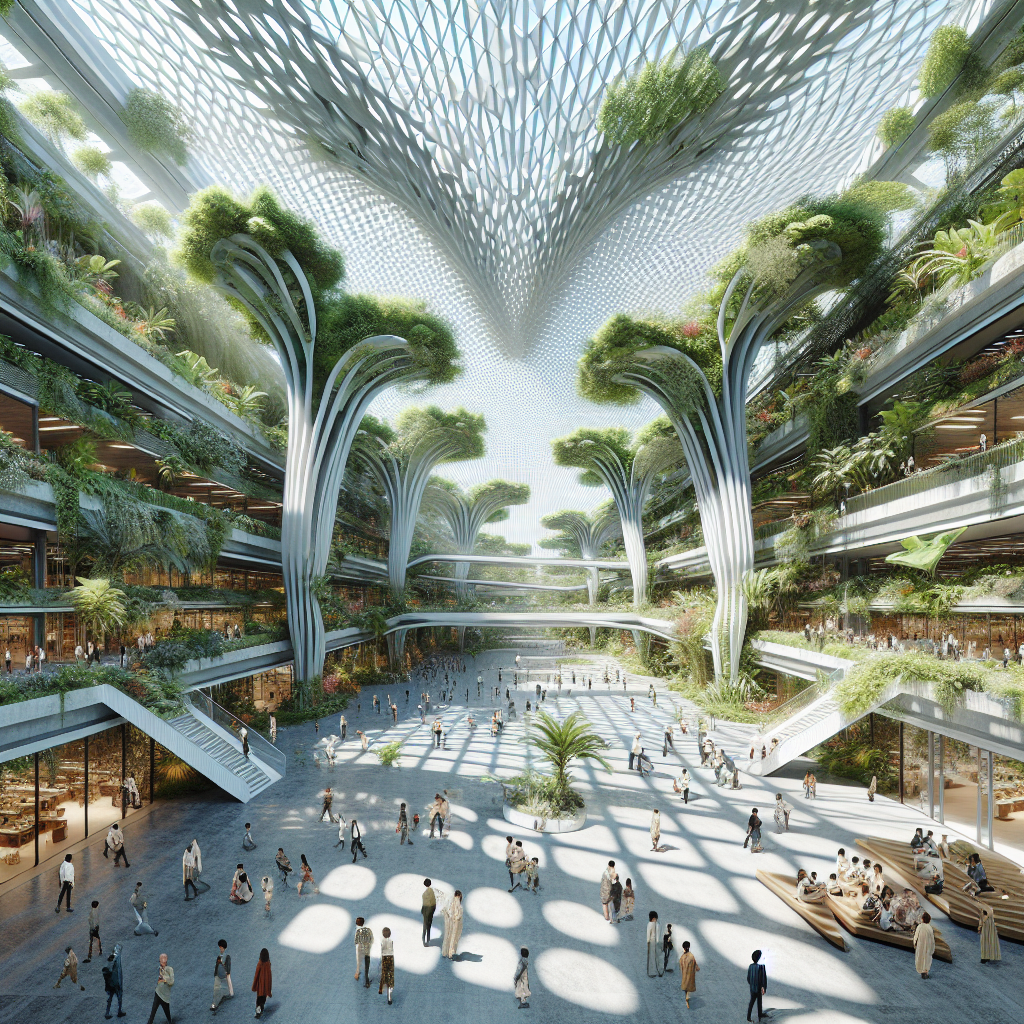
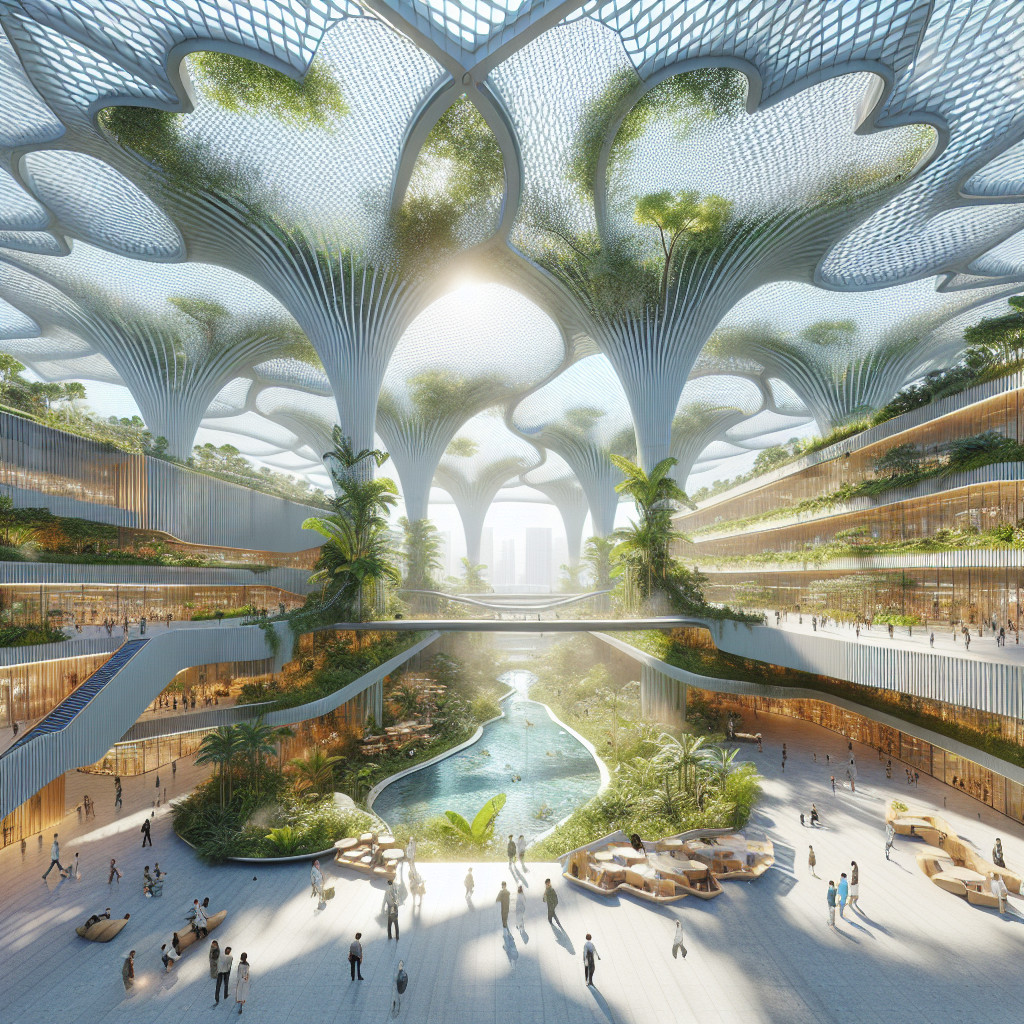
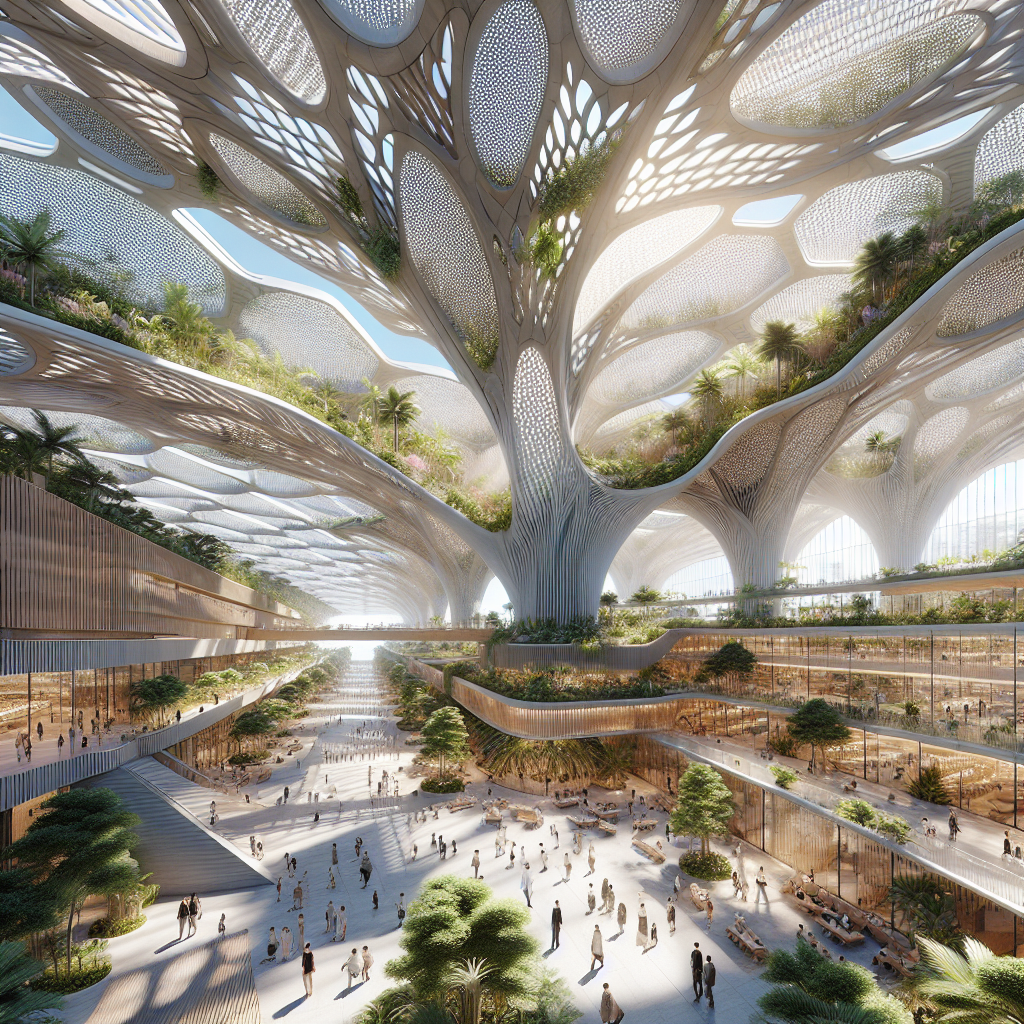
Subtropical atrium design: giant leaf canopies for temperature control

Subtropical Atrium Design: Giant Leaf Canopies for Temperature Control
As urban landscapes continue to evolve, architects and designers are constantly exploring innovative solutions to address the pressing challenges of climate change and sustainability. One such