Generative Art: Unveiling Creativity Powered by Algorithms

Generative Art: Unveiling Creativity Powered by Algorithms
In an era where technology continually reshapes the boundaries of creativity, generative art emerges as a revolutionary force, blending human imagination with algorithmic precision. This intriguing synthesis of art and technology not only redefines aesthetic expression but also profoundly influences contemporary architecture and interior design. From parametric façades that dance with sunlight to algorithmically crafted interiors that resonate with human emotion, generative art has become an indispensable tool for today’s visionary designers and architects.
The Algorithmic Renaissance: Understanding Generative Art
Generative art refers to artwork produced through autonomous systems, often employing algorithms and computational processes. Rather than traditional methods where the artist meticulously controls every detail, generative art thrives on unpredictability, allowing the algorithm to introduce elements of randomness and complexity. This method creates intricate patterns, organic forms, and visually captivating designs that would be nearly impossible to achieve manually.
At its core, generative art harnesses the power of mathematics, particularly fractals, chaos theory, and cellular automata, to generate mesmerizing visuals. These mathematical foundations ensure that each creation is unique, dynamic, and endlessly fascinating. As a result, generative art has become a pivotal component in contemporary architecture and interior design, enabling professionals to explore previously unattainable aesthetic dimensions.
Architectural Innovations: Algorithmic Expressions in Built Environments
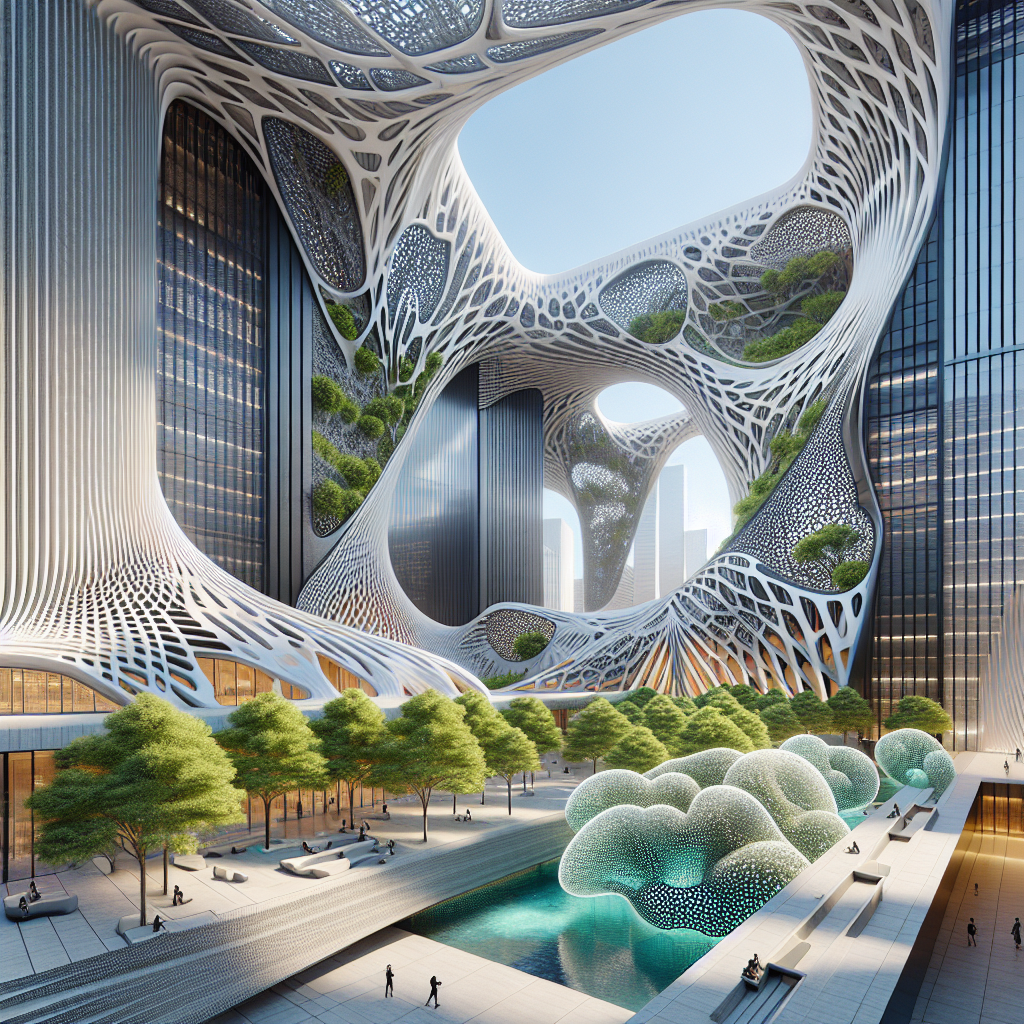
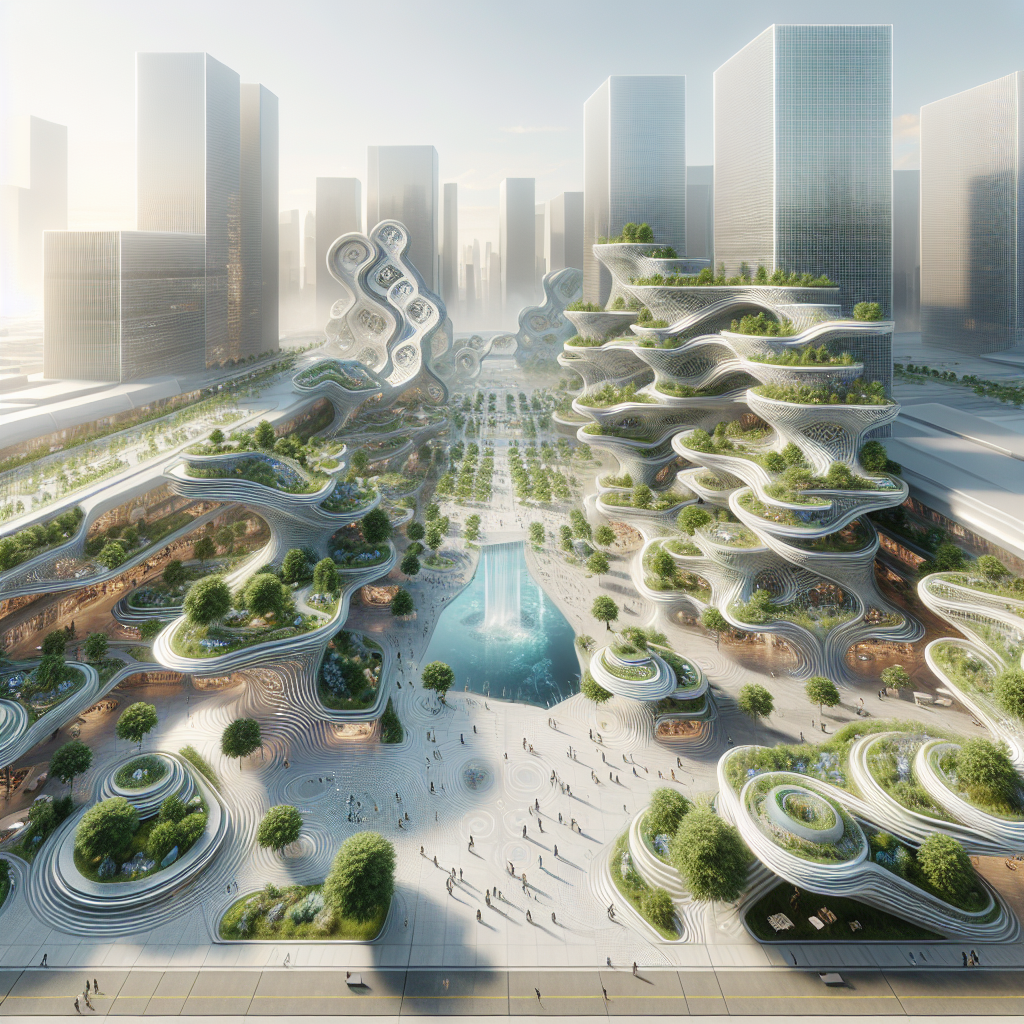
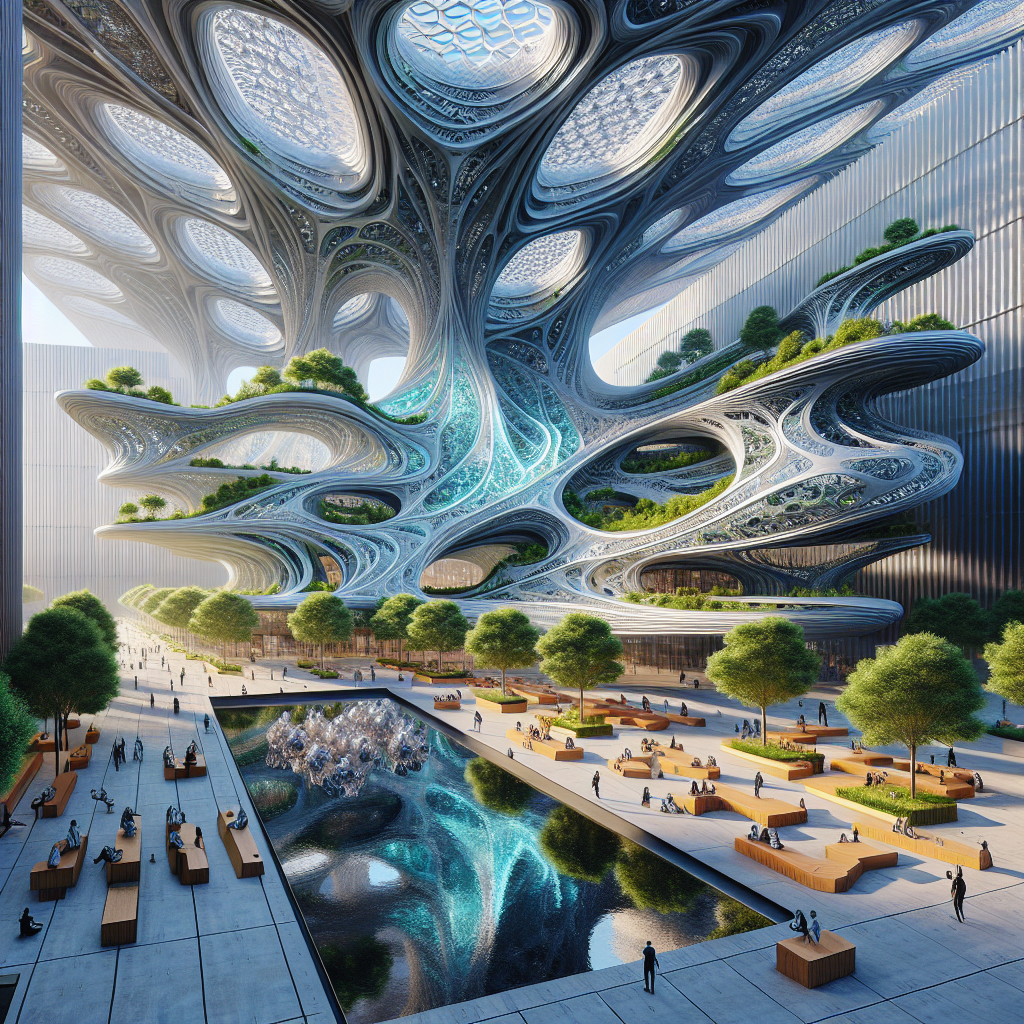
In recent years, generative art has profoundly impacted architectural design, enabling architects to push the boundaries of form and function. A prime example is the rise of parametric design, a methodology that employs algorithms to create complex, adaptive structures. Parametric architecture leverages generative algorithms to optimize building performance, aesthetics, and sustainability, resulting in groundbreaking structures that harmonize with their surroundings.
