Augmented glass illusions: interactive surfaces overlaying historical references
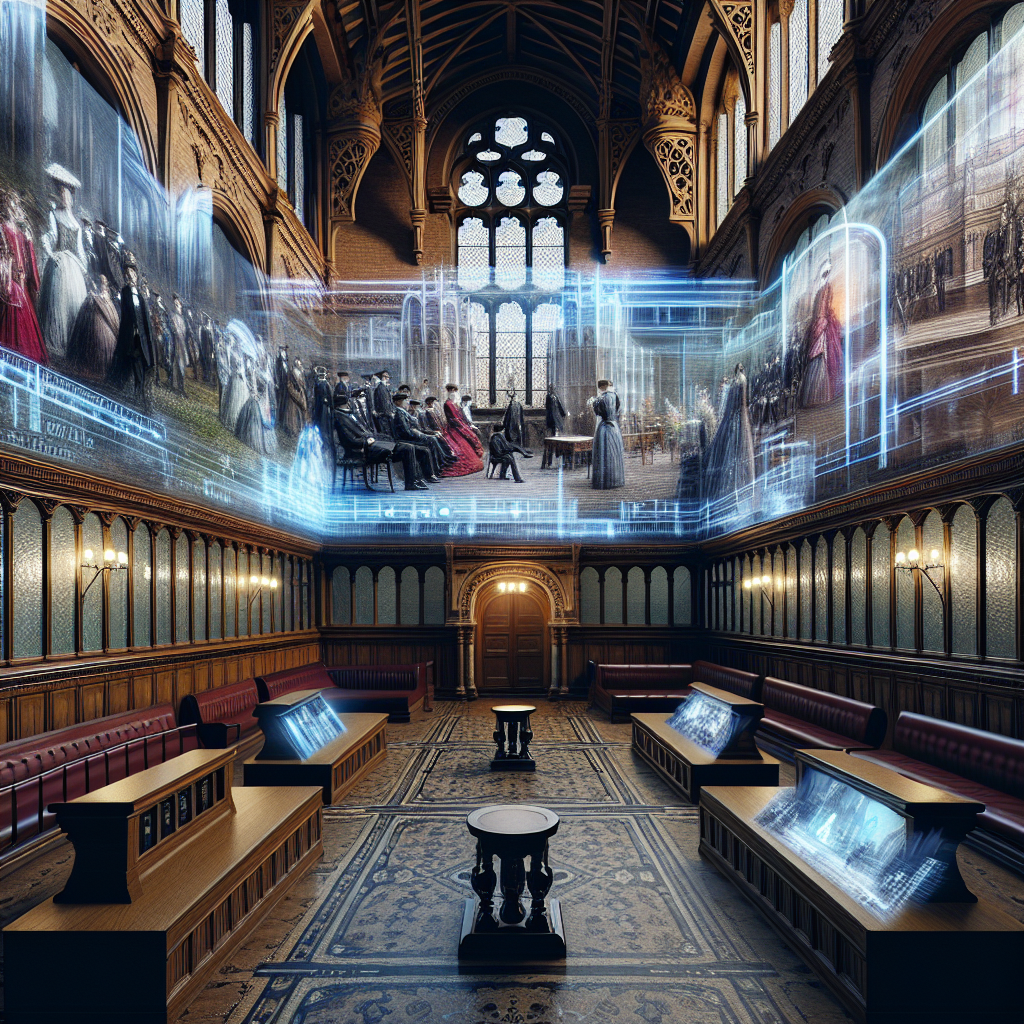

Augmented Glass Illusions: Interactive Surfaces Overlaying Historical References
In an era where digital innovation continually reshapes our built environment, augmented reality (AR) emerges as a powerful tool for architects and designers, breathing new life into historical spaces. Among the most compelling applications is the use of augmented glass illusions, interactive surfaces that seamlessly overlay digital imagery onto physical glass, transforming architectural heritage into dynamic, immersive experiences. As we explore this fascinating intersection of technology and tradition, we delve into how AR-enhanced glass is revolutionizing the preservation and reinterpretation of historical references in contemporary design.
