Urban jungles redefined climbing vines weaving through steel beams

Urban Jungles Redefined: Climbing Vines Weaving Through Steel Beams
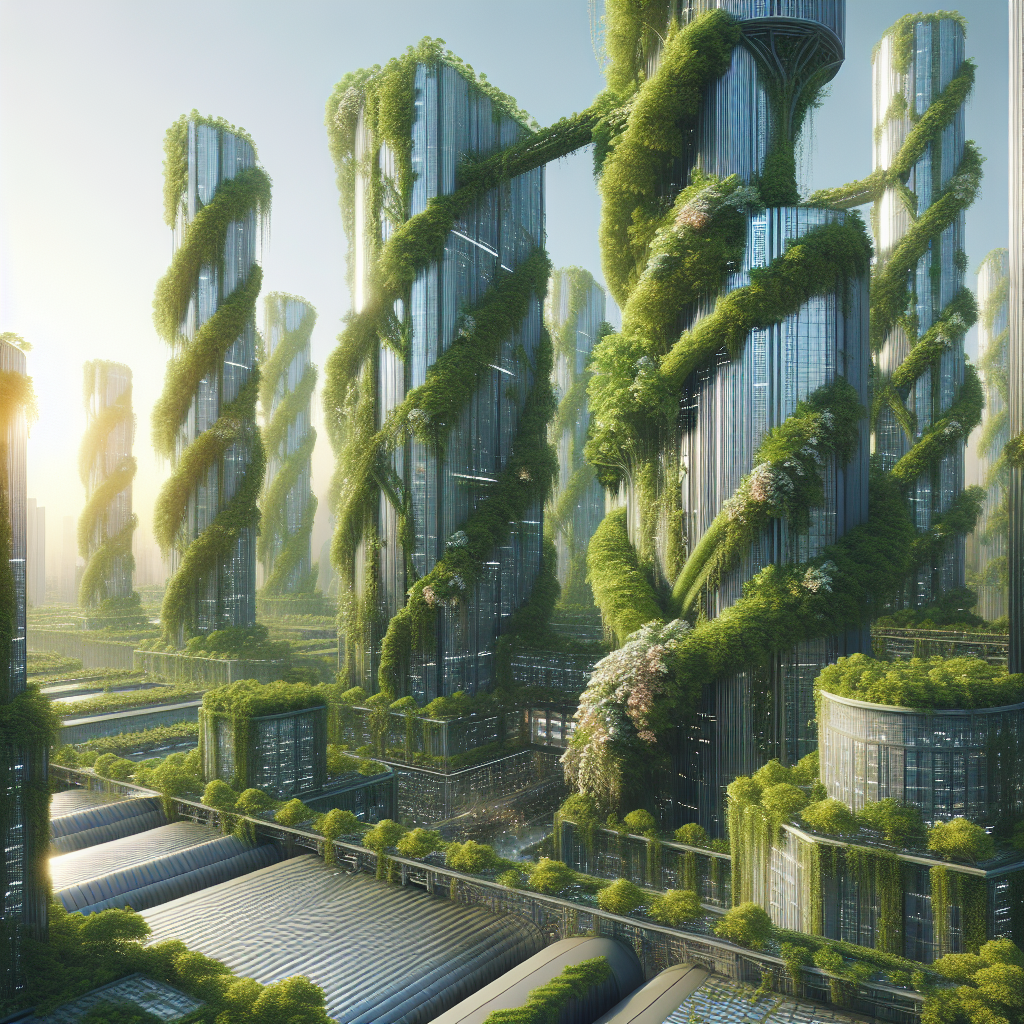
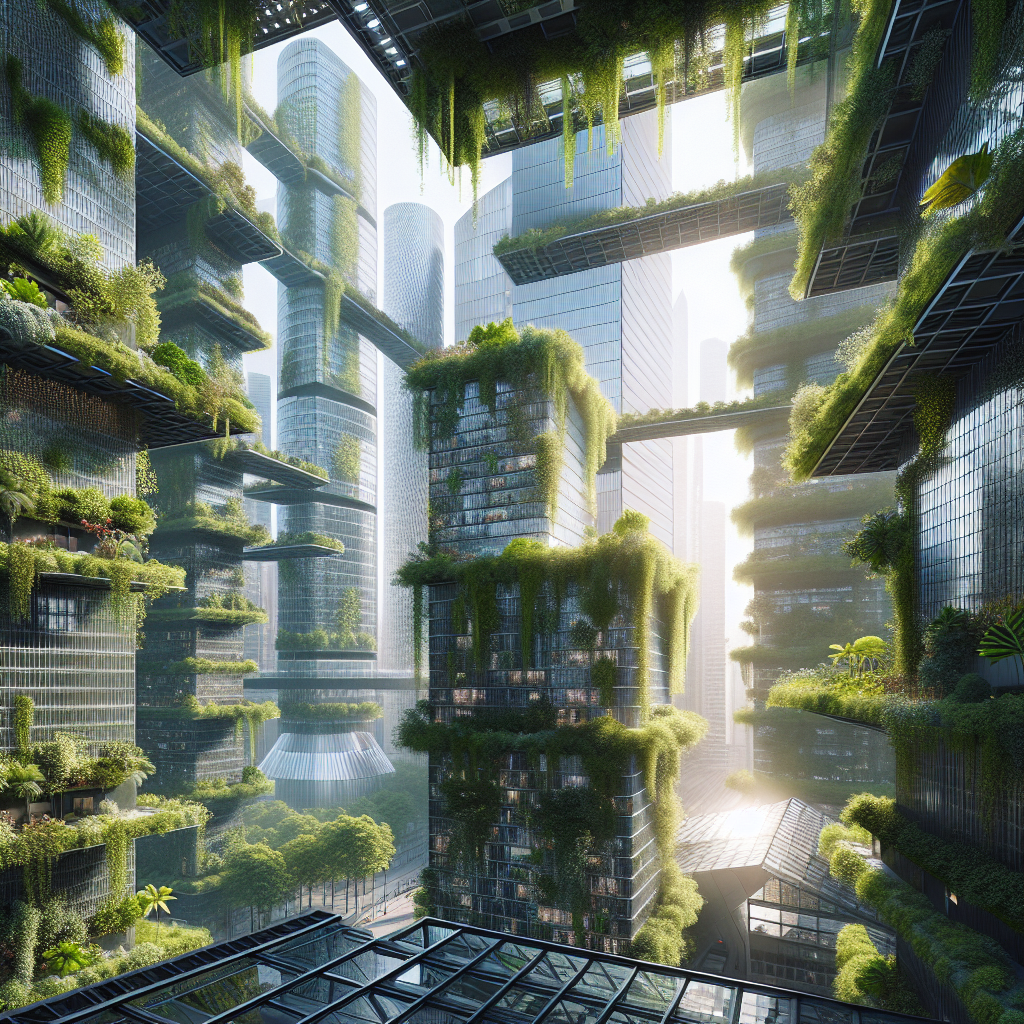
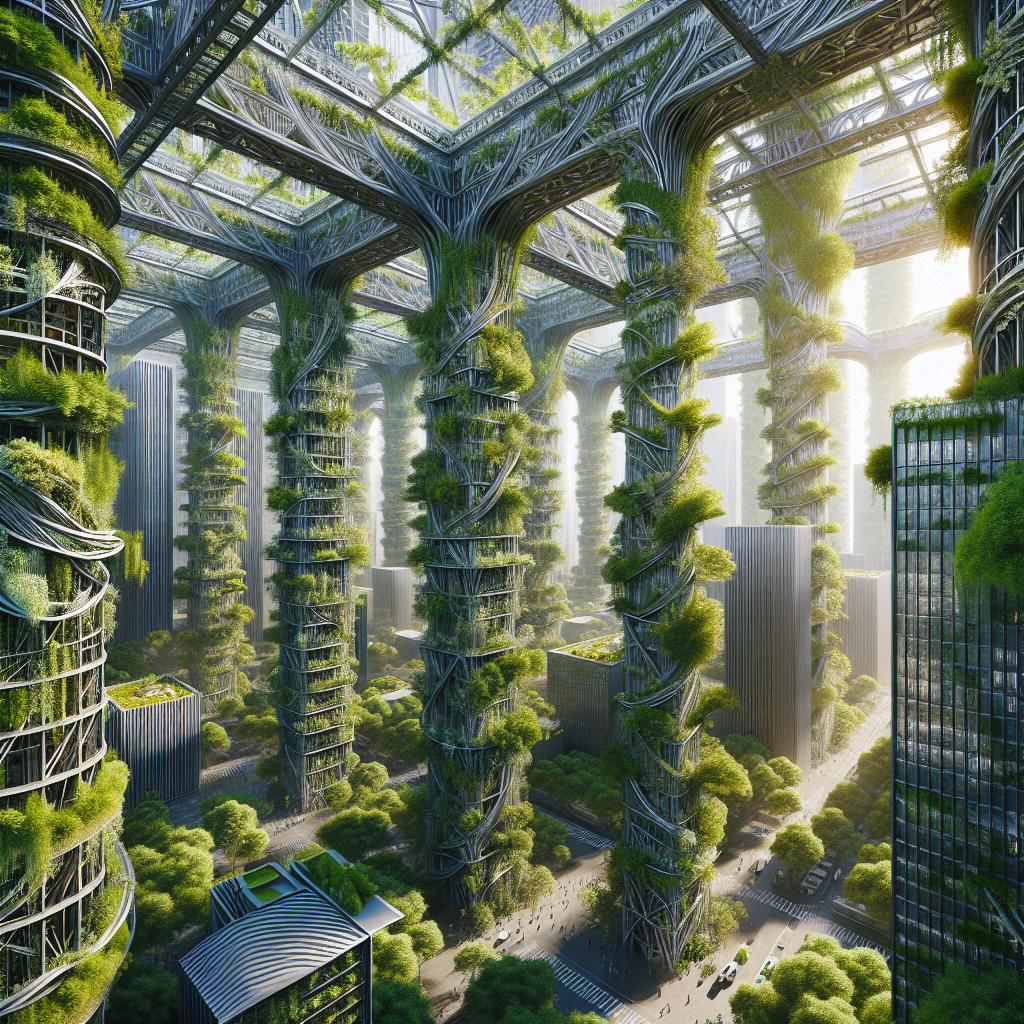
Imagine a cityscape where lush greenery intertwines effortlessly with the industrial charm of steel beams, crafting an architectural symphony that redefines urban aesthetics. This isn’t merely a whimsical vision but a tangible reality emerging in cities worldwide. Architects and designers are increasingly turning to biophilic design, integrating nature directly into urban structures to enhance sustainability, aesthetics, and human well-being.
