Tiny House Design: Innovative Ideas for Compact Living
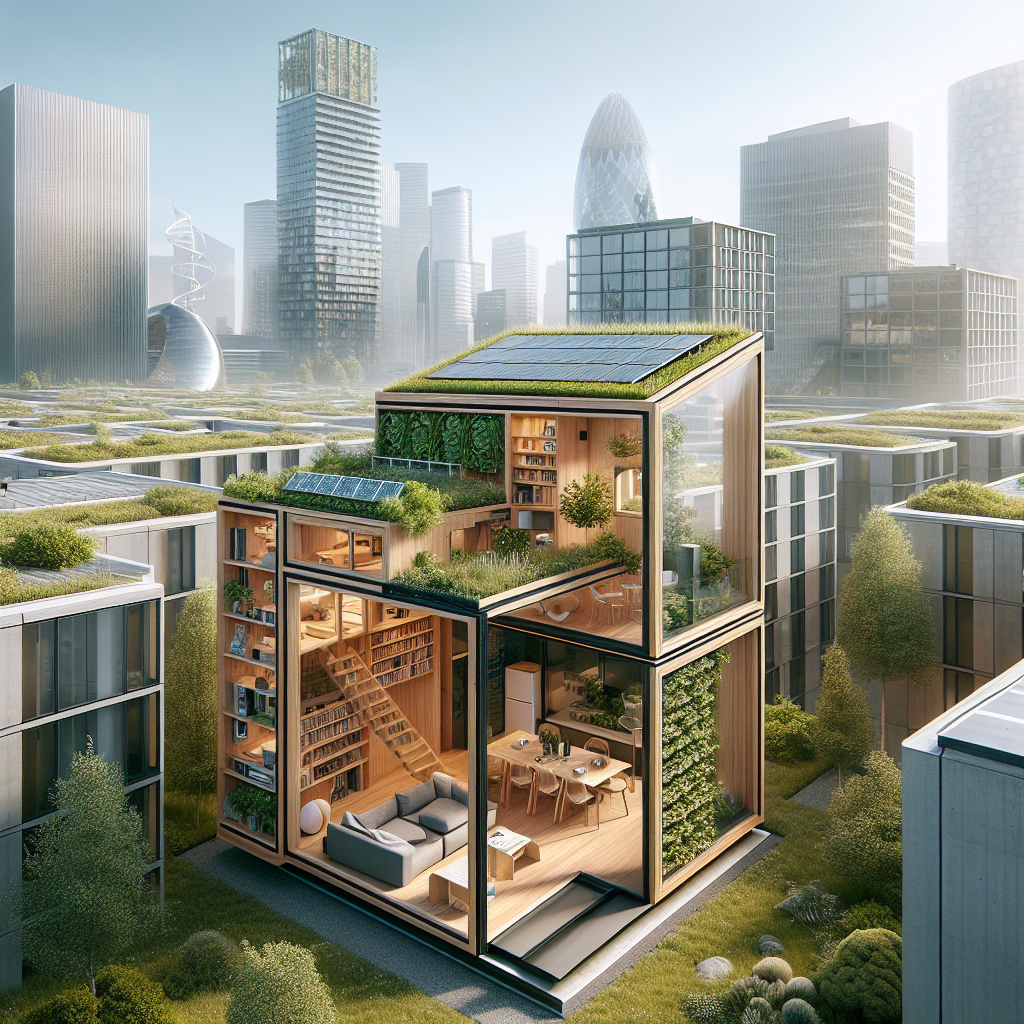

Tiny House Design: Innovative Ideas for Compact Living
In an era defined by rapid urbanization, escalating housing costs, and a collective yearning for sustainability, the tiny house movement has emerged as a compelling architectural response. These compact dwellings, often under 400 square feet, challenge conventional notions of space, luxury, and functionality. For design professionals and sophisticated enthusiasts alike, tiny house design represents a frontier where creativity, sustainability, and innovation converge. From ingenious space-saving solutions to pioneering eco-friendly materials, the tiny house movement is reshaping the way we perceive and inhabit our built environments.
