Adaptive Reuse Projects: Giving Historic Buildings New Life

Adaptive Reuse Projects: Giving Historic Buildings New Life
In an era where sustainability and cultural preservation converge, adaptive reuse projects are emerging as transformative forces in contemporary architecture. These innovative endeavors not only breathe new life into historic structures but also offer a sustainable solution to urban development challenges. By repurposing existing buildings, architects and designers are creatively merging the past with the present, crafting spaces that honor heritage while meeting modern needs.
The Renaissance of Adaptive Reuse
Adaptive reuse, the practice of repurposing old buildings for new functions, has become increasingly popular among architects, designers, and urban planners. Driven by a desire to preserve architectural heritage, reduce environmental impact, and revitalize urban areas, adaptive reuse projects are reshaping cities worldwide. According to a recent report by the American Institute of Architects, adaptive reuse projects have increased by 25% over the past five years, highlighting a growing commitment to sustainable urban development.
This approach not only conserves resources but also maintains the cultural fabric of communities, providing continuity and a sense of identity. From abandoned factories transformed into vibrant residential complexes to historic churches reimagined as community centers, adaptive reuse projects are redefining urban landscapes.
Preserving History Through Innovative Design
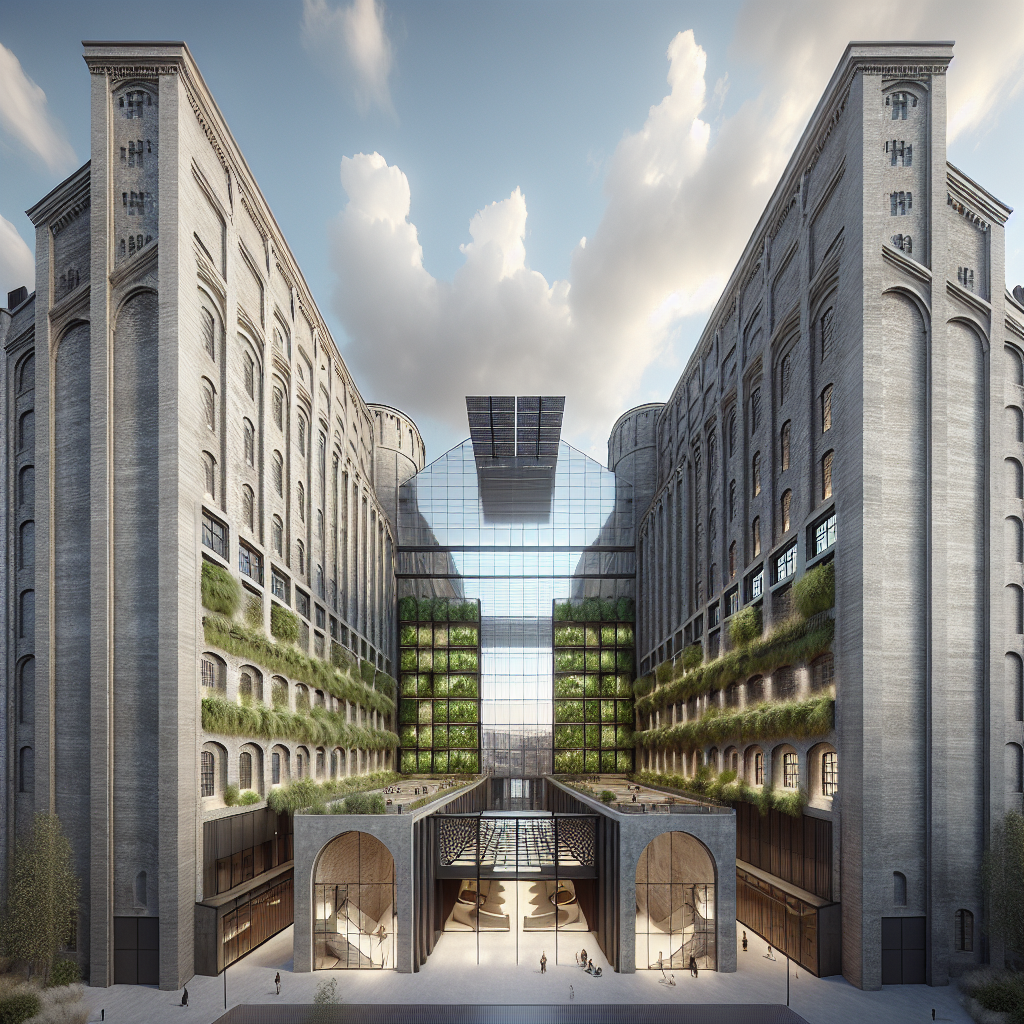
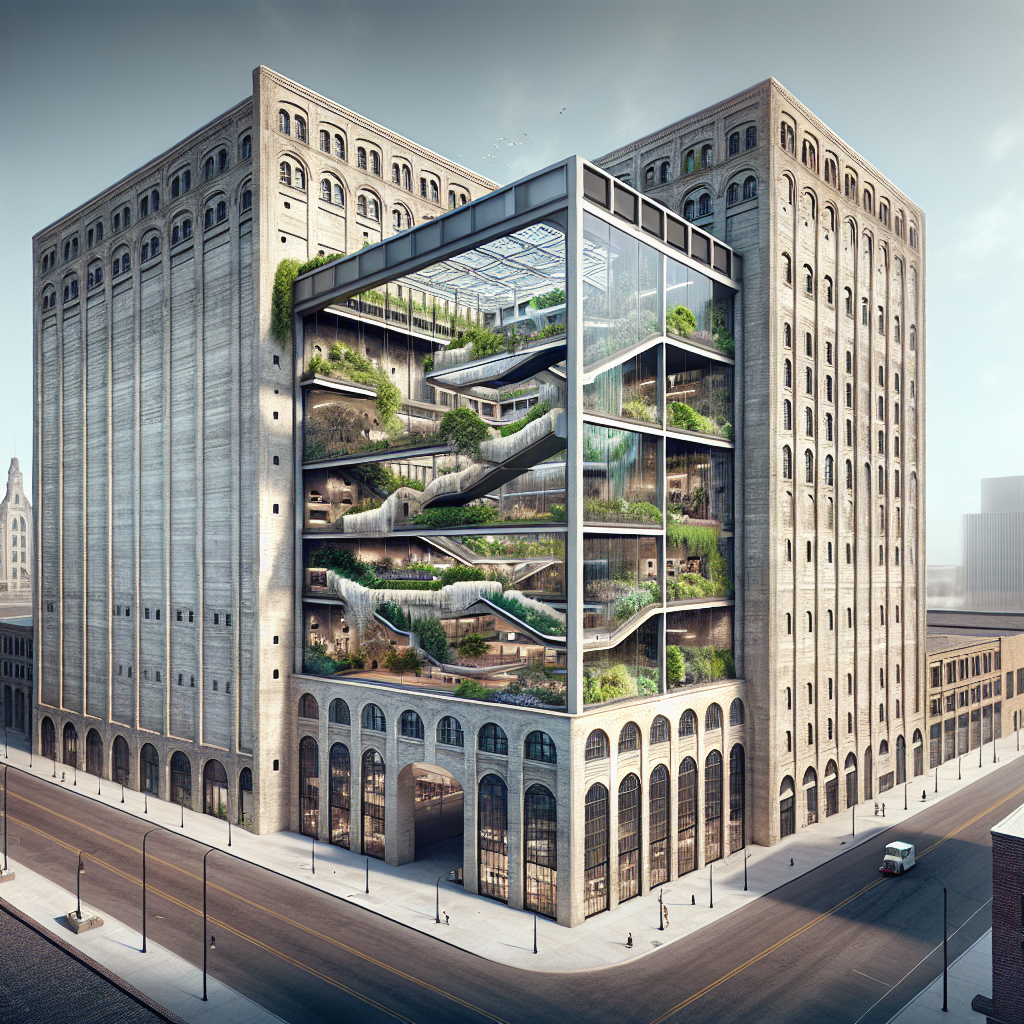
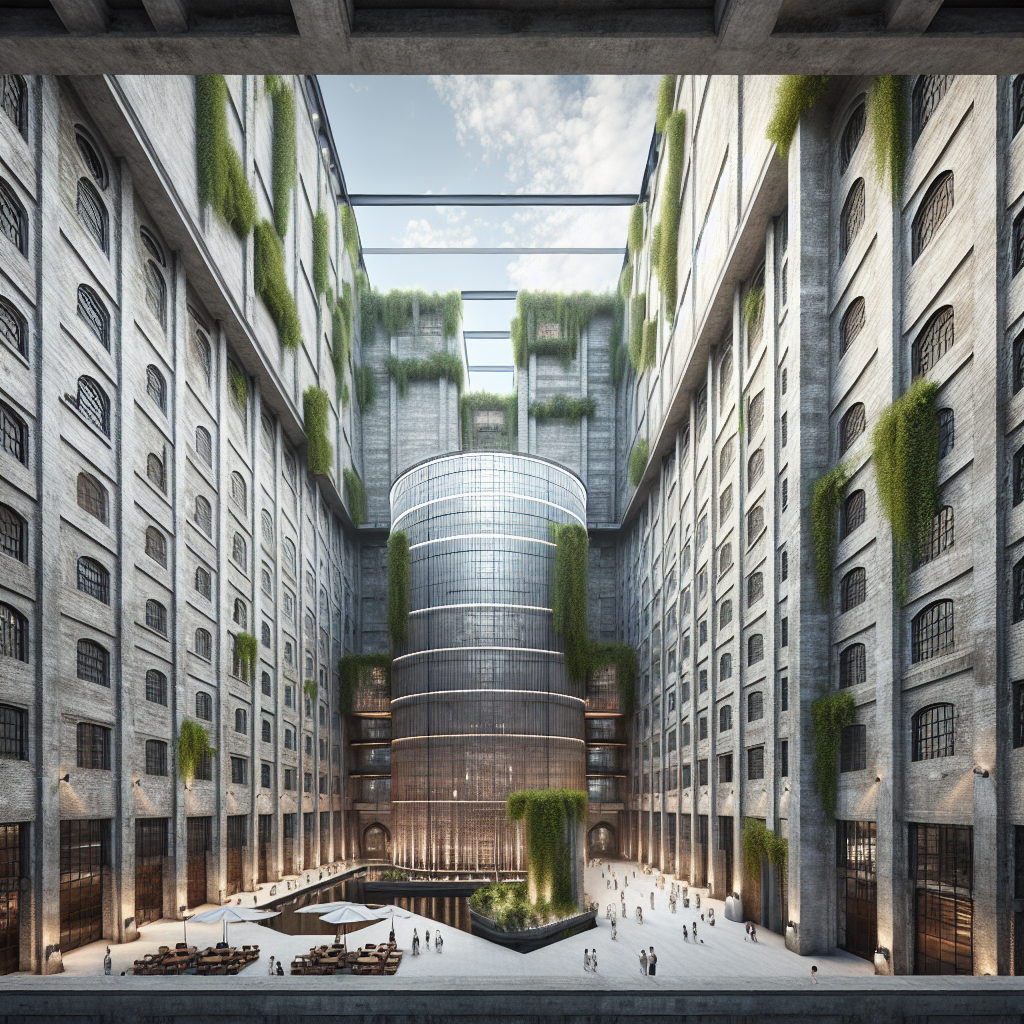
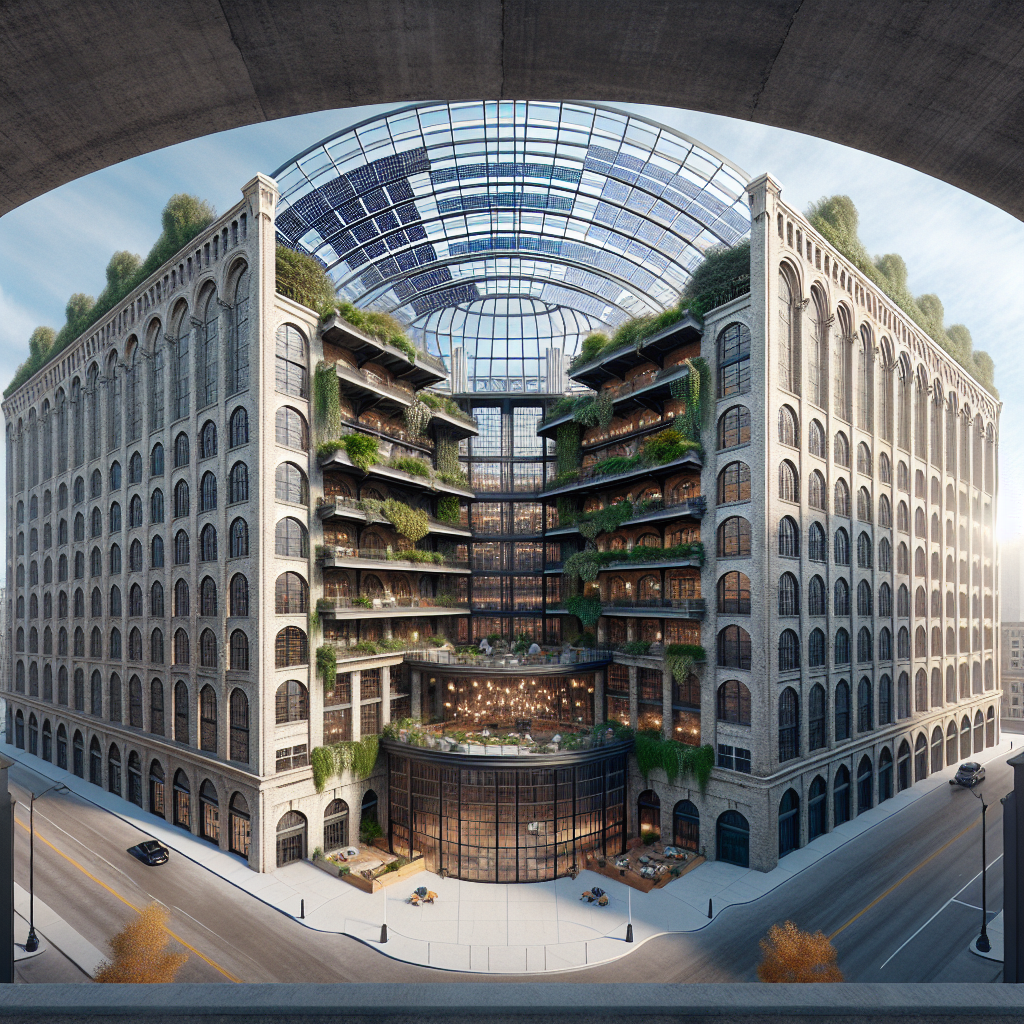
One compelling example of adaptive reuse is the transformation of industrial warehouses into dynamic residential and commercial spaces. The Zeitz Museum of Contemporary Art Africa (MOCAA) in Cape Town, South Africa, stands as a testament to this trend. Originally a grain silo complex built in the 1920s, the structure was meticulously redesigned by Heatherwick Studio, preserving its historic exterior while creating an awe-inspiring interior atrium carved from the original concrete tubes. This project not only revitalized a neglected industrial landmark but also created a cultural beacon that attracts visitors from around the globe.