Historically, urban architecture has been dominated by concrete, glass, and steel, often devoid of natural elements. Yet, the growing awareness of environmental issues and the need for sustainable urban living has propelled architects to rethink traditional designs. The concept of urban jungles, characterized by climbing vines weaving through steel beams, is a testament to this shift, marrying the rigidity of industrial materials with the fluidity of nature.
The Rise of Biophilic Architecture
Biophilic architecture isn’t merely about aesthetics; it’s deeply rooted in enhancing human health and environmental sustainability. Studies indicate that integrating natural elements into urban environments significantly improves mental health, reduces stress, and boosts productivity. A detailed exploration of this phenomenon can be found in our article on biophilic design and its impact on human health and well-being.
Moreover, climbing plants like ivy, wisteria, and jasmine don’t just beautify buildings; they actively contribute to reducing urban heat islands, improving air quality, and supporting biodiversity. These plants act as natural insulators, cooling buildings in summer and providing warmth in winter, thus significantly reducing energy consumption.
Iconic Examples of Urban Jungles
One of the most celebrated examples of this architectural style is Milan’s Bosco Verticale, or “Vertical Forest,” designed by Stefano Boeri. This groundbreaking project features two residential towers adorned with over 900 trees and thousands of shrubs and plants. Bosco Verticale not only enhances the city’s skyline but also serves as a vertical ecosystem, absorbing CO2 and producing oxygen, thus contributing to Milan’s environmental sustainability goals.
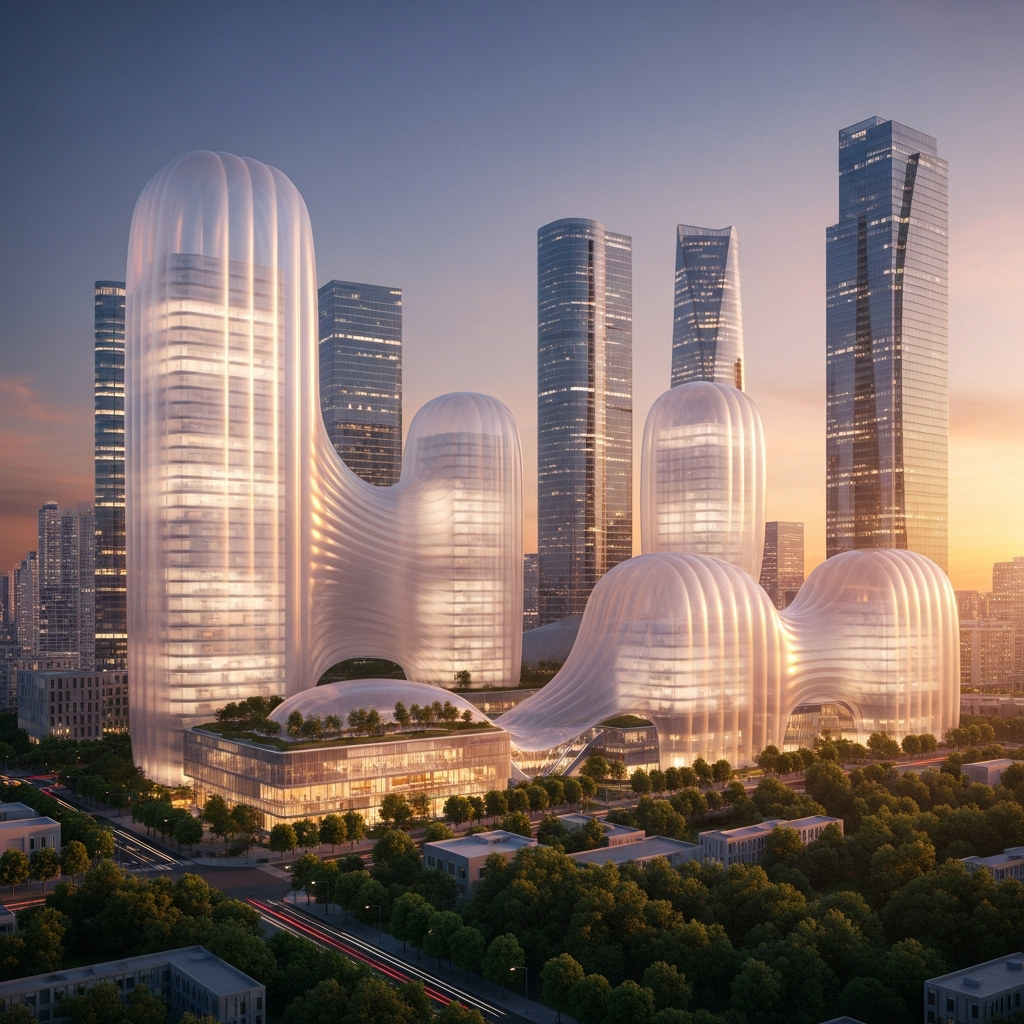
Another striking example is Singapore’s Gardens by the Bay, particularly the Supertree Grove. These towering structures, composed of steel frames wrapped in climbing plants, serve multiple purposes: they generate solar power, collect rainwater, and function as air exhaust receptacles for nearby conservatories. Gardens by the Bay is a testament to how innovative design can seamlessly blend technology and nature, a concept explored further in our article on the impact of technology on futuristic city design.
Benefits Beyond Aesthetics
The advantages of integrating climbing vines into urban architecture extend far beyond visual appeal. These green façades actively mitigate urban pollution by filtering particulate matter and absorbing harmful gases. According to research, green walls can reduce nitrogen dioxide levels by up to 40%, significantly improving urban air quality. Furthermore, these natural elements create habitats for birds and insects, promoting urban biodiversity.
Moreover, buildings enveloped in greenery have proven to be more resilient to climate change impacts. The vegetation provides natural insulation, reducing the need for artificial heating and cooling, thus lowering energy costs and carbon footprints. This aligns perfectly with the global push towards net-zero energy buildings, where sustainability meets innovative design.