Glass as a Canvas: The Evolution of Augmented Reality in Architecture
Historically, glass has been revered for its transparency, elegance, and ability to connect interior spaces with the external environment. From the stained glass windows of medieval cathedrals to the sleek curtain walls of modernist skyscrapers, glass has always played a pivotal role in architectural expression. Today, however, architects and designers are exploring glass not merely as a passive medium but as an active participant in storytelling, thanks to advancements in augmented reality technology.
Augmented reality, a technology that superimposes digital content onto the physical world, has significantly impacted various design disciplines, from interior design to urban planning. Its application to glass surfaces, however, is particularly transformative. By embedding interactive AR displays within glass panels, designers can now offer viewers an enriched experience, merging historical imagery, narratives, and contemporary digital artistry in real-time.
Historical Narratives Revitalized: Case Studies in Augmented Glass
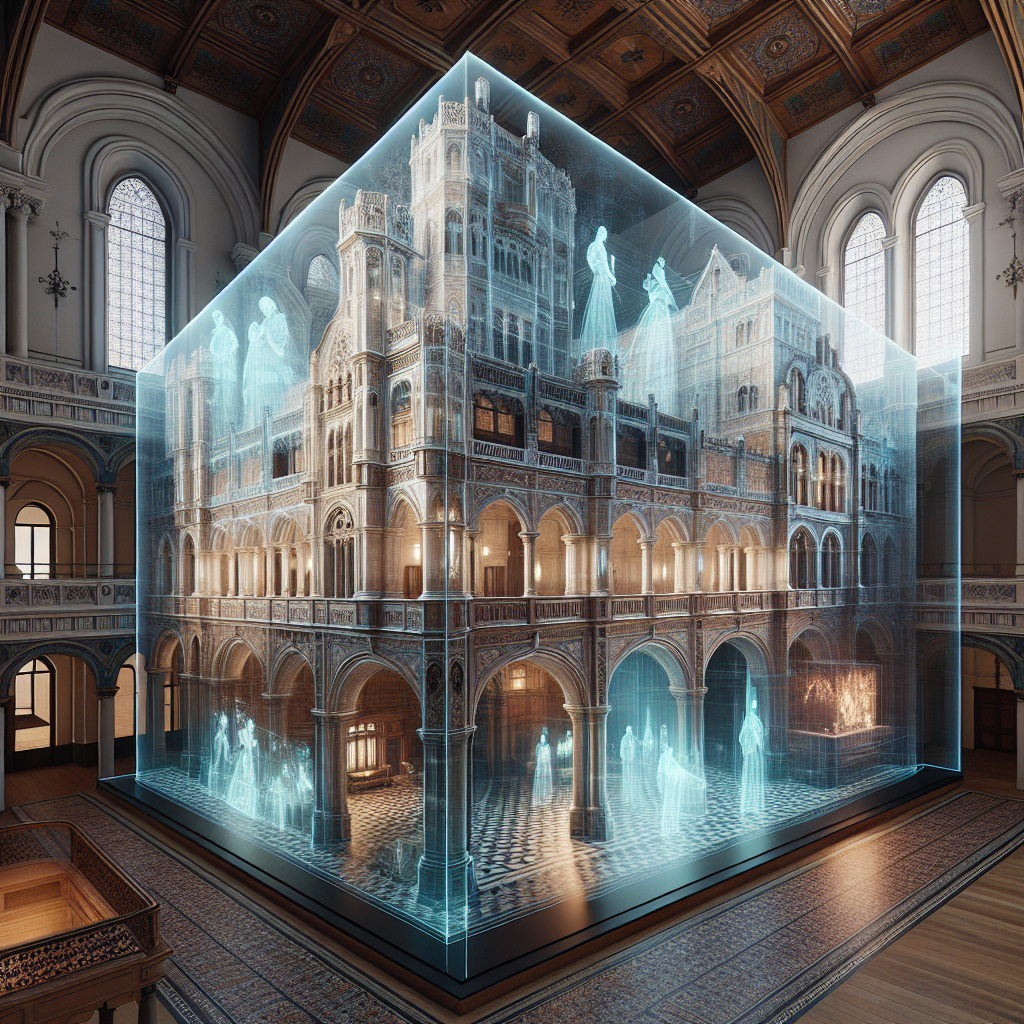
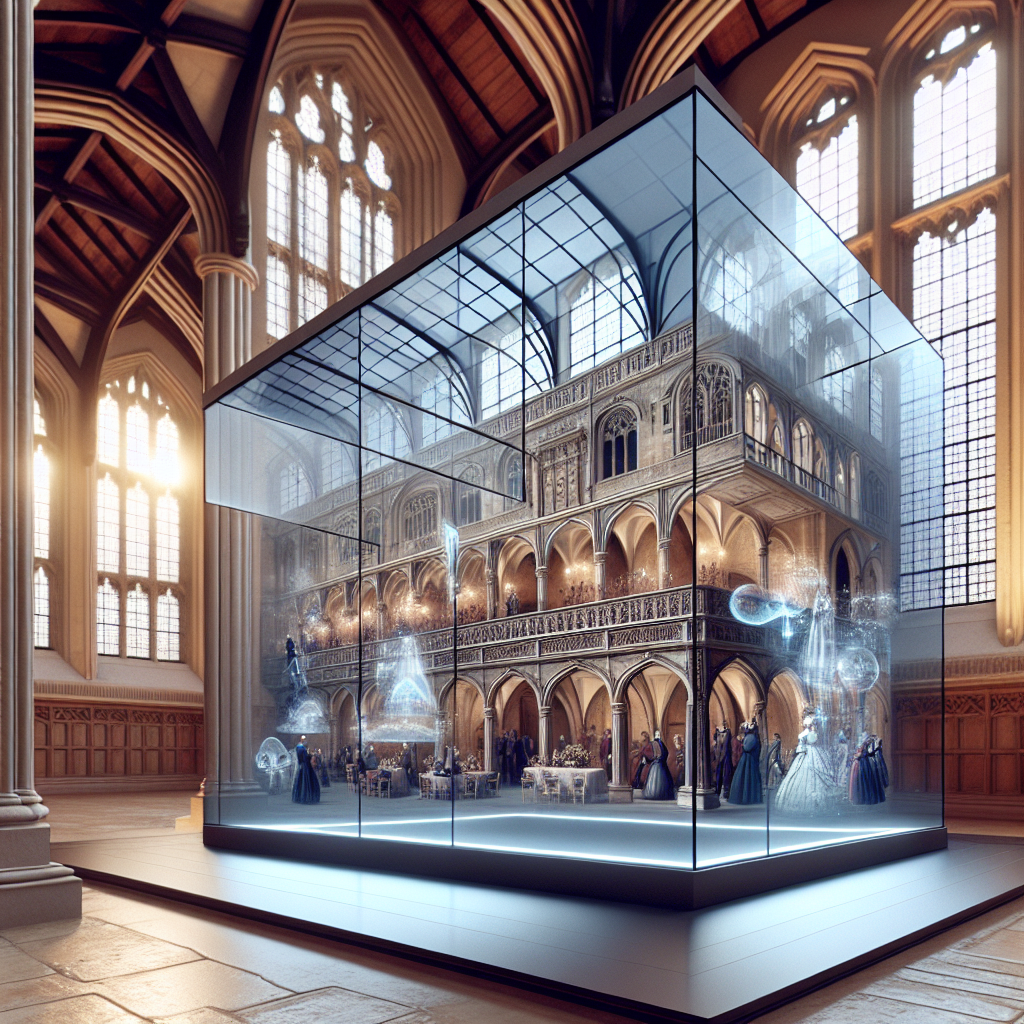
One of the most compelling examples of augmented glass illusions is the recent renovation of the iconic Gare d’Orsay in Paris. Originally constructed as a railway station in 1900 and later transformed into the Musée d’Orsay, the building has long stood as a testament to Beaux-Arts architecture. In 2024, as part of the city’s preparations for the Summer Olympic Games, architects integrated augmented glass panels into the museum’s grand clock façade. Visitors now witness an enchanting digital overlay that animates historical scenes of Parisian life, seamlessly blending past and present through sophisticated AR technology.
