3D Printed Houses: Revolutionizing Affordable and Sustainable Housing

3D Printed Houses: Revolutionizing Affordable and Sustainable Housing
The architectural landscape is experiencing a transformative shift, one that marries technological innovation with sustainable living. At the forefront of this evolution stands the phenomenon of 3D printed houses, a groundbreaking solution poised to redefine the future of affordable and eco-friendly housing. With the global housing crisis intensifying and environmental concerns escalating, architects and designers are increasingly turning to advanced technologies like 3D printing to address these pressing challenges. This article explores how 3D printed houses are reshaping the built environment, offering insights into their design possibilities, sustainability credentials, and real-world implementations that inspire and captivate design professionals and enthusiasts alike.
The Emergence of 3D Printing in Architecture
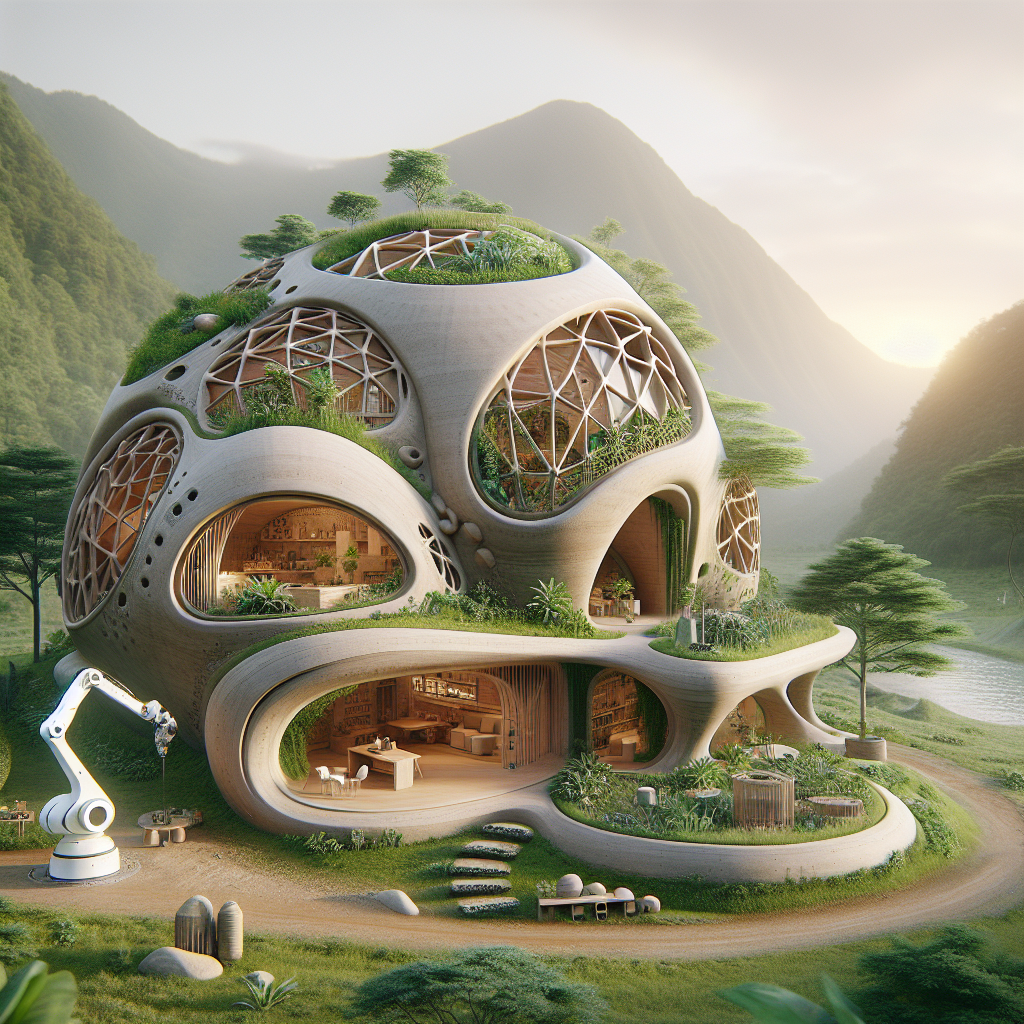
The concept of 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, involves creating three-dimensional objects by layering materials based on digital models. Initially embraced in manufacturing and prototyping, this technology has now found a revolutionary application in architecture. By utilizing large-scale 3D printers capable of extruding concrete, clay, or even recycled materials, architects can rapidly construct structures with unprecedented precision and efficiency.