Challenges and Solutions
Despite the numerous benefits, integrating climbing plants into urban structures isn’t without challenges. Maintenance, structural integrity, and plant selection are critical considerations. For instance, unchecked growth can lead to structural damage, moisture retention, and pest infestations. Architects and horticulturists must collaborate closely to select appropriate plant species and design effective maintenance strategies.
Advancements in building materials and techniques, such as corrosion-resistant steel and automated irrigation systems, have significantly mitigated these challenges. Furthermore, digital tools like Building Information Modeling (BIM) allow architects to simulate plant growth and assess potential impacts on structural integrity, ensuring sustainable and safe integration of greenery.
The Future of Urban Jungles
As urban populations continue to grow, the need for sustainable, resilient, and aesthetically pleasing architecture becomes increasingly critical. Urban jungles, characterized by climbing vines weaving through steel beams, offer a compelling solution to these challenges. They not only enhance urban aesthetics but also significantly contribute to environmental sustainability and human well-being.
Looking ahead, we can expect to see more innovative designs that integrate nature into urban environments. Concepts like vertical farming, rooftop gardens, and green façades will become standard features in future urban planning. The potential of these designs is immense, offering solutions to urban heat islands, air pollution, and biodiversity loss, all while creating visually stunning cityscapes.
In Paris, the upcoming 2024 Summer Olympic Games have already sparked innovative architectural projects that embrace biophilic principles, promising to transform the city’s urban landscape dramatically.
Embracing Nature in Urban Design
The integration of climbing vines into steel structures symbolizes a broader shift towards sustainable and resilient urban design. It’s a movement that acknowledges the intrinsic value of nature in enhancing urban life quality. As cities evolve, architects and designers must continue to explore and innovate, creating spaces that harmoniously blend natural and built environments.
Ultimately, the redefinition of urban jungles through climbing vines and steel beams represents a visionary approach to urban planning. It’s an approach that prioritizes sustainability, resilience, and human well-being, setting a new standard for future cities worldwide. For further insights into sustainable urban transformations, explore our article on sustainable cities.
Urban jungles are no longer a distant dream but a present reality, transforming cityscapes into vibrant, living ecosystems. As we continue to embrace this architectural evolution, we pave the way for healthier, more sustainable, and visually captivating urban environments.