Similarly, in New York City, the iconic High Line park exemplifies adaptive reuse on an urban scale. Once an abandoned elevated railway, the High Line has been transformed into a lush, linear park that winds through Manhattan’s West Side, offering green space, art installations, and breathtaking city views. This innovative project has sparked urban renewal in surrounding neighborhoods, boosting property values and fostering community engagement.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Adaptive reuse aligns seamlessly with sustainable architecture principles, significantly reducing environmental impact compared to new construction. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, building construction and demolition account for approximately 40% of landfill waste. By repurposing existing structures, adaptive reuse projects minimize waste, conserve resources, and reduce carbon emissions associated with new construction.
Moreover, adaptive reuse often incorporates energy-efficient technologies and sustainable materials, further enhancing environmental benefits. For instance, integrating green roofs and renewable energy systems into historic buildings can dramatically improve energy performance while preserving architectural integrity.
Embracing Biophilic Design in Adaptive Reuse
Recent trends in adaptive reuse projects increasingly embrace biophilic design, integrating natural elements to enhance occupant well-being and environmental harmony. By incorporating greenery, natural light, and organic materials, architects create spaces that foster human connection to nature, improving mental health and productivity.
The adaptive reuse of London’s Battersea Power Station exemplifies this approach. Once a coal-fired power plant, the iconic building has been transformed into a mixed-use development featuring residential units, offices, retail spaces, and extensive green areas. The design thoughtfully integrates biophilic elements, including rooftop gardens, vertical greenery, and expansive windows that flood interiors with natural light, creating a harmonious balance between industrial heritage and contemporary sustainability.
Challenges and Opportunities in Adaptive Reuse
While adaptive reuse offers numerous benefits, it also presents unique challenges. Preserving historic integrity while meeting modern building codes and accessibility standards requires innovative design solutions and meticulous planning. Structural limitations, outdated infrastructure, and environmental hazards such as asbestos can complicate redevelopment efforts.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for creativity and innovation. Architects and designers are increasingly leveraging advanced technologies, such as virtual reality visualization and digital fabrication, to navigate complexities and optimize design outcomes. Additionally, the use of reclaimed materials, as explored in reclaimed materials in design, further enhances sustainability and authenticity in adaptive reuse projects.
Future Trends in Adaptive Reuse
Looking ahead, adaptive reuse is poised to play an even more significant role in urban development, driven by increasing awareness of sustainability and cultural preservation. Emerging trends include the integration of smart technologies, modular design, and innovative materials to enhance functionality and adaptability.
The ongoing development of timber construction, as highlighted in wooden skyscrapers, presents exciting possibilities for adaptive reuse. Combining traditional building methods with contemporary innovations, architects can create flexible, sustainable spaces that honor history while embracing the future.
Moreover, adaptive reuse will increasingly intersect with urban planning initiatives, such as those surrounding major events like the Paris 2024 Olympic Games, where historic venues are being repurposed to serve long-term community needs. This holistic approach ensures that adaptive reuse projects contribute meaningfully to urban vitality and resilience.
Conclusion: Honoring the Past, Shaping the Future
Adaptive reuse projects represent a powerful synthesis of preservation, innovation, and sustainability. By thoughtfully repurposing historic buildings, architects and designers are not only conserving cultural heritage but also creating vibrant, sustainable spaces that enrich communities. As cities continue to evolve, adaptive reuse will undoubtedly remain a cornerstone of responsible, forward-thinking urban development, bridging the gap between history and modernity with elegance and ingenuity.
Ultimately, adaptive reuse embodies a profound respect for the past and a visionary commitment to the future, demonstrating that the most sustainable building is often the one already standing.