Maximizing Minimalism: The Art of Spatial Efficiency
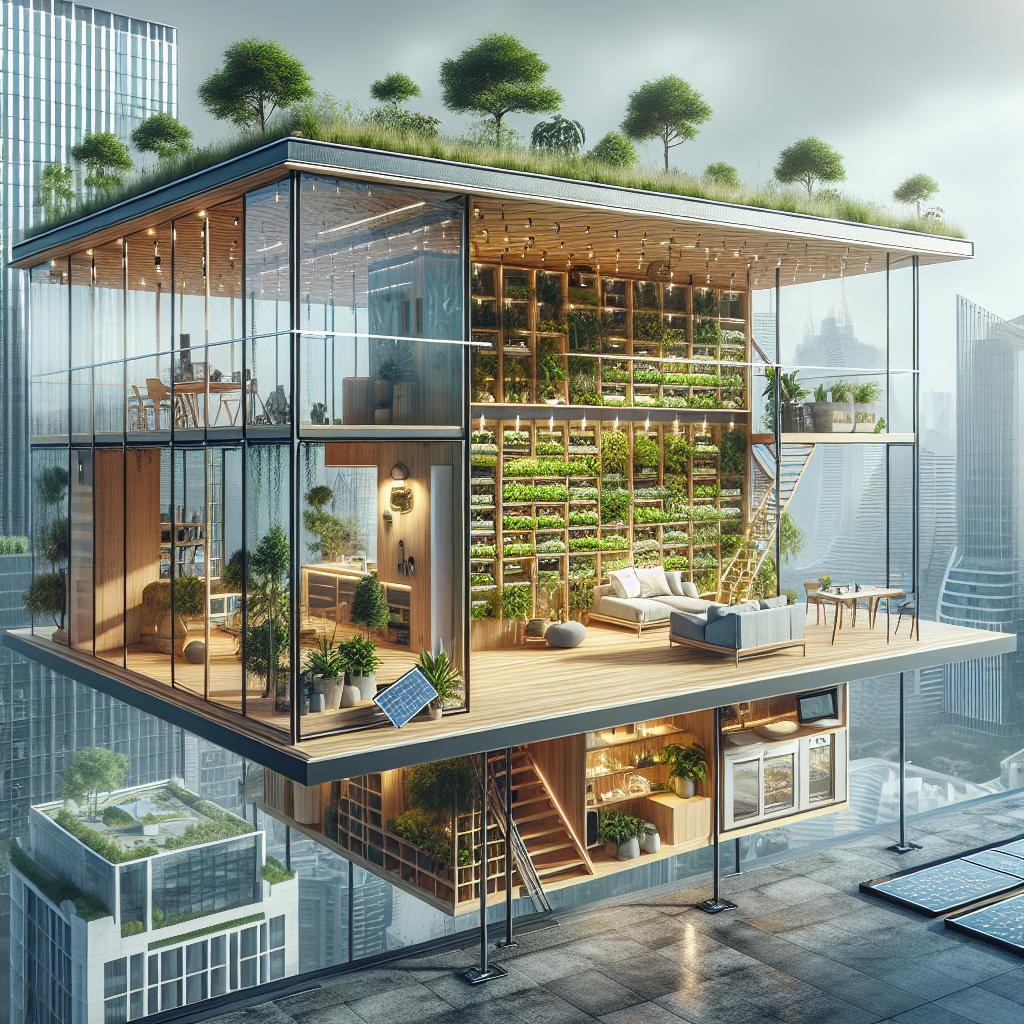
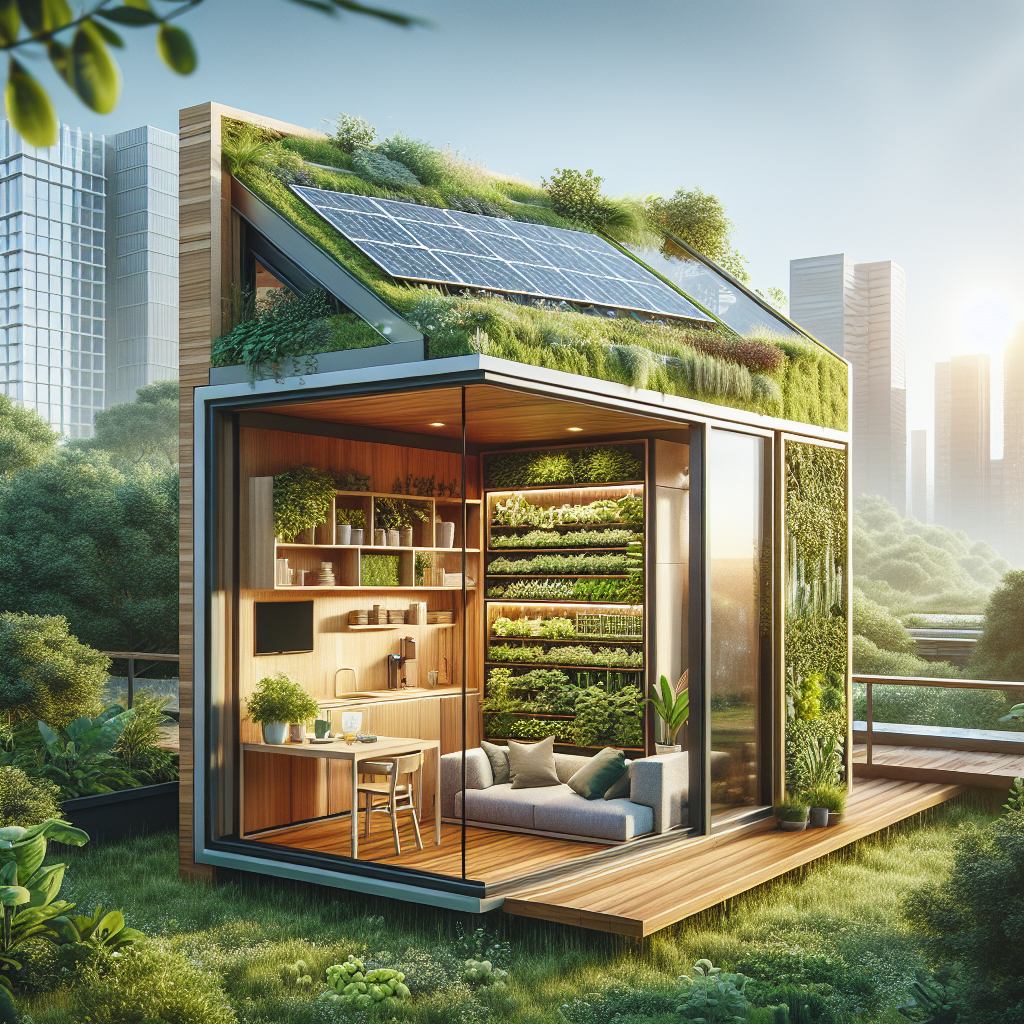
At the heart of tiny house design lies the mastery of spatial efficiency. Every square inch counts, demanding meticulous planning and innovative solutions. Multifunctional furniture, for instance, has become indispensable. Consider convertible sofas that transform into beds, foldable dining tables, and hidden storage compartments seamlessly integrated into staircases. These clever designs not only maximize functionality but also maintain aesthetic elegance, proving that minimalism need not sacrifice style.
One remarkable example is the rise of modular and transformable furniture, a trend explored extensively in our previous article on space-saving transformable furniture innovations. Designers are crafting pieces that adapt fluidly to various needs, from retractable kitchen islands to beds that ascend into ceilings, liberating valuable floor space during daytime hours.
Biophilic Integration: Bringing Nature Indoors
The tiny house movement aligns harmoniously with biophilic design principles, emphasizing our innate connection to nature. Incorporating natural elements into compact spaces not only enhances aesthetics but significantly improves occupants’ mental and physical well-being. As discussed in our exploration of biophilic design and its impact on human health, integrating greenery, natural light, and organic materials can transform small interiors into tranquil sanctuaries.