Consider the breathtaking façade of the Al Bahar Towers in Abu Dhabi, designed by Aedas Architects. Inspired by traditional Islamic geometric patterns, the façade features a dynamic shading system generated algorithmically. These kinetic panels open and close in response to sunlight, significantly reducing energy consumption while creating a mesmerizing visual display reminiscent of blooming flowers. Such innovative applications of generative art underscore its transformative potential in modern architecture.
Similarly, generative algorithms have facilitated the development of wooden skyscrapers, where structural optimization and material efficiency are paramount. Algorithms analyze structural loads, material properties, and environmental factors to produce timber structures that are both aesthetically pleasing and environmentally sustainable. This approach exemplifies how generative art aligns with contemporary sustainability goals, promoting eco-friendly and efficient design solutions.
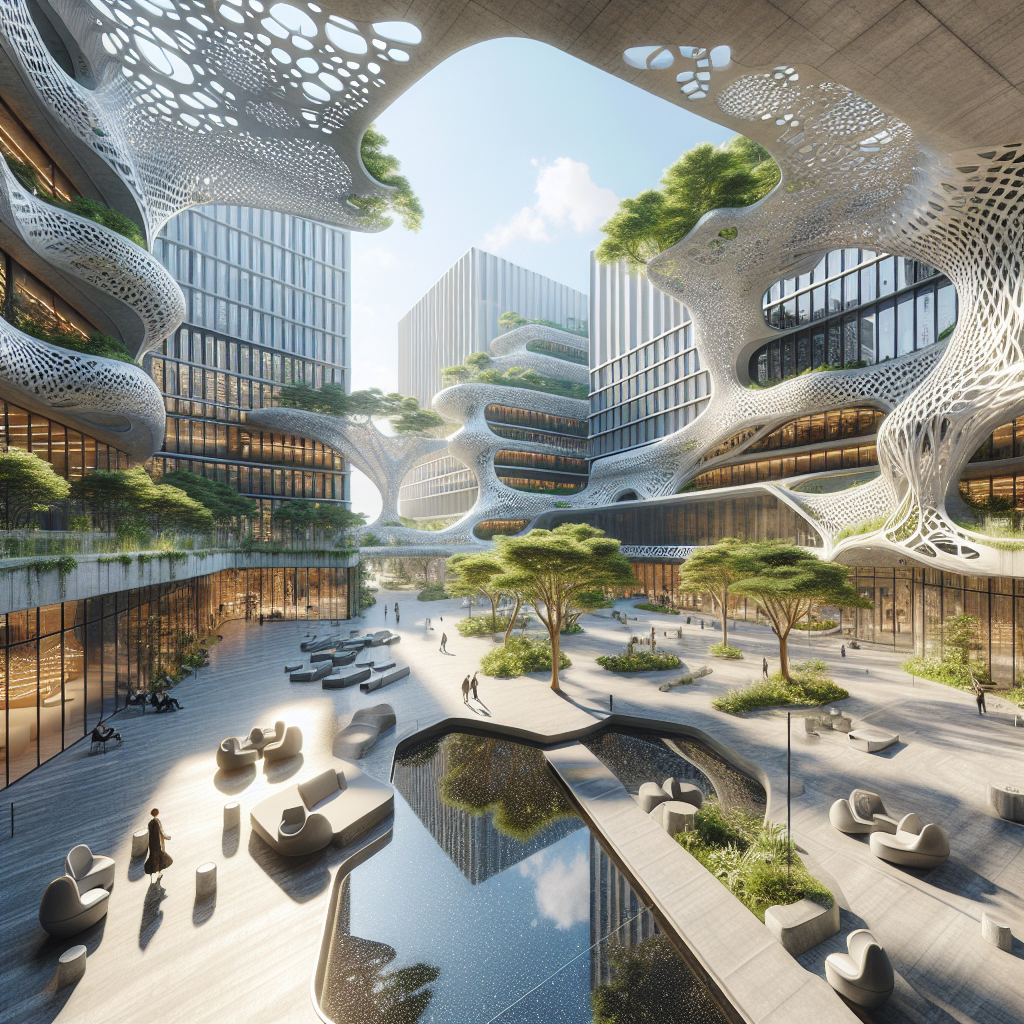
Interior Spaces Reimagined: Algorithmic Aesthetics in Interior Design
Generative art also profoundly influences interior design, introducing innovative aesthetics and enhancing user experiences. Designers now utilize algorithmic processes to create interiors that respond dynamically to human interaction, emotional states, and environmental conditions. For instance, interactive installations employing generative algorithms can adjust lighting, textures, and spatial configurations in real-time, creating personalized and immersive environments.