Similarly, the Tower of London recently unveiled an innovative augmented glass installation within its medieval White Tower. By gazing through specially designed glass panels, visitors can observe digitally recreated historical events, from royal coronations to infamous imprisonments, projected directly onto the ancient stone walls. This immersive experience enhances visitor engagement, providing an interactive and educational encounter with the site’s storied past.
Technological Innovation Meets Architectural Heritage
The integration of augmented glass illusions requires a harmonious balance between technological sophistication and architectural sensitivity. Designers must carefully consider the preservation of historical integrity while embracing digital innovation. Recent advancements in transparent OLED displays and holographic projection technologies have significantly facilitated this integration, enabling high-resolution, interactive content without compromising the visual purity of glass surfaces.
Moreover, the development of responsive glass systems, capable of adapting to environmental conditions and user interactions, has opened new possibilities for dynamic architectural experiences. These systems not only enrich historical narratives but also contribute to sustainability efforts by optimizing natural lighting and energy efficiency within heritage buildings.
Augmented Glass in Contemporary Interior Design
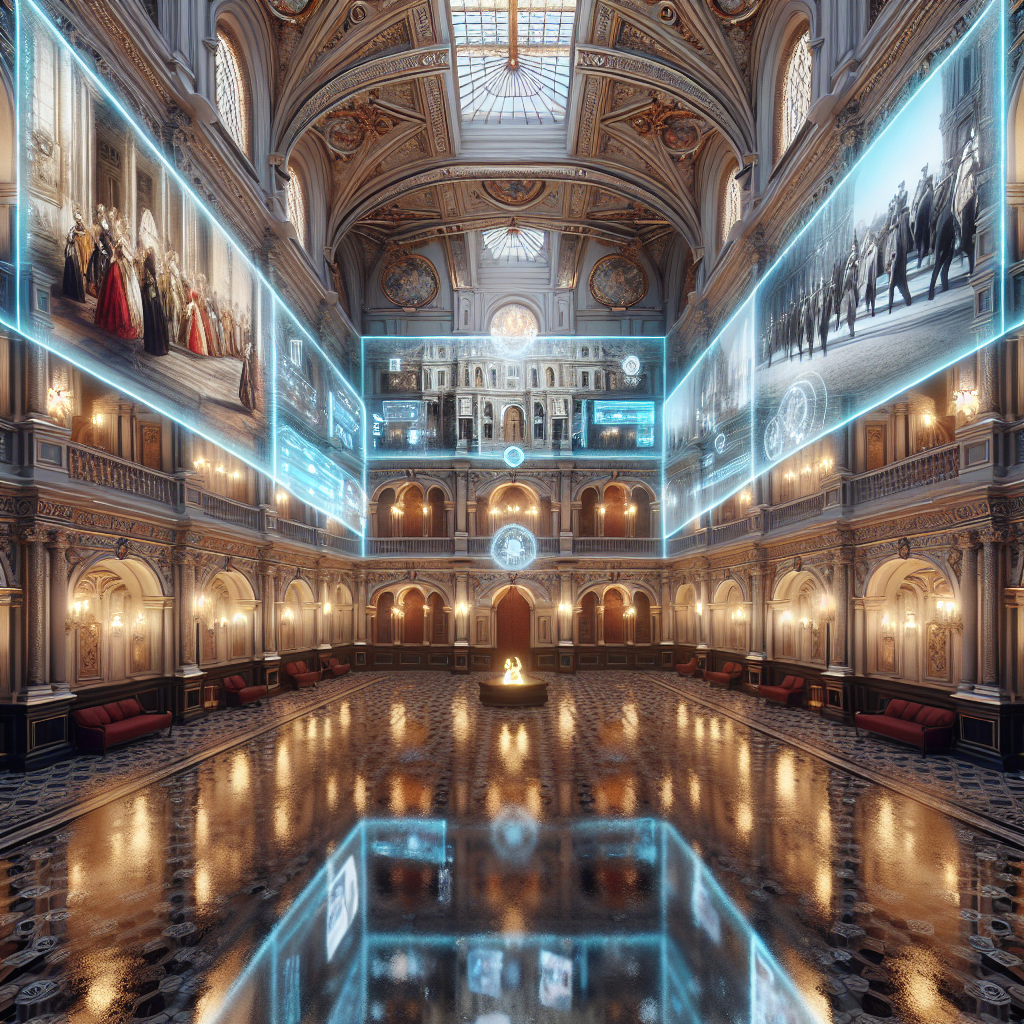
Beyond monumental architecture, augmented glass illusions are increasingly finding their way into sophisticated interior design projects. High-end hospitality spaces, luxury retail environments, and residential interiors are embracing this technology to create bespoke, interactive experiences that reference historical aesthetics and narratives.