Architects are increasingly utilizing expansive windows, skylights, and vertical gardens to blur the boundaries between indoor and outdoor spaces. Imagine a tiny home featuring floor-to-ceiling glass panels that open onto a modest yet lush patio, or a vertical herb garden adorning a kitchen wall, infusing the space with freshness and vitality. Such thoughtful integrations exemplify how compact living can coexist beautifully with nature.
Sustainable Materials: Pioneering Eco-Friendly Innovations
Sustainability remains a cornerstone of the tiny house ethos, prompting designers to explore groundbreaking eco-friendly materials. From reclaimed wood and recycled metals to biodegradable composites, the materials chosen significantly impact both environmental footprint and interior ambiance. Our recent analysis of biodegradable architecture highlights how innovative materials are reshaping sustainable construction practices.
For instance, architects are increasingly embracing cross-laminated timber (CLT), a renewable material praised for its strength, insulation properties, and aesthetic warmth. Similarly, cork, bamboo, and hempcrete are gaining popularity for their sustainability credentials and unique textures, adding depth and character to tiny house interiors. These materials not only reduce environmental impact but also create inviting, tactile spaces that resonate deeply with occupants.
Smart Technology: Enhancing Compact Living Experiences
The integration of smart home technology has revolutionized tiny house living, enhancing convenience, efficiency, and comfort. Automated systems controlling lighting, heating, and security optimize energy consumption and simplify daily routines. As explored in our article on smart home technology revolutionizing home automation, intelligent systems are becoming integral to contemporary architectural design.
Imagine voice-activated lighting systems, app-controlled thermostats, and space-saving appliances designed specifically for compact environments. These innovations not only elevate functionality but also underscore the potential of technology to transform small spaces into sophisticated, responsive living environments.
Case Study: The Ecocapsule—A Futuristic Vision of Compact Living
A striking example of innovative tiny house design is the Ecocapsule, a self-sustainable micro-home that embodies futuristic aesthetics and environmental responsibility. Shaped like a sleek, aerodynamic pod, the Ecocapsule integrates solar panels, wind turbines, and rainwater harvesting systems, enabling complete off-grid living. Its interior, though compact, is meticulously designed, featuring a kitchenette, bathroom, sleeping area, and ample storage—all within a mere 86 square feet.