groundbreaking approach is the use of giant leaf canopies in subtropical atrium design, an emerging trend that beautifully merges aesthetics with functionality. These striking structures not only enhance visual appeal but also play a pivotal role in regulating temperature, creating comfortable and sustainable indoor environments.
Nature-Inspired Design: The Essence of Giant Leaf Canopies
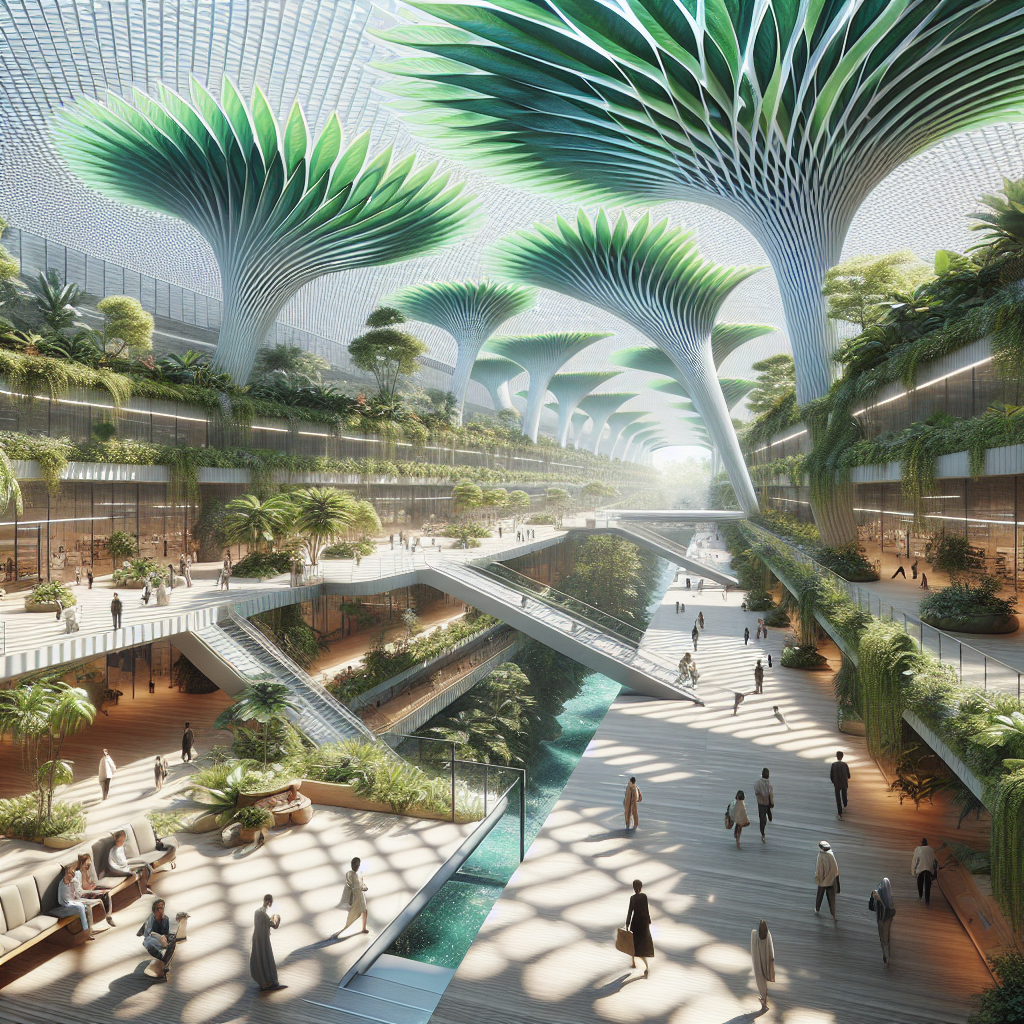
Inspired by the intricate forms and functions found in nature, architects are increasingly turning to biomimicry to develop innovative design solutions. Giant leaf canopies are a prime example of this approach, mimicking the cooling properties of natural foliage to regulate temperature and humidity within subtropical atriums. These expansive structures, often crafted from sustainable materials, act as shading devices, reducing solar heat gain and providing a naturally ventilated environment.