A prime example of this innovative approach is the TECLA project in Italy, designed by Mario Cucinella Architects. Constructed entirely from locally sourced clay, TECLA’s organic, dome-shaped structures exemplify the aesthetic and functional potential of 3D printed architecture. Its design not only harmonizes with the natural environment but also provides a sustainable, low-cost housing solution adaptable to diverse climates and geographies.
Affordability and Efficiency: Tackling the Global Housing Crisis
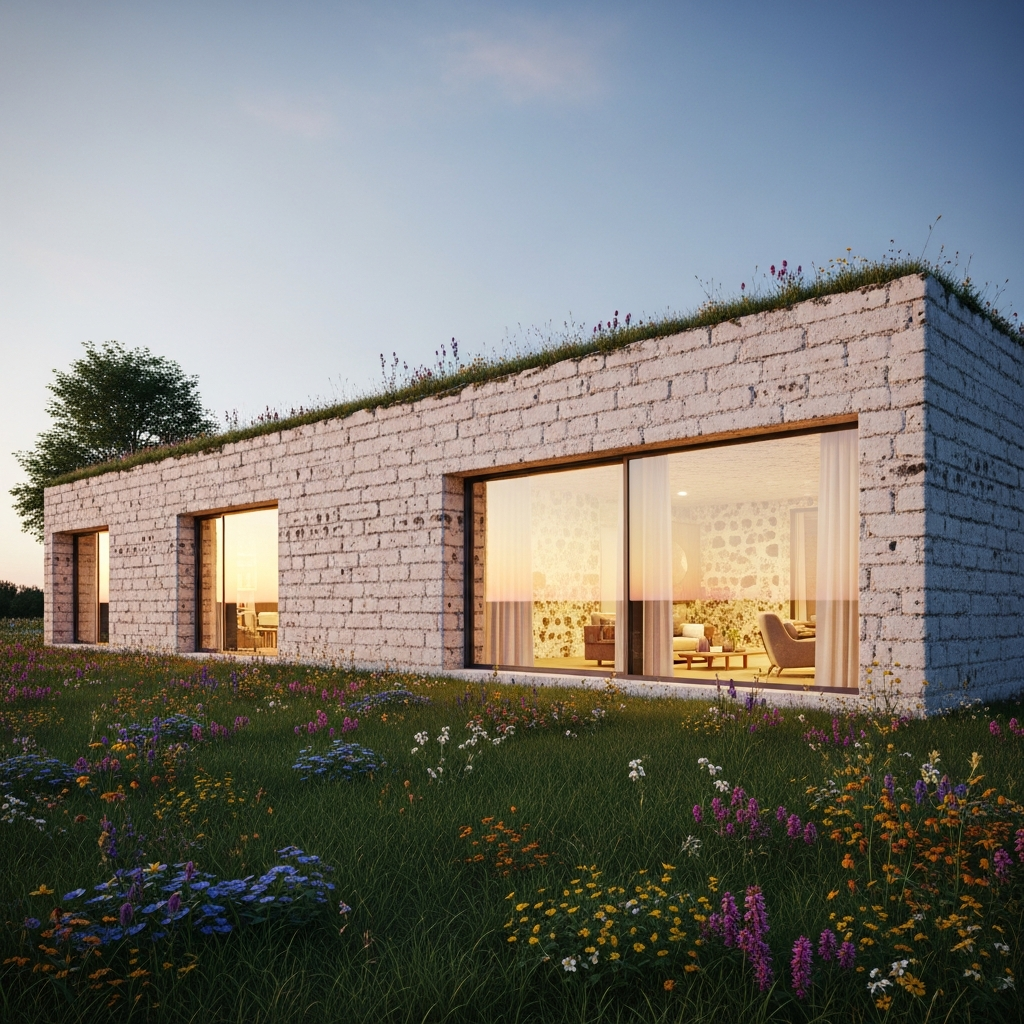
As urban populations swell and housing shortages intensify, affordability has become a critical concern for architects and urban planners. Traditional construction methods often entail high labor costs, extended timelines, and substantial material waste. In contrast, 3D printed houses significantly reduce these constraints, offering a streamlined and cost-effective alternative.
Recent studies indicate that 3D printing can reduce construction costs by up to 40% compared to conventional methods. Furthermore, projects that typically take months can be completed within days, dramatically accelerating the provision of housing in underserved communities. ICON, a Texas-based construction technology company, exemplifies this potential through its innovative Vulcan printer, which has successfully built affordable homes in Mexico and the United States. These homes, characterized by sleek, minimalist aesthetics and robust structural integrity, underscore the promise of 3D printing in addressing global housing needs.
For further insights into affordable housing solutions, explore our previous article on innovative solutions for the housing crisis.
Sustainability at the Core: Eco-Friendly Construction
In an era marked by climate change and environmental degradation, sustainability has become a non-negotiable aspect of contemporary architecture. 3D printed houses inherently align with sustainable principles, minimizing waste and reducing carbon footprints through precise material usage and energy-efficient processes.
Moreover, architects are increasingly integrating biophilic design principles into 3D printed structures, enhancing occupants’ well-being by fostering connections with nature. As detailed in our exploration of biophilic design and its impact on human health, incorporating natural elements into architectural spaces significantly improves psychological and physiological health.
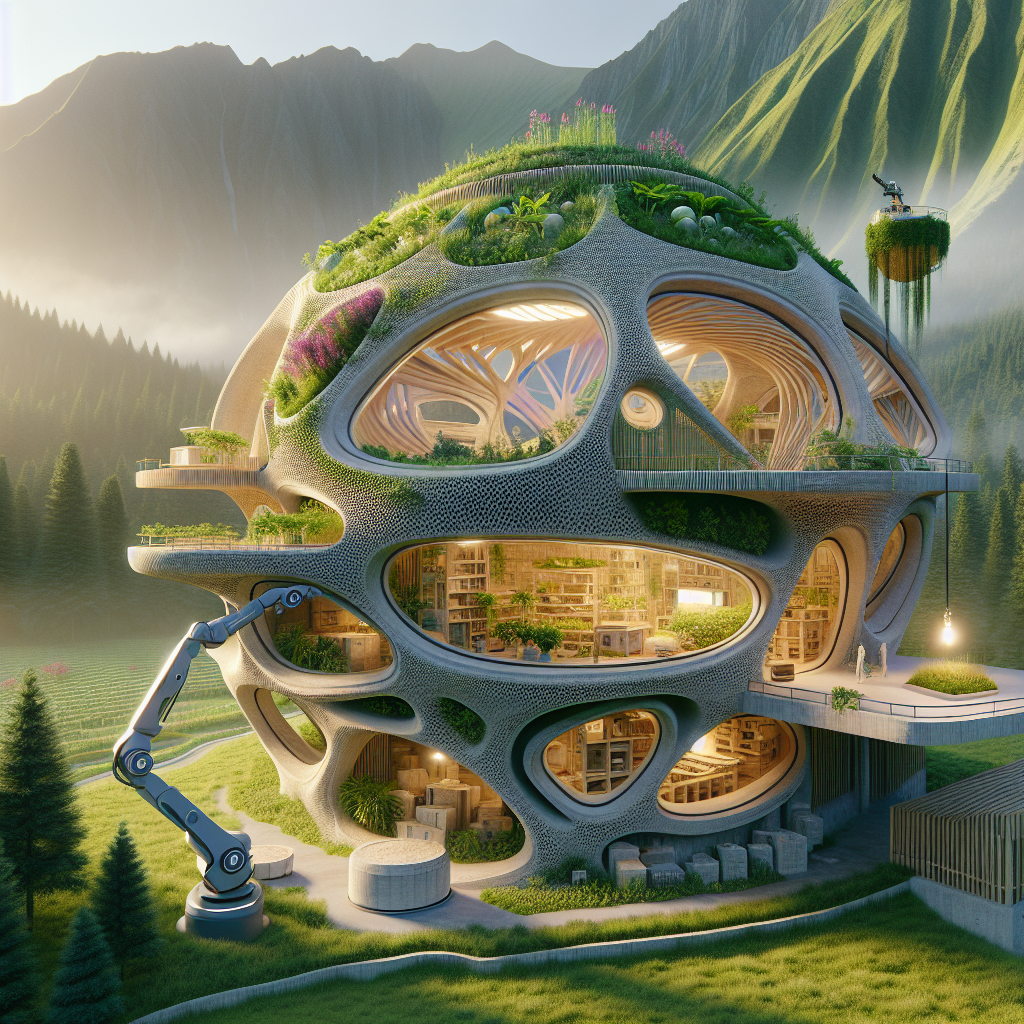
An inspiring case is the Gaia house, another project by Mario Cucinella Architects, constructed using soil, rice husks, and straw. This innovative blend not only ensures structural stability but also promotes thermal insulation and reduces environmental impact. Gaia’s design, featuring curved walls and natural textures, evokes a sense of harmony and tranquility, embodying the essence of sustainable living.
Design Freedom: Pushing Architectural Boundaries
Beyond affordability and sustainability, 3D printing offers architects unparalleled design freedom, enabling the creation of complex geometries and intricate forms previously unattainable through traditional methods. The technology’s ability to realize ambitious, unconventional designs is redefining architectural aesthetics and pushing creative boundaries.
For instance, the innovative “Curve Appeal” project by WATG Urban Architecture Studio showcases a fluid, organic structure with sinuous curves and seamless transitions. The design leverages 3D printing’s capabilities to achieve structural elegance and visual dynamism, illustrating the transformative potential of additive manufacturing in architecture.
Moreover, the integration of parametric design algorithms further enhances the creative possibilities of 3D printed architecture. As discussed in our article on parametric design and algorithmic architecture, this approach allows architects to generate adaptive, responsive structures tailored to specific environmental conditions and user needs.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its remarkable potential, the widespread adoption of 3D printed housing faces several challenges. Regulatory frameworks, building codes, and public perceptions must evolve to accommodate this innovative construction method. Additionally, further research into sustainable materials and long-term durability is essential to ensure the viability and scalability of 3D printed structures.
Nevertheless, the trajectory of 3D printed housing remains promising. Industry forecasts predict significant growth in the coming decade, driven by technological advancements, increasing environmental awareness, and pressing housing demands. Collaborative efforts between architects, engineers, policymakers, and communities will be crucial in harnessing this technology’s full potential to create inclusive, sustainable, and resilient urban environments.
In parallel, complementary innovations such as wooden skyscrapers and vertical farming are reshaping urban landscapes, highlighting a broader shift towards sustainable urbanism and ecological consciousness.
Conclusion: A New Architectural Paradigm
3D printed houses represent more than a technological novelty; they embody a profound shift in architectural philosophy, emphasizing affordability, sustainability, and creative innovation. As architects and designers continue to explore and refine this revolutionary approach, the built environment stands poised to become more accessible, eco-friendly, and visually captivating than ever before.
By embracing 3D printing technology, the architecture and design community can actively contribute to addressing global challenges, from housing shortages to environmental sustainability. The journey toward a future defined by additive manufacturing has begun, promising a world where architecture is not only beautiful and functional but also profoundly responsible and inclusive.
For further exploration of how technology is reshaping urban environments, consider our analysis of technology’s impact on futuristic city design.
As we stand at the threshold of this architectural revolution, the potential of 3D printed houses to transform our cities and communities is undeniable. It is an exciting time for architects, designers, and urban planners, who now have the tools to build a more sustainable, equitable, and inspiring future.