For instance, luxury hotels in Milan’s Brera Design District have adopted augmented glass panels in their lobbies and suites, offering guests immersive glimpses into the city’s rich design heritage. Guests can interact with digital overlays that depict iconic Milanese furniture designs, from mid-century classics to contemporary masterpieces, effectively transforming glass partitions into interactive museums of design history.
In residential settings, augmented glass is employed to create personalized experiences that reflect homeowners’ cultural interests and historical passions. Imagine a glass partition in a modern apartment that, upon activation, reveals intricate patterns inspired by 18th-century French furniture, seamlessly blending contemporary minimalism with historical opulence. Such integrations not only enhance aesthetic appeal but also deepen the emotional connection between inhabitants and their living spaces.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing Augmented Glass
Despite its compelling potential, the adoption of augmented glass illusions in architectural and interior design projects presents several challenges. Chief among these is the need for meticulous calibration between digital content and physical environments. Ensuring accurate alignment, realistic visual effects, and seamless user interactions demands precise technological expertise and rigorous testing.
Additionally, designers must navigate considerations related to privacy, accessibility, and user experience. Transparent displays, while visually captivating, may raise concerns about data security and personal privacy, particularly in residential or hospitality contexts. Addressing these concerns through thoughtful design strategies and transparent communication is essential for the successful integration of augmented glass technologies.
The Future of Augmented Glass: Bridging Past and Future
Looking ahead, augmented glass illusions promise to redefine our relationship with architectural heritage, transforming static historical references into dynamic, interactive experiences. As technology continues to evolve, we can anticipate increasingly sophisticated integrations that not only enhance visual storytelling but also foster deeper emotional connections with our built environment.
Moreover, the convergence of augmented reality with other emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and digital fabrication, will further expand the creative possibilities for designers and architects. Imagine adaptive glass facades that respond intelligently to user preferences, environmental conditions, and historical contexts, creating truly personalized architectural experiences.
In this context, augmented glass illusions represent more than mere technological innovation; they embody a profound shift in how we perceive, engage with, and preserve our architectural heritage. By overlaying historical references with interactive digital content, designers are crafting immersive narratives that bridge past and future, tradition and innovation, ultimately enriching our collective experience of space and time.
As we continue to explore the potential of augmented glass, it becomes clear that this technology is not merely an aesthetic enhancement but a transformative force in contemporary architecture and design. It invites us to reconsider the boundaries between physical and digital realms, heritage and modernity, and to envision a future where architectural storytelling is as dynamic and interactive as the spaces we inhabit.
From the medieval cathedrals of Europe to the modernist masterpieces of the 20th century, glass has always been a medium of architectural expression. Today, augmented glass illusions propel this tradition into the digital age, offering architects and designers unprecedented opportunities to reimagine historical narratives, engage audiences, and shape the future of our built environment.
In embracing this innovative approach, we not only preserve the past but also illuminate the path forward, creating spaces that resonate deeply with history, culture, and human experience.
Explore further insights into how technology shapes our built environment in our analysis of Blade Runner 2049’s futuristic city design, or discover sustainable architectural innovations in our feature on wooden skyscrapers.
For additional historical context, consider exploring the Beaux-Arts architectural style, the Tower of London’s rich history, or the Brera Design District.