Incorporating giant leaf canopies into architectural design is not merely an aesthetic choice; it represents a thoughtful integration of form and function. By emulating the natural cooling mechanisms of leaves, these canopies create microclimates that significantly reduce the need for artificial cooling systems, thereby lowering energy consumption and promoting environmental sustainability.
Thermal Comfort: How Giant Leaf Canopies Regulate Temperature
In subtropical climates, where temperatures can soar, achieving thermal comfort is a critical consideration in architectural design. Giant leaf canopies effectively address this challenge by providing ample shade and facilitating passive cooling. The expansive surface area of these canopies blocks direct sunlight, reducing indoor temperatures and creating a pleasant, comfortable atmosphere.
Moreover, the strategic placement and orientation of giant leaf canopies can enhance natural ventilation, allowing air to circulate freely and dissipate heat. This passive cooling approach significantly reduces reliance on energy-intensive air conditioning systems, contributing to a more sustainable and eco-friendly built environment.
One remarkable example of this design approach is Singapore’s iconic Gardens by the Bay, where towering artificial “Supertrees” mimic the cooling effects of natural foliage. These structures not only provide shade but also house vertical gardens, showcasing the seamless integration of nature and architecture. According to Wikipedia, these innovative designs have become a symbol of sustainable urban development, inspiring architects worldwide.
Sustainable Materials: Crafting Eco-Friendly Canopies
The choice of materials plays a crucial role in the sustainability and effectiveness of giant leaf canopies. Architects and designers are increasingly opting for eco-friendly materials such as recycled metals, sustainably harvested timber, and innovative bio-based composites. These materials not only minimize environmental impact but also enhance the durability and longevity of the structures.
For instance, the growing trend of wooden skyscrapers highlights the potential of timber as a sustainable building material. Similarly, giant leaf canopies crafted from sustainably sourced timber offer an elegant and environmentally responsible solution for subtropical atrium design.
Additionally, advancements in digital fabrication and 3D printing technologies have opened new possibilities for creating intricate, lightweight canopy structures. These cutting-edge techniques enable architects to design complex, organic forms that closely mimic natural leaves, enhancing both aesthetic appeal and functional performance.
Biophilic Design: Enhancing Human Well-Being
Beyond their practical benefits, giant leaf canopies also embody the principles of biophilic design, which emphasizes the importance of connecting people with nature. Incorporating natural elements into architectural spaces has been shown to improve mental health, reduce stress, and enhance overall well-being.
By creating lush, green environments within urban settings, giant leaf canopies foster a sense of tranquility and harmony, offering residents and visitors a respite from the hustle and bustle of city life. The integration of natural elements into architectural design not only enhances aesthetic appeal but also promotes a healthier, more balanced lifestyle.
Global Inspirations: Iconic Examples of Giant Leaf Canopies
Around the world, architects are embracing the potential of giant leaf canopies to transform subtropical atriums into sustainable, visually stunning spaces. One notable example is the Eden Project in Cornwall, UK, where massive geodesic domes house diverse ecosystems beneath giant leaf-inspired structures. According to Wikipedia, this innovative design has attracted millions of visitors, highlighting the public’s growing appreciation for sustainable architecture.
Similarly, the Amazon Spheres in Seattle, USA, feature a striking design inspired by the natural form of leaves, creating a lush indoor environment that supports both plant life and human well-being. As detailed on Wikipedia, these structures exemplify the potential of biophilic design to enhance urban spaces.
