and geometry. For instance, a hospitality project in Milan features a cascading wall of ferns and philodendrons that mimic the fluidity of a waterfall, blurring the line between architecture and landscape art.
2. Integrated Lighting
Lighting design is being seamlessly integrated into plant walls, enhancing both plant health and visual drama. Warm LED strips highlight textures of moss and trailing vines, while adjustable grow lights ensure photosynthetic efficiency. This trend echoes the broader exploration of light as a design medium, where illumination is not merely functional but atmospheric.
3. Edible Walls
With the rise of vertical farming and urban agriculture, edible plant walls are making their way into residential kitchens and boutique restaurants. Imagine a chef harvesting basil, mint, or microgreens directly from a living wall—a fusion of gastronomy and design that redefines the farm-to-table concept.
4. Hybrid Materiality
Contemporary plant walls often incorporate mixed materials such as reclaimed wood, stone, or metal frameworks. These hybrid compositions create a dialogue between organic and industrial aesthetics, resonating with the ongoing fascination for reclaimed materials in design. The result is a layered, tactile experience that elevates the wall beyond greenery into a holistic architectural statement.
Case Studies: Plant Walls in Iconic Projects
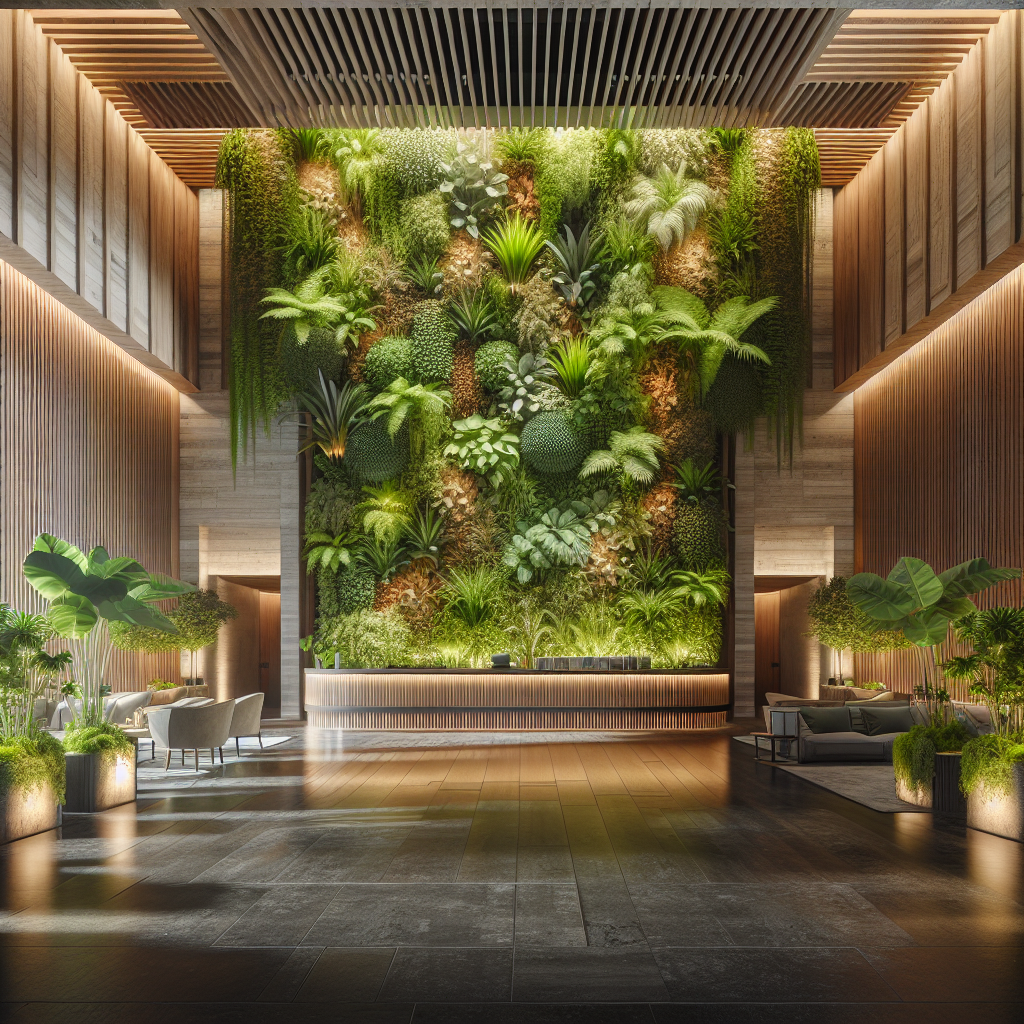
One of the most celebrated examples of indoor plant walls is Patrick Blanc’s installation at the Musée du Quai Branly in Paris. Though primarily an exterior project, its influence has permeated interior design globally, inspiring architects to embrace vertical greenery as a defining feature. In New York, boutique hotels are incorporating plant walls in lobbies as immersive backdrops, creating an immediate sense of serenity amidst the city’s density.
In corporate environments, companies like Amazon and Google have integrated large-scale living walls into their headquarters. These installations serve not only as biophilic design statements but also as branding tools, signaling a commitment to sustainability and employee well-being.
Technological Innovations Driving the Trend
The success of indoor plant walls hinges on technological innovation. Automated irrigation systems, hydroponic substrates, and IoT-enabled sensors now monitor moisture, light, and nutrient levels in real time. This ensures plant vitality while reducing maintenance costs. The integration of smart technology aligns with the broader movement toward smart home and building systems, where automation enhances both efficiency and user experience.
Moreover, advances in hydroponics and aeroponics are expanding the palette of plants that can thrive indoors, from tropical species to edible herbs. These systems reduce water consumption by up to 90% compared to traditional soil-based cultivation, making them an environmentally responsible choice for large-scale installations.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their appeal, plant walls are not without challenges. Designers must carefully consider plant selection, microclimate conditions, and maintenance logistics. Not all species thrive indoors, and improper irrigation can lead to mold or pest issues. Furthermore, installation costs can be significant, particularly for large-scale or custom-designed walls. Yet, as demand grows and technologies advance, costs are gradually becoming more accessible, opening opportunities for broader adoption.
The Future of Indoor Plant Walls
Looking ahead, indoor plant walls are poised to become standard features in sustainable architecture. As cities grapple with pollution, density, and climate change, these living systems offer a tangible way to reconnect urban dwellers with nature. They are not merely decorative flourishes but vital contributors to healthier, more resilient built environments.
In luxury interiors, plant walls are evolving into status symbols of eco-conscious sophistication. In workplaces, they are tools for wellness and productivity. In hospitality, they are immersive experiences that define brand identity. Their versatility ensures they will remain at the forefront of design innovation well into the next decade.
Final Thoughts
Indoor plant walls embody the convergence of aesthetics, sustainability, and human well-being. They are not just walls adorned with greenery but architectural interventions that redefine how we inhabit space. For architects and designers seeking to craft environments that are both visually striking and environmentally responsible, plant walls represent one of the most compelling tools of our time.
As we continue to reimagine the relationship between nature and the built environment, these vertical gardens remind us that beauty and utility can coexist—rooted in soil, yet reaching toward the future.