One compelling example is the biophilic design movement, which integrates natural elements into interior spaces to enhance human well-being. Generative algorithms facilitate the creation of organic patterns, textures, and forms inspired by nature, resulting in interiors that evoke tranquility and connection. Imagine a lobby adorned with algorithmically generated patterns reminiscent of flowing water or forest canopies, subtly shifting in response to occupants’ movements, fostering a harmonious and restorative atmosphere.
Moreover, generative art enables designers to explore novel material applications and fabrication techniques. Digital fabrication technologies, such as 3D printing and CNC milling, combined with generative algorithms, allow for the creation of intricate furniture pieces and decorative elements previously unattainable through traditional methods. These bespoke creations not only elevate aesthetic appeal but also promote sustainability by optimizing material usage and reducing waste.
Generative Art in Popular Culture and Media
The influence of generative art extends beyond architecture and interior design, permeating popular culture and media. Films like “Blade Runner 2049” showcase futuristic cityscapes that integrate generative design principles, illustrating how technology shapes urban environments. For a deeper exploration of technology’s impact on futuristic city design, see our analysis of Blade Runner 2049’s architectural vision.
Additionally, generative art has found its way into digital art marketplaces, notably through NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens). Artists utilize algorithms to produce unique digital artworks, attracting collectors and enthusiasts worldwide. This phenomenon underscores generative art’s versatility and growing significance in contemporary creative industries.
The Future of Generative Art: Challenges and Opportunities
As generative art continues to evolve, it presents both exciting opportunities and notable challenges. On one hand, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning promises unprecedented creative possibilities, enabling algorithms to learn from human preferences and generate increasingly sophisticated designs. On the other hand, ethical considerations regarding authorship, originality, and intellectual property rights emerge, prompting critical discussions within the creative community.
Moreover, as sustainability becomes an urgent global priority, generative art’s potential to optimize resource usage and promote eco-friendly practices gains prominence. Designers and architects increasingly adopt generative algorithms to achieve net-zero energy buildings and sustainable interiors, aligning creativity with environmental responsibility.
However, the widespread adoption of generative art necessitates a balance between technological innovation and human intuition. While algorithms offer remarkable precision and efficiency, the human touch remains essential in guiding creative direction, ensuring emotional resonance, and addressing cultural contexts. Thus, the future of generative art lies in a harmonious collaboration between human creativity and algorithmic ingenuity.
Conclusion: Embracing Algorithmic Creativity
Generative art represents a profound shift in the creative landscape, redefining the possibilities of architectural and interior design. By harnessing algorithmic processes, designers and architects unlock new realms of aesthetic expression, sustainability, and innovation. As we navigate an increasingly technology-driven world, embracing generative art becomes imperative, offering pathways to design environments that are not only visually captivating but also deeply responsive to human needs and aspirations.
Ultimately, generative art invites us to reconsider the boundaries of creativity, urging a dynamic dialogue between human imagination and technological advancement. In this exciting interplay, we discover endless possibilities for shaping the built environment, enriching our lives, and inspiring future generations.