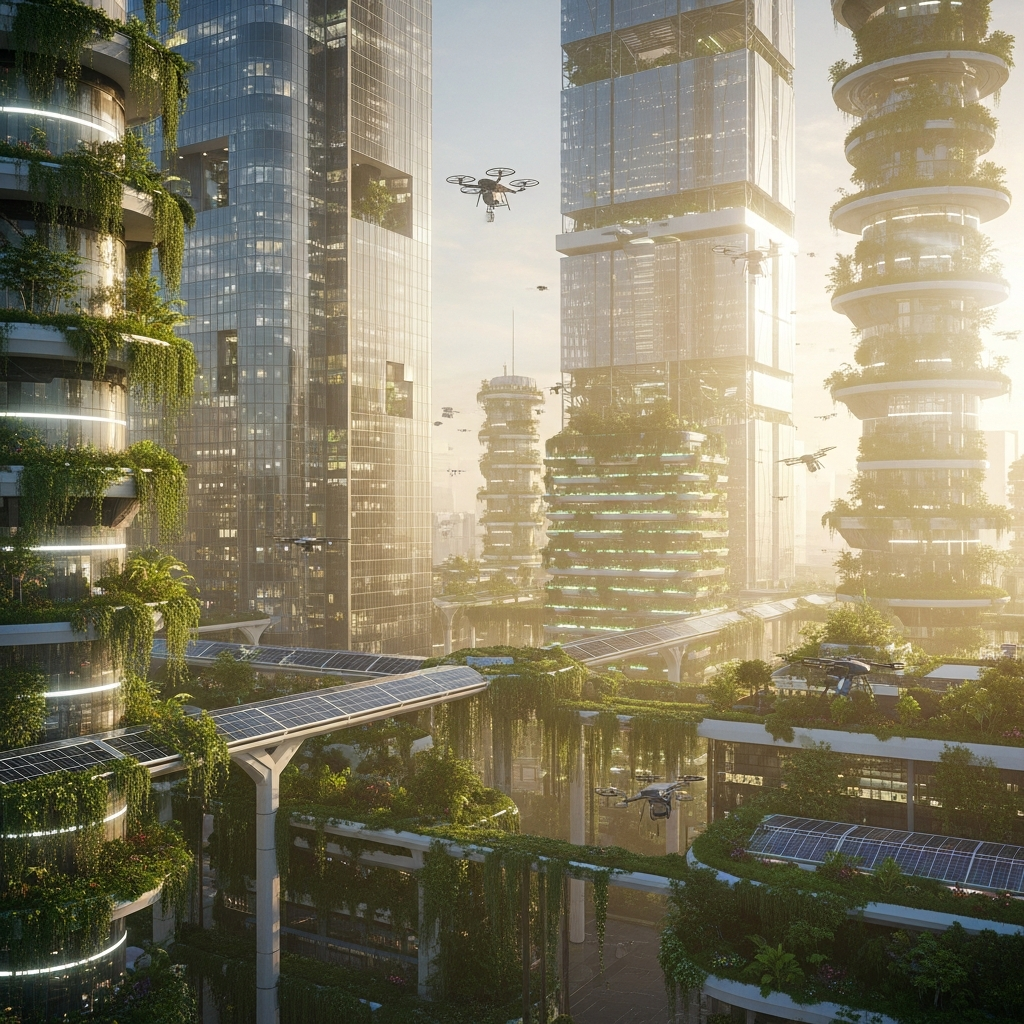
Future Prospects: The Role of Technology and Innovation
As cities continue to grapple with the challenges of climate change, the integration of giant leaf canopies into architectural design offers a promising path forward. Emerging technologies, such as smart home systems and advanced sensors, can further enhance the performance of these structures, optimizing temperature control and energy efficiency.
Moreover, the growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental responsibility is driving architects and designers to explore innovative solutions that minimize ecological impact. The adoption of giant leaf canopies in subtropical atrium design represents a significant step toward achieving net-zero energy buildings, paving the way for a more sustainable future.
Embracing Nature: A New Paradigm in Architectural Design
The integration of giant leaf canopies into subtropical atrium design marks a significant shift toward embracing nature-inspired solutions in architecture. By harnessing the cooling properties of natural foliage, these structures offer a sustainable, aesthetically pleasing approach to temperature control, enhancing both environmental performance and human well-being.
As architects and designers continue to explore the potential of biomimicry and biophilic design, giant leaf canopies are poised to become an increasingly prominent feature in urban landscapes. By fostering a deeper connection with nature and promoting sustainable living, these innovative structures represent a bold step toward a more harmonious and resilient built environment.
Ultimately, the adoption of giant leaf canopies in subtropical atrium design reflects a broader commitment to sustainability, innovation, and the well-being of both people and the planet. As we look to the future, embracing nature-inspired solutions will be essential in creating vibrant, sustainable cities that thrive in harmony with the natural world.