The Ecocapsule’s design exemplifies how technology and sustainability can converge to create autonomous living solutions, echoing themes explored in our analysis of innovative building technologies. Its portability and independence make it an ideal solution for remote locations, disaster relief, or urban dwellers seeking minimalistic lifestyles without sacrificing modern comforts.
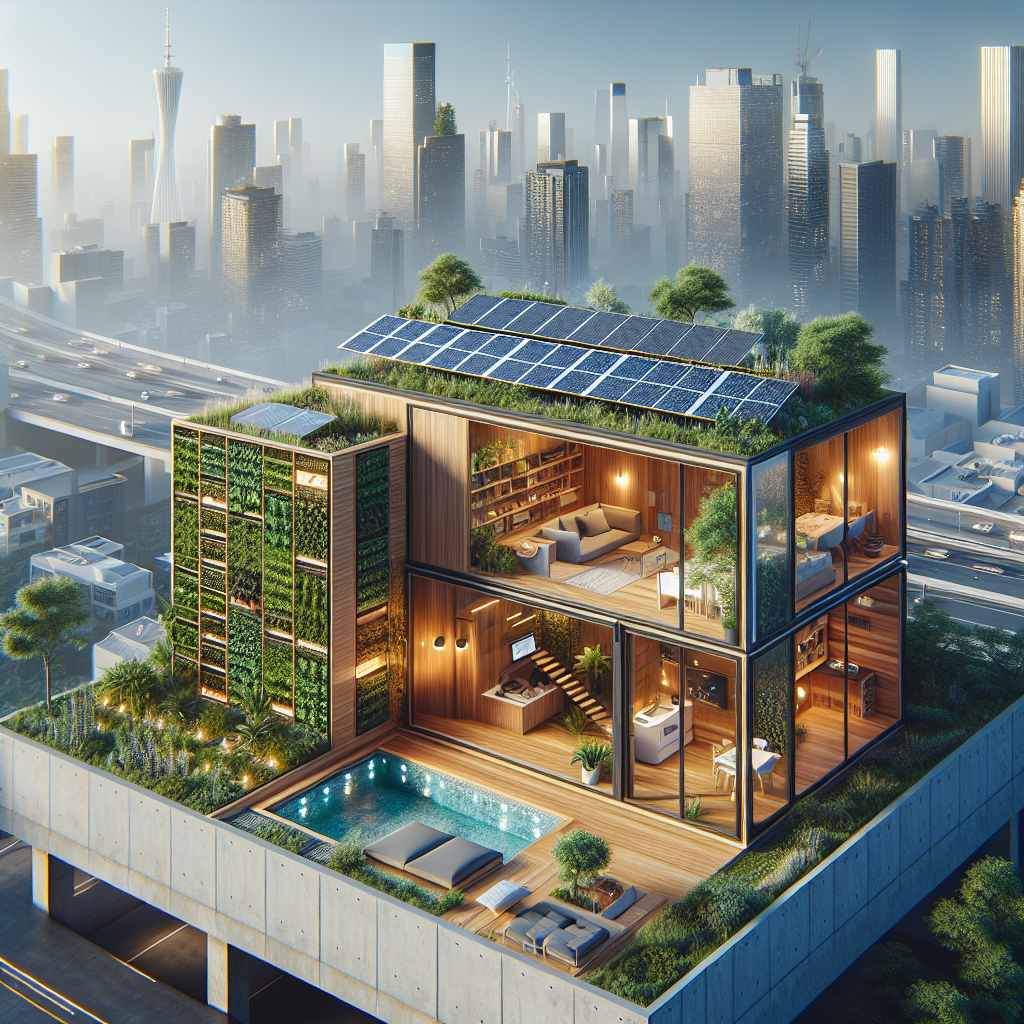
Urban Integration: Tiny Houses in Cityscapes
While tiny houses are often associated with rural or suburban settings, their integration into urban environments presents exciting possibilities for addressing housing shortages and promoting sustainable urban living. Cities worldwide are experimenting with tiny house communities, rooftop dwellings, and micro-apartments, redefining urban density and livability.
For example, Amsterdam’s pioneering initiatives in compact urban housing have inspired global interest, showcasing how tiny homes can seamlessly integrate into bustling cityscapes. Similarly, innovative vertical housing solutions, such as those discussed in our article on vertical farming and sustainable urban solutions, illustrate the potential for combining residential and agricultural spaces within limited urban footprints.
Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating Regulatory Landscapes
Despite their growing popularity, tiny houses face regulatory challenges, including zoning restrictions, building codes, and land-use policies. Navigating these complexities requires collaboration between architects, urban planners, policymakers, and communities. Advocates argue that embracing tiny house developments can alleviate housing crises, reduce environmental impact, and foster vibrant, diverse communities.
Addressing these challenges demands innovative thinking and adaptive policy frameworks, as highlighted in our exploration of adaptive reuse and urban revitalization. By reimagining regulatory landscapes, cities can unlock the full potential of tiny house design, creating inclusive, sustainable, and resilient urban environments.
The Future of Compact Living: A Paradigm Shift in Architecture
As the tiny house movement continues to evolve, it challenges architects and designers to rethink traditional paradigms of space, luxury, and sustainability. The fusion of spatial efficiency, biophilic principles, sustainable materials, and smart technology positions tiny houses at the forefront of architectural innovation. By embracing compact living, we not only address pressing environmental and social challenges but also cultivate spaces that resonate deeply with human needs and aspirations.
Ultimately, tiny house design exemplifies a broader shift towards mindful, intentional living—a movement that transcends mere architectural trends to embody a profound cultural transformation. For design professionals and enthusiasts alike, this compact revolution offers boundless opportunities to reimagine the